In this in-depth integrated EDI guide you’ll learn:

Integrated EDI solution can help streamline your business operations by directly integrating with your ERP systems without which businesses end up using many systems or sometimes manual processes to send and receive documents which can significantly affect the overall business performance. An integrated EDI solution automates and streamlines data flow from one end to the other end of the supply chain process.
Integrated EDI solution,
In our latest podcast episode, we dive into the world of Integrated EDI—an essential tool for businesses looking to automate and optimize their data flow. Integrated EDI connects directly with your existing systems, allowing for seamless, real-time data exchanges that improve accuracy, reduce manual tasks, and enhance collaboration with business partners. Drawing from insights in Commport’s Integrated EDI Guide, we’ll explore how this approach can streamline your operations, minimize errors, and ultimately, boost your bottom line. Join us to discover how Integrated EDI could be a transformative solution for your business, without needing to read the full guide!
In this chapter, we will talk about following topics:
Definition of Integrated EDI
Manual process vs integrated EDI
Supply chain challenges
Biggest IT Challenge
An Integrated EDI solution translates your inbound documents, like purchase orders, from your trading partners’ EDI files into a format that can be imported directly into your ERP, accounting, or other business system.
Manual processing of your messages is no longer necessary. Achieving automation of communications between internally developed applications is simple by integrating an effective EDI solution that can send and receive documents integrating into the business ERP system.
Users of Integrated software enjoy the benefits of streamlined EDI processes that are electronic, versus manually driven. This results in reduced error rates and confidence in reliable data maintenance that is integrated throughout the EDI document-sharing process.
One of the biggest challenges in today’s supply chain management is to digitalizing the entire end-to-end process from receiving orders, managing inventory, and processing shipments. The only way this can be achieved is by using an integrated EDI solution which not only reduces costs but also helps streamline the business process.
These integrated EDI solutions integrate with your internal management system such as ERP, automating the processing of your EDI messages for comprehensive and transparent communications management directly from your own ERP.
Without integrated EDI, you have isolated pieces of technology that require human intervention. The biggest IT challenge that many organizations face is the integration of different applications and systems. Data flow is interrupted in the absence of integrated EDI, and data fragmentation hurts businesses. Without integration, many B2B projects fail to deliver the benefits that users expect.
In this chapter, we will talk about the importance of integrated EDI and who uses integrated EDI solution?
Integrated EDI is used by many industries from automotive to retail, healthcare to construction companies and many more!
In the following chapters, we will discuss some of the important benefits of integrated EDI
These solutions are aimed at businesses with medium to high volumes of EDI transactions both in issuance and receipt, in which manual management such as that in web-based solutions would not be workable.
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) refers to the process of exchanging form information electronically. In many cases, it has saved thousands of hours (and countless dollars) for businesses with scores of documents to complete and file.
Integrated EDI has been used in the past primarily by automotive and retail businesses, however, in the past few years, the format has been more widely adopted. Manufacturing, healthcare, pharmaceutical, utility, and construction companies are good examples of EDI clients.
Here is the list of EDI use cases in various industries,
Basically, any type of business that deals with large amounts of identical paperwork/form data can directly benefit from adopting an EDI solution
Major retailers – Walmart, 99 Cents Only Stores, Lowes, Office Depot, and Costco, to name a few – use EDI to manage their transportation and routing instructions.
it’s possible to use EDI to integrate purchase orders into the sales order system simply and efficiently. Files can then be archived for accurate accounting and reporting, as well as for future reference during the drafting of additional documents.
Invoice processing is an essential component of effective business practice – EDI ensures accurate and fast invoicing, eliminating inaccuracies and facilitating fast payment.
EDI can extract data from an Advanced Shipping Notice infrastructure and produce a clear graphic depiction of sequential processing steps. Furthermore, EDI is commonly used for remote and third-party warehousing fulfillment processes.
EDI solutions can expedite delivery of current products and pricing information to any and all partners, providing individualized information pertinent to the specific needs of the particular partner, in their required format
100% EDI Compliance Guaranteed!
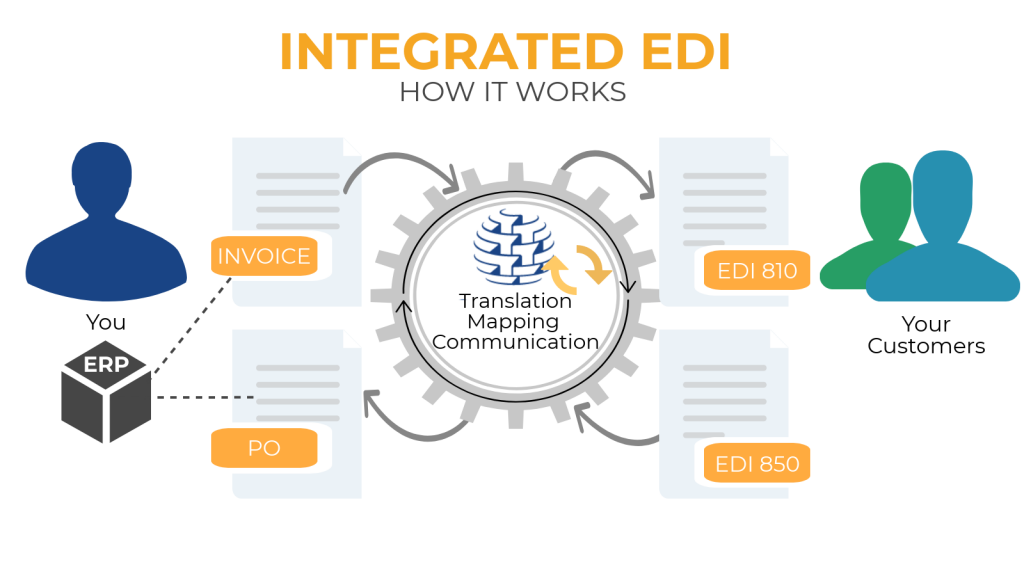
In this chapter, we will discuss how integrated EDI works,
The complete 4 step process from formating, to translation and getting back the data into the ERP system.
When you’re ready to send out invoices, PO acknowledgments, or other outbound documents, it takes the format exported from your system and translates it into the EDI formats required by your trading partners.
The translation is fast and reliable – so you can focus on your business.

Step 1 – Your business ERP system generates the key data structures that will form part of the messages.
Step 2 – These data from the ERP will be transferred to the Integrated EDI software, which then translates and forward to the recipient in the format they expect to receive.
Step 3 – Upon receiving the document at the recipient end the process gets reversed, so that the document received by the EDI software is transformed back into a data structure that can be processed by the ERP.
Step 4 – After the transformation, communication takes place between the internal management system and the integrated EDI software which will integrate these data into the receipt ERP system.
Here are some of the important integrated EDI benefits,
Achieve seamless translation
Reduce costs, improve cash flow
Increase accuracy and boost productivity
Easy inventory control
Integrate business documents with your internal operations using Commport’s extensive library of available plug-ins for mid-market and higher business systems.
Achieve seamless translation, converting business system documents into documents that are global standards compliant.
Connect to the powerful Commport VAN, which supports all of today’s communications protocols and connectivity with other Value Added Networks globally
Connect directly with your trading partners using protocols such as AS2 or sFTP.
User visibility into activity on the Commport Network through Commport Monitor and Commport Portal.
Mappings and translation are managed by Commport, so there is no software to install or maintain.
In this chapter, we will be explaining ' EDI X12 Document Types'
Companies and trading partners exchange these documents using EDI standards
10 common EDI communication standards used
Importance of each communication standards
EDI transactions are standardized electronic business documents used by trading partners to send and receive business information, such as when one company wants to electronically send a purchase order to another organization.
EDI transactions were designed to be standardized and are independent of the communications used by companies or the software technology that sends and receives the EDI data.
Companies and trading partners exchange these documents using EDI standards to automate and streamline purchase orders, invoices, acknowledgments, payments, tracking, and other reports.
Any EDI transaction document must contain a certain minimum amount of vital data. Without these EDI compliance requirements, an EDI document becomes useless. Adhering to strict EDI
Feed formatting rules helps define precisely how and where each part of data on the document will be found and used. Each document is assigned one of the dozens of transaction numbers from the EDI public format.
EDI 104: Air Shipment Information
EDI 106: Motor Carrier Rate Proposal
EDI 107: Request for Motor Carrier Rate Proposal
EDI 108: Response to a Motor Carrier Rate Proposal
EDI 109: Vessel Content Details
EDI 110: Air Freight Details and Invoice
EDI 120: Vehicle Shipping Order
EDI 121: Vehicle Service
EDI 125: Multilevel Railcar Load Details
EDI 126: Vehicle Application Advice
EDI 127: Vehicle Baying Order
EDI 128: Dealer Information
EDI 129: Vehicle Carrier Rate Update
EDI 160: Transportation Automatic Equipment Identification
EDI 161: Train Sheet
EDI 163: Transportation Appointment Schedule Information
EDI 204: Motor Carrier Load Tender
EDI 210: Motor Carrier Freight Details and Invoice
EDI 211: Motor Carrier Bill of Lading
EDI 212: Motor Carrier Delivery Trailer Manifest
EDI 213: Motor Carrier Shipment Status Inquiry
EDI 214: Transportation Carrier Ship. Status Message
EDI 215: Motor Carrier Pick-up Manifest
EDI 216: Motor Carrier Shipment Pick-up Notification
EDI 217: Motor Carrier Loading and Route Guide
EDI 219: Logistics Service Request
EDI 220: Logistics Service Response
EDI 222: Cartage Work Assignment
EDI 223: Consolidators Freight Bill and Invoice
EDI 224: Motor Carrier Summary Freight Bill Manifest
EDI 225: Response to a Cartage Work Assignment
EDI 227: Trailer Usage Report
EDI 228: Equipment Inspection Report
EDI 240: Motor Carrier Package Status
EDI 250: Purchase Order Shipment Management Document
EDI 300: Reservation (Booking Request) (Ocean)
EDI 301: Confirmation (Ocean)
EDI 303: Booking Cancellation (Ocean)
EDI 304: Shipping Instructions
EDI 309: Customs Manifest
EDI 310: Freight Receipt and Invoice (Ocean)
EDI 311: Canada Customs Information
EDI 312: Arrival Notice (Ocean)
EDI 313: Shipment Status Inquiry (Ocean)
EDI 315: Status Details (Ocean)
EDI 317: Delivery/Pickup Order
EDI 319: Terminal Information
EDI 322: Terminal Operations and Intermodal Ramp Activity
EDI 323: Vessel Schedule and Itinerary (Ocean)
EDI 324: Vessel Stow Plan (Ocean)
EDI 325: Consolidation of Goods in Container
EDI 326: Consignment Summary List
EDI 350: Customs Status Information
EDI 352: U.S. Customs Carrier General Order Status
EDI 353: Customs Events Advisory Details
EDI 354: U.S. Customs Auto. Manifest Archive Status
EDI 355: U.S. Customs Acceptance/Rejection
EDI 356: U.S. Customs Permit to Transfer Request
EDI 357: U.S. Customs In-Bond Information
EDI 358: Customs Consist Information
EDI 359: Customs Customer Profile Management
EDI 361: Carrier Interchange Agreement (Ocean)
EDI 404: Rail Carrier Shipment Information
EDI 410: Rail Carrier Freight Details and Invoice
EDI 412: Trailer or Container Repair Billing
EDI 414: Rail Carhire Settlements
EDI 417: Rail Carrier Waybill Interchange
EDI 418: Rail Advance Interchange Consist
EDI 419: Advance Car Disposition
EDI 420: Car Handling Information
EDI 421: Estimated Time of Arrival & Car Scheduling
EDI 422: Equipment Order
EDI 423: Rail Industrial Switch List
EDI 424: Rail Carrier Services Settlement
EDI 425: Rail Waybill Request
EDI 426: Rail Revenue Waybill
EDI 429: Railroad Retirement Activity
EDI 431: Railroad Station Master File
EDI 432: Rail Deprescription
EDI 433: Railroad Reciprocal Switch File
EDI 434: Railroad Mark Register Update Activity
EDI 435: Standard Transportation Commodity Code Master
EDI 436: Locomotive Information
EDI 437: Railroad Junctions & Interchanges Activity
EDI 440: Shipment Weights
EDI 451: Railroad Event Report
EDI 452: Railroad Problem Log Inquiry or Advice
EDI 453: Railroad Service Commitment Advice
EDI 455: Railroad Parameter Trace Registration
EDI 456: Railroad Equipment Inquiry or Advice
EDI 460: Railroad Price Distribution Request or Response
EDI 463: Rail Rate Reply
EDI 466: Rate Request
EDI 468: Rate Docket Journal Log
EDI 470: Railroad Clearance
EDI 475: Rail Route File Maintenance
EDI 485: Ratemaking Action
EDI 486: Rate Docket Expiration
EDI 490: Rate Group Definition
EDI 492: Miscellaneous Rates
EDI 494: Rail Scale Rates
EDI 601: U.S. Customs Export Shipment Information
EDI 603: Transportation Equipment Registration
EDI 715: Intermodal Group Loading Plan
EDI 854: Shipment Delivery Discrepancy Info.
EDI 858: Shipment Information
EDI 859: Freight Invoice
EDI 920: Loss or Damage Claim: Gen. Commodities
EDI 924: Loss or Damage Claim: Motor Vehicle
EDI 925: Claim Tracer
EDI 926: Claim Status Report and Tracer Reply
EDI 928: Automotive Inspection Detail
EDI 980: Functional Group Totals
EDI 990: Response to a Load Tender
EDI 998: Set Cancellation
EDI 130: Student Educational Record (Transcript)
EDI 131: Student Educational Record (Transcript) Acknowledgment
EDI 132: Human Resource Information
EDI 133: Educational Institution Record
EDI 135: Student Aid Origination Record
EDI 139: Student Loan Guarantee Result
EDI 144: Student Loan Transfer and Status Verification
EDI 146: Request for Student Educational Record (Transcript)
EDI 147: Response to Request for Student Educational Record (Transcript)
EDI 155: Business Credit Report
EDI 188: Educational Course Inventory
EDI 189: Application for Admission to Educational Institutions
EDI 190: Student Enrollment Verification
EDI 191: Student Loan Pre-Claims and Claims EDI 194: Grant or Assistance Application
EDI 102: Associated Data
EDI 242: Data Status Tracking
EDI 815: Cryptographic Service Message
EDI 864: Text Message
EDI 868: Electronic Form Structure
EDI 993: Secured Receipt or Acknowledgment
EDI 997: Functional Acknowledgment
EDI 999: Implementation Acknowledgment
EDI 100: Insurance Plan Description
EDI 111: Individual Insurance Policy & Client Info.
EDI 112: Property Damage Report
EDI 124: Vehicle Damage
EDI 148: Report of Injury, Illness, or Incident
EDI 186: Insurance Underwriting Requirements Reporting
EDI 187: Premium Audit Request and Return
EDI 252: Insurance Producer Administration
EDI 255: Underwriting Information Services
EDI 256: Periodic Compensation
EDI 267: Individual Life Annuity & Disability Application
EDI 268: Annuity Activity
EDI 269: Health Care Benefit Coordination Verification
EDI 270: Eligibility, Coverage or Benefit Inquiry
EDI 271: Eligibility, Coverage or Benefit Information
EDI 272: Property and Casualty Loss Notification
EDI 273: Insurance/Annuity Application Status
EDI 274: Health Care Provider Information
EDI 275: Patient Information
EDI 276: Health Care Claim Status Request
EDI 277: Health Care Information Status Notification
EDI 278: Health Care Services Review Information
EDI 362: Cargo Insurance Advice of Shipment
EDI 834: Benefits Enrollment and Maintenance
EDI 835: Health Care Claim Payment/Advice
EDI 837: Health Care Claim
EDI 101: Name and Address Lists
EDI 140: Product Registration
EDI 141: Product Service Claim Response
EDI 142: Product Service Claim
EDI 143: Product Service Notification
EDI 159: Motion Picture Booking Confirmation
EDI 170: Revenue Receipts Statement
EDI 180: Return Merchandise Authorization & Notification
EDI 244: Product Source Information
EDI 290: Cooperative Advertising Agreements
EDI 503: Pricing History
EDI 504: Clauses and Provisions
EDI 620: Excavation Communication
EDI 625: Well Information
EDI 753: Request For Routing Instructions
EDI 754: Routing Instructions
EDI 816: Organizational Relationships
EDI 818: Commission Sales Report
EDI 830: Planning Schedule w/ Release Capability
EDI 832: Price/Sales Catalog
EDI 840: Request for Quotation
EDI 841: Specifications/Technical Information
EDI 842: Nonconformance Report
EDI 843: Response to Request for Quotation
EDI 845: Price Authorization Acknowledgment/Status
EDI 846: Inventory Inquiry/Advice
EDI 847: Material Claim
EDI 848: Material Safety Data Sheet
EDI 850: Purchase Order
EDI 851: Asset Schedule
EDI 852: Product Activity Data
EDI 853: Routing and Carrier Instruction
EDI 855: Purchase Order Acknowledgment
EDI 856: Ship Notice/Manifest
EDI 857: Shipment and Billing Notice
EDI 860: Purchase Order Change Request: Buyer Initiated
EDI 861: Receiving Advice/Acceptance Certificate
EDI 862: Shipping Schedule
EDI 863: Report of Test Results
EDI 865: Purchase Order Change Acknowledgment/Request: Seller Initiated
EDI 866: Production Sequence
EDI 867: Product Transfer and Resale Report
EDI 869: Order Status Inquiry
EDI 870: Order Status Report
EDI 873: Commodity Movement Services
EDI 874: Commodity Movement Services Response
EDI 875: Grocery Products Purchase Order
EDI 876: Grocery Products Purchase Order Change
EDI 877: Manufacturer Coupon Family Code Structure
EDI 878: Product Authorization/De-authorization
EDI 879: Price Information
EDI 881: Manufacturer Coupon Redemption Detail
EDI 882: Direct Store Delivery Summary Information
EDI 883: Market Development Fund Allocation
EDI 884: Market Development Fund Settlement
EDI 885: Retail Account Characteristics
EDI 886: Customer Call Reporting
EDI 887: Coupon Notification
EDI 888: Item Maintenance
EDI 889: Promotion Announcement
EDI 890: Contract & Rebate Management
EDI 891: Deduction Research Report
EDI 893: Item Information Request
EDI 894: Delivery/Return Base Record
EDI 895: Delivery/Return Acknowledgment or Adjustment
EDI 896: Product Dimension Maintenance
EDI 940: Warehouse Shipping Order
EDI 943: Warehouse Stock Transfer Shipment Advice
EDI 944: Warehouse Stock Transfer Receipt Advice
EDI 945: Warehouse Shipping Advice
EDI 947: Warehouse Inventory Adjustment Advice
EDI 197: Real Estate Title Evidence
EDI 198: Loan Verification Information
EDI 199: Real Estate Settlement Information
EDI 200: Mortgage Credit Report
EDI 201: Residential Loan Application
EDI 202: Secondary Mortgage Market Loan Delivery
EDI 203: Secondary Mortgage Market Investor Report
EDI 205: Mortgage Note
EDI 206: Real Estate Inspection
EDI 245: Real Estate Tax Service Response
EDI 248: Account Assignment/Inquiry & Service/Status
EDI 259: Residential Mortgage Insurance Explanation of Benefits
EDI 260: Application for Mortgage Insurance Benefits
EDI 261: Real Estate Information Request
EDI 262: Real Estate Information Report
EDI 263: Residential Mortgage Insurance Application Response
EDI 264: Mortgage Loan Default Status
EDI 265: Real Estate Title Insurance Services Order
EDI 266: Mortgage or Property Record Change Notification
EDI 810: Invoice
EDI 811: Consolidated Service Invoice/Statement
EDI 812: Credit/Debit Adjustment
EDI 814: General Request, Response, or Confirmation
EDI 819: Joint Interest Billing and Operating Expense Statement
EDI 820: Payment Order/Remittance Advice
EDI 821: Financial Information Reporting
EDI 822: Account Analysis
EDI 823: Lockbox
EDI 824: Application Advice
EDI 827: Financial Return Notice
EDI 828: Debit Authorization
EDI 829: Payment Cancellation Request
EDI 831: Application Control Totals
EDI 833: Mortgage Credit Report Order
EDI 844: Product Transfer Account Adjustment
EDI 849: Response to Product Transfer Account Adjustment
EDI 872: Residential Mortgage Insurance Application
EDI 880: Grocery Products Invoice
EDI 103: Abandoned Property Filings
EDI 105: Business Entity Filings
EDI 113: Election Campaign & Lobbyist Reporting
EDI 149: Notice of Tax Adjustment or Assessment
EDI 150: Tax Rate Notification
EDI 151: Electronic Filing of Tax Return Data Acknowledgment
EDI 152: Statistical Government Information
EDI 153: Unemployment Insurance Tax Claim or Charge Information
EDI 154: Secured Interest Filing
EDI 157: Notice of Power of Attorney
EDI 158: Tax Jurisdiction Sourcing
EDI 175: Court and Law Enforcement Notice
EDI 176: Court Submission
EDI 179: Environmental Compliance Reporting
EDI 185: Royalty Regulatory Report
EDI 194: Grant or Assistance Application
EDI 195: Federal Communications Commission (FCC) License Application
EDI 196: Contractor Cost Data Reporting
EDI 249: Animal Toxicological Data
EDI 251: Pricing Support
EDI 280: Voter Registration Information
EDI 283: Tax or Fee Exemption Certification
EDI 284: Commercial Vehicle Safety Reports
EDI 285: Commercial Vehicle Safety and Credentials Information Exchange
EDI 286: Commercial Vehicle Credentials
EDI 288: Wage Determination
EDI 500: Medical Event Reporting
EDI 501: Vendor Performance Review
EDI 511: Requisition
EDI 517: Material Obligation Validation
EDI 521: Income or Asset Offset
EDI 527: Material Due-In and Receipt
EDI 536: Logistics Reassignment
EDI 540: Notice of Employment Status
EDI 561: Contract Abstract
EDI 567: Contract Completion Status
EDI 568: Contract Payment Management Report
EDI 650: Maintenance Service Order
EDI 805: Contract Pricing Proposal
EDI 806: Project Schedule Reporting
EDI 813: Electronic Filing of Tax Return Data
EDI 826: Tax Information Exchange
EDI 836: Procurement Notices
EDI 838: Trading Partner Profile
EDI 839: Project Cost Reporting
EDI 996: File Transfer
EDI communication standards are the requirements for the format and composition of EDI documents. EDI standards delineate the correct order and location of units of data in a given EDI document.
EDI standards began to emerge in the mid-1980s, and were purposely designed to be entirely separate (not dependent upon) changes in communication and software technologies
Because EDI documents must be processed by computers rather than humans, a standard format must be used so that the computer will be able to read and understand the documents.
American National Standard Institute (ANSI) founded the Accredited Standards Committee (ASC) in 1979 to develop uniform standards for the inter-industry electronic exchange of business transactions, namely electronic data interchange (EDI). This standard is also sometimes called ANSI X12 Standard or just simply X12.
ANSI X12 was originally developed to support companies across different industry sectors in North America however, today there are more than 300,000 companies worldwide using X12 EDI standards in daily business transactions.
Each EDI X12 transaction type is differentiated by a unique 3-digit number and there are more than 300 different types of X12 EDI standards for various industries from finance, government, healthcare, insurance, banking, transportation, and many more. ASC also contributes to UN/EDIFACT messages that are used widely outside of the United States and develop standards for CICA (Context Inspired Component Architecture) and XML schemas.
Tradacoms (Trading DAA Communications) is an early EDI standard that was originally introduced in 1982 and was primarily used in the UK retail sector. It was maintained and extended by the UK Article Numbering Association, now called GS1 UK. Slowly this standard become less obsolescent as its development of it effectively ceased in 1995. Despite this, it has proved durable and most of the retail EDI traffic in the UK still uses it today.
TRADACOMS uses multi messages instead of relying on a format of single messaging. TRADACOMS communication is comprised of 26 messages structured in a hierarchy. Each TRADACOMS message, much like EDIFACT, is given a six-letter application reference. For example, an invoice message is INVFIL, a payment order is PAYORD, a utility bill is UTLHDR, and so on.
United Nations/Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce and Transport is the international standard that was developed by the United Nations. The work of maintenance and further development of this standard is done through the United Nations Centre for Trade Facilitation and Electronic Business (UN/CEFACT) under the UN Economic Commission for Europe. The EDIFACT standard provides a set of syntax rules to structure, an interactive exchange protocol and provides a set of standard messages which allow multi-country and multi-industry exchange of electronic business documents. EDIFACT is widely used across Europe, mainly due to the fact that many companies adopted it very early on. EDIFACT has seen some adoption in the ASPAC region, however, there are currently more XML-based standards being used in this particular region today.
UN/EDIFACT, which is short for United Nations rules for Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport, is a set of internationally standardized communication guidelines for exchanged data tags and message types between computer systems in different networks. UN/EDIFACT standards structure data into segments, segments into messages, and messages into an interactive exchange protocol.
The syntax rules for EDIFACT describe the message (nesting, character sets, structures, etc.) The data tags detail the different types of data being exchanged and how each is represented. The message types are also known as UNSMs (United Nations Standard Messages).
ODETTE stands for Organization of Data Exchange by Tele Transmission in Europe and creates data exchange and communications standards for the European automotive industry. It is similar to North America’s AIAG (Automotive Industry Action Group). ODETTE develops protocols such as OFTP and the more advanced OFTP2, which provides enhanced security through encryption methods and digital certificates for EDI data exchange.
Deploying B2B and MFT (managed file transfer) solutions that are ODETTE-certified for OFTP and OFTP2 allows a company to securely and efficiently communicate with various software to successfully exchange data.
The Organization for Data Exchange by Tele Transmission in Europe is a group that represents the interests of the automotive industry in Europe. They are the equivalent of the Automotive Industry Action Group (AIAG) in North America. The organization develops tools and recommendations that improve the flow of goods, services product data and business information across the whole automotive value chain. ODETTE has been responsible for developing communications standards such as OFTP and OFTP2.0, constant improvement processes such as Materials Management Operations Guideline / Logistics Evaluation (MMOG/LE) and automotive-specific document standards as defined via the link below.
This standard was originally conceived in 1987 by the EAN General Assembly and was to be developed on the then emerging international UN/EDIFACT standard. The EANCOM messages, maintained by GS1, are more detailed in nature compared to the TRADACOMS message set. EANCOM was originally developed for the retail sector and has subsequently grown to become the most widely used UN/EDIFACT subset and is now found in a variety of other industry sectors such as healthcare, construction and publishing.
EANCOM provides a logical sequence of messages used in business. Trading companies agree together on messages adapted to their needs. Standard messages available in EANCOM can be divided into the following categories, Master Data, Commercial Transactions, Report & Planning and Transporter.
The Voluntary Inter-industry Commerce Standard is used by the general merchandise retail industry across North America. It is a subset of the ANSI ASC X12 national standard. VICS EDI is being utilized by thousands of companies, department and specialty retail stores, mass merchandisers and their respective suppliers. In 1988 GS1 US became the management and administrative body for VICS EDI. GS1 US also manages the ASC X12 derived Uniform Communication Standard (UCS) for the grocery industry and Industrial/Commercial Standard (I/C) for the industrial sector.
This organization develops standards and best practices to serve the needs of companies within the German automotive industry. The VDA has developed over thirty messages to meet the need of companies such as VW, Audi, Bosch, Continental and Daimler AG. Further information about these messages can be found via the link below.
VDA develops standards and best practices to serve the needs of companies within the German automotive industry. The VDA has developed over thirty messages to meet the need of companies such as VW, Audi, Bosch, Continental and Daimler AG.
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act was enacted by the U.S congress in 1996. A key component of HIPAA is the establishment of national standards for electronic health care transactions and national identifiers for providers, health insurance plans and employers. The standards are meant to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of the North American health care system by encouraging the widespread use of EDI in the U.S health care system. The HIPAA EDI transaction sets are based on X12 and the key message types are described below.
This consists of a consortium of major computer, consumer electronics, semi-conductor manufacturers, telecommunications and logistics companies working together to create and implement industry-wide, open e-business process standards. These standards form a common e-business language, aligning processes between supply chain partners on a global basis. The RosettaNet document standard is based on XML and defines message guidelines, business processes interface and implementation frameworks for interactions between companies. Using RosettaNet Partner Interface Processes (PIPs), business partners of all sizes can connect electronically to process transactions and move information within their extended supply chains. Further information about RosettaNet PIP documents can be found from the link below.
The Society of Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication was formed in 1973 and is headquartered in Brussels. SWIFT operates a worldwide financial messaging network which exchanges messages between banks and financial institutions. SWIFT also markets software and services to financial institutions, much of it for use on the SWIFTNet Network. SWIFTNet is the infrastructure used to exchange these documents and FIN, InterAct and FileAct are used to encode the SWIFT documents for transmission. The majority of interbank messages use the SWIFT network. As of November 2008, SWIFT linked 8740 financial institutions across 209 countries. The SWIFT document standard is split into four areas, Payments, Trade Services, Securities and Trading.
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
An Integrated EDI solution translates your inbound documents, like purchase orders, from your trading partners’ EDI files into a format that can be imported directly into your ERP, accounting or other business system.
Here is how our Integrated EDI Solution works,
Commport’s Integrated EDI software as a service solution is a proven and cost-effective platform without the initial outlay associated with traditional EDI Software.
Integrate your EDI information with your specific business systems, including Sage and Microsoft software options. Commport’s Integrated EDI software as a service (SaaS) solution is a proven and cost effective platform without the initial outlay associated with traditional EDI software.
Users of Commport’s integrated software enjoy the benefits of streamlined EDI processes that are electronically, verses manually driven. This results in reduced error rates and confidence in reliable data maintenance that is integrated throughout the EDI document sharing process.
If you manage a high volume of EDI documents, Commport’s Integrated EDI solution can help you to reduce the hours of manpower required to re-key information into your internal accounting and business systems.
At best, a manual process of re-keying data is time consuming, costly, and can be a drain on your resources. At worst, a manual process is at risk for re-keying errors that can occur when data is manually entered into multiple systems.
An Integrated EDI solution translates your inbound documents, like purchase orders, from your trading partners’ EDI files into a format that can be imported directly into your ERP, accounting or other business system.
When you’re ready to send out invoices, PO acknowledgments or other outbound documents, it takes the format exported from your system and translates it into the EDI formats required by your trading partners.
Translation is fast and reliable – so you can focus on your business.
The solution grows easily as your business grows and adding new customers is easy.

This quick infographic breaks down how an integrated EDI solution works, the difference between cloud EDI and finally the benefits of having an Integrated EDI solution for your business.
Key Features of Commport’s Integrated EDI solution:
Commport is a single-source solution with a commitment to end-to-end service: we own and operate 100% of the infrastructure and provide the service and support to back it up
In this current digital world, integrated EDI can be a competitive advantage. It can manage crucial aspects of your supply chain lifecycle efficiently with little effort. It helps you take care of your internal processes and allows you to build better trade partnerships with other businesses.
Without integrated EDI, you have isolated pieces of technology that require human intervention. The biggest IT challenge that many organizations face is the integration of different applications and systems. Data flow is interrupted in the absence of integrated EDI, and data fragmentation hurts businesses. Without integration, many B2B projects fail to deliver the benefits that users expect.
No doubt, investing in integrated EDI offers long-term benefits than the up-front costs. If you’d like to dedicate more time to become a market share leader and innovator, then it’s time to track your business goals and set your EDI integration goals.
If you are looking for an end-to-end integrated EDI solution look no further and contact commport team. We provide the most affordable and reliable integrated EDI solution in the market.
Unlike standalone or web-based EDI, Integrated EDI directly integrates with internal business systems. This setup allows for a higher level of automation, reducing manual intervention, increasing accuracy, and streamlining workflows across the organization.
Yes, Integrated EDI is highly scalable. As businesses grow and transaction volumes increase, the system can expand to handle larger data volumes and connect with additional systems or trading partners, supporting continued growth and scalability.
To implement Integrated EDI, a company should assess its specific integration needs, choose an EDI provider experienced in integrating with its ERP or other internal systems, and plan for customization to meet unique business processes. The provider typically supports the setup and ensures compatibility with existing systems.
Key features include seamless ERP integration, real-time data processing, automated workflows, robust security measures, customizable document formats, and compliance with industry EDI standards. These features ensure efficient and secure data exchanges with trading partners.
By directly connecting with internal systems, Integrated EDI eliminates the need for repetitive data entry, reducing the risk of human error. Automation speeds up transaction processing, enabling quicker order fulfillment and reducing delays in the supply chain.