Introduction
We understand how frustrating supply chain bottlenecks can be.
That’s why 71% of surveyed leaders plan to increase their investment in supply chain software like EDI this year compared to previous years.
Fortunately, companies implementing EDI systems are seeing remarkable results, including a 335% three-year ROI and 50% reduction in late orders.
EDI transforms supply chain management by automating document exchange and enabling real-time communication, directly addressing the delays that plague 65% of manufacturers today.
Key Takeaways
- EDI reduces transaction costs by 35% minimum while cutting error rates from 30% to below 1% through automated validation and standardized formats.
- Real-time data sharing eliminates communication delays between trading partners, providing instant updates on inventory, shipping, and order status across the entire supply chain.
- Partner onboarding accelerates by up to 70% with pre-connected EDI networks, allowing faster business relationships and reduced setup time.
- Companies achieve 335% three-year ROI with EDI implementation, demonstrating substantial financial benefits beyond operational improvements.
- Successful implementation requires strategic planning: assess current processes, choose cloud or on-premise solutions, integrate with existing systems, and train teams thoroughly.
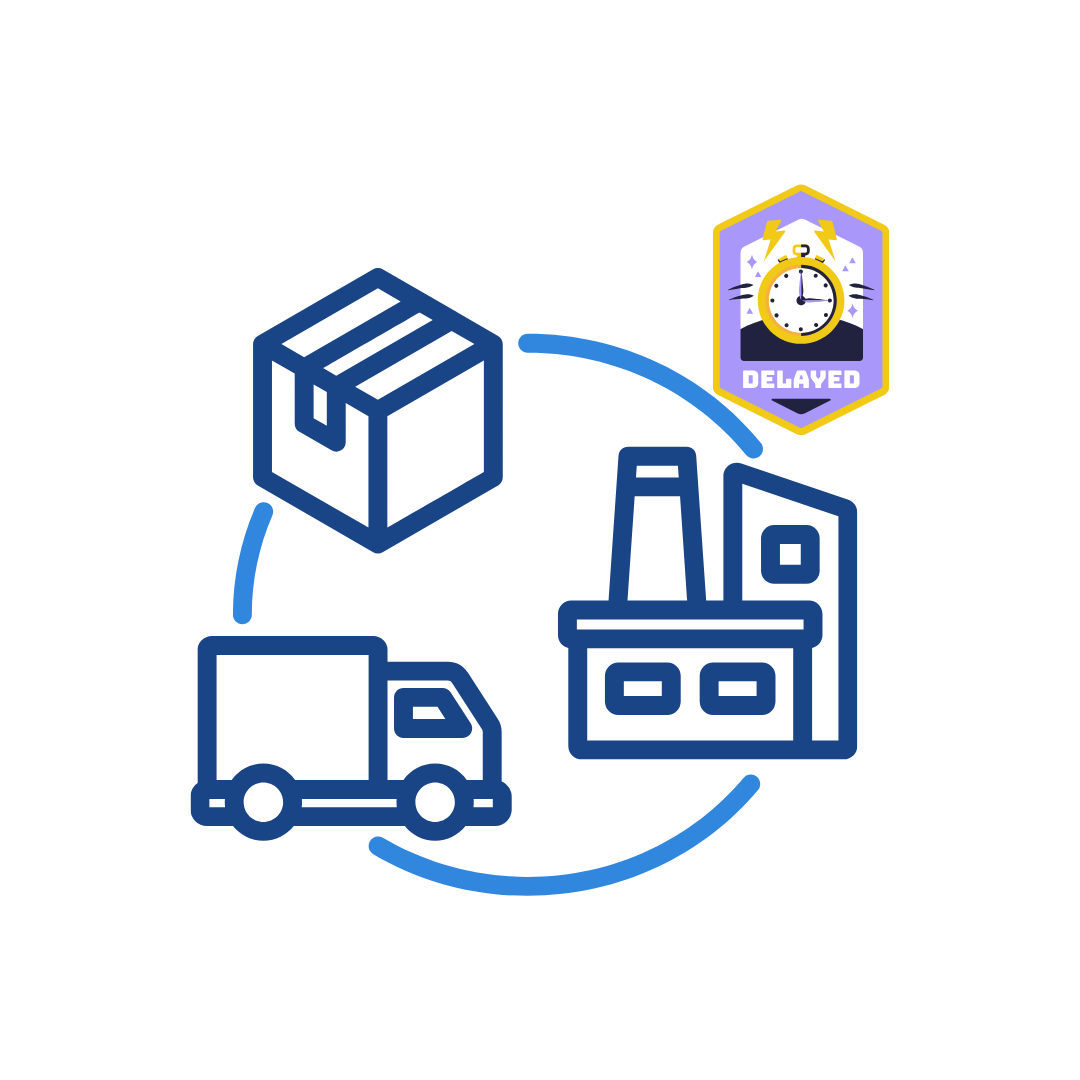
Understanding Supply Chain Delays and Their Impact
Almost 80% of businesses experienced supply chain disruptions in 2025 alone due to an increase in tariffs and labor disruptions, creating ripples that affect entire operations. Despite technological advancements, supply chains continue to face significant bottlenecks that hinder efficiency and create costly delays.

1. Communication Delays Between Trading Partners
Communication breakdowns represent a fundamental cause of supply chain delays. Supply chains involve numerous stakeholders – from raw material suppliers to manufacturers, distributors, and delivery agencies. Without clear messaging, companies experience confusion, missed handoffs, and breakdowns in coordination. Furthermore, businesses can be reluctant to collaborate in an increasingly globalized market, making it difficult to gain comprehensive visibility. Consequently, 76% of businesses still lack end-to-end visibility across their supply chains.
2. Inventory Management Challenges
Poor inventory management creates serious bottlenecks throughout the supply chain. The primary issues include:
- Stock imbalances (too much or too little inventory)
- Inaccurate forecasting and limited visibility
- Systems designed for speed that crumble under disruptions
Retailers faced a staggering $818 billion in losses due to inventory distortions last year, with 52% coming from stockouts and 44% from overstocks. The average retailer operates with just 91.3% inventory accuracy, leading to an estimated annual revenue loss of $1.75 million.
3. Manual Processing Bottlenecks
Manual data entry introduces costly errors and inefficiencies. The typical error rate reaches as high as 4%, meaning that a business processing 10,000 transactions monthly will have approximately 400 transactions containing mistakes. At an average cost of $50 to correct each error, this translates to $20,000 in monthly losses – or $240,000 annually.
Beyond direct costs, manual processes create fragmented information across multiple systems, leading to inconsistent data that undermines decision-making. Additionally, rekeying data between systems introduces unnecessary friction into workflows that could otherwise flow freely.
4. Lack of Real-Time Visibility
Only 6% of companies have achieved full supply chain visibility. This absence of transparency creates significant blind spots around inventory levels, shipment status, and production timelines. Without real-time information, managers operate with incomplete or outdated data, resulting in poor decisions that lead to delays, stockouts, and overstocking. Moreover, the lack of interoperability between different technological systems complicates information sharing and further limits visibility.
What is EDI in Supply Chain Management
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) serves as a vital tool in modern supply chains, automating and streamlining critical processes between trading partners. Specifically, EDI enables the seamless exchange of standardized business documents between computers without human intervention, replacing traditional paper-based transactions with digital communication.
Core Components of EDI Systems
EDI systems consist of several interconnected elements that work together to facilitate data exchange. The primary components include:
- EDI Standards: Predefined formats like ANSI X12 (North America) and EDIFACT (international) that ensure consistent communication
- Translation Software: Converts internal data to standardized EDI formats and vice versa, enabling system compatibility
- Communication Protocols: Secure transmission methods such as AS2, FTP/SFTP, or Value-Added Networks (VANs)
- Data Mapping: Aligns internal data fields with corresponding EDI standard fields
- EDI Envelopes: Digital packaging containing sender and receiver information
- EDI Integrations: Connections with internal systems like ERP, CRM, and WMS
How EDI Works in Supply Chains
The EDI process begins when a business system generates a document based on a business event. Subsequently, this data is mapped to a standardized format, then converted by an EDI translator into a machine-readable EDI document. Once properly formatted, the document travels through secure communication channels to the recipient, who acknowledges receipt and processes it in their system.
Common EDI Transaction Types
EDI encompasses numerous transaction types, each identified by specific codes:
- Purchase Orders (850) for ordering products directly from suppliers
- Invoices (810) for payment requests
- Advanced Shipping Notices (856) for goods in transit notifications
- Inventory Reports (846) for stock level updates
- Order Responses (855) for purchase order confirmations
- Shipping Orders (940) and Advices (945) for warehouse operations
By implementing EDI, companies eliminate manual data entry, reduce errors, and gain real-time visibility—all critical factors in mitigating supply chain delays through standardized electronic communication.
How EDI Mitigates Supply Chain Delays
In manufacturing and distribution, EDI implementation leads to up to 70% faster partner onboarding, creating immediate improvements in supply chain efficiency. By streamlining communication and automating crucial processes, EDI directly addresses the core issues causing supply chain bottlenecks.
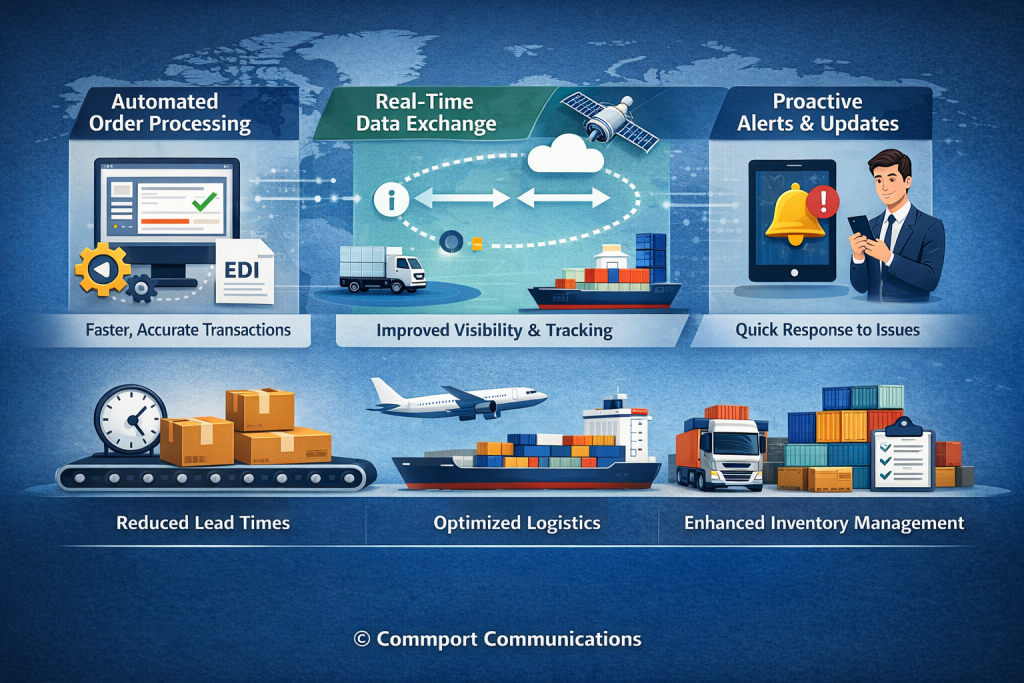
1. Automating Document Exchange
EDI replaces manual paperwork with standardized electronic document exchange, eliminating repetitive tasks like digging through spreadsheets and sending emails. Rather than manually locating, collating, and sending information, companies can automate the entire process—from purchase orders to shipping notices. This automation ensures all messaging occurs in a standardized way, 24/7, every day of the year.
2. Enabling Real-Time Data Sharing
With EDI, key supply chain stakeholders receive instant updates about inventory levels, shipping schedules, and payment status. Notably, a retailer can automatically receive inventory data from suppliers, placing replenishment orders without manual intervention. This immediate exchange allows businesses to react quickly to changing market demands, preventing stockouts and overstock situations.
3. Reducing Manual Data Entry Errors
Manual processes typically produce error rates approaching 30%, while integrated automation with validation pushes error rates below 1%. These improvements come from:
- Eliminating rekeying from emails, PDFs, and spreadsheets
- Automatic validation of required fields and partner rules
- Standardized formats reducing mismatched data
4. Improving Order Processing Speed
EDI transforms processing times dramatically, reducing what would take days through manual processes to mere minutes or hours. This acceleration shortens order-to-cash cycles, minimizes processing bottlenecks, and enables faster decision-making. Companies implementing EDI typically experience a minimum 35% reduction in transaction costs.
5. Enhancing Inventory Visibility
EDI inventory systems create a shared, trusted view of stock across trading partners. As inventory changes due to receipts, production, or shipments, updates flow electronically without waiting for manual reports or end-of-day reconciliations. Commport EDI Solutions Help You Streamline Your Supply Chain Operations by Standardizing and Automating all Your Document Transactions. Trusted by 6000+ Happy Customers.
6. Accelerating Partner Communication
Pre-connected EDI networks enable companies to find partners already active on the same network, reuse established configurations, avoid manual communication setups, and start exchanging documents faster. This approach eliminates half the onboarding cycle by skipping communication setup, mailbox creation, protocol validation, and routing configuration.
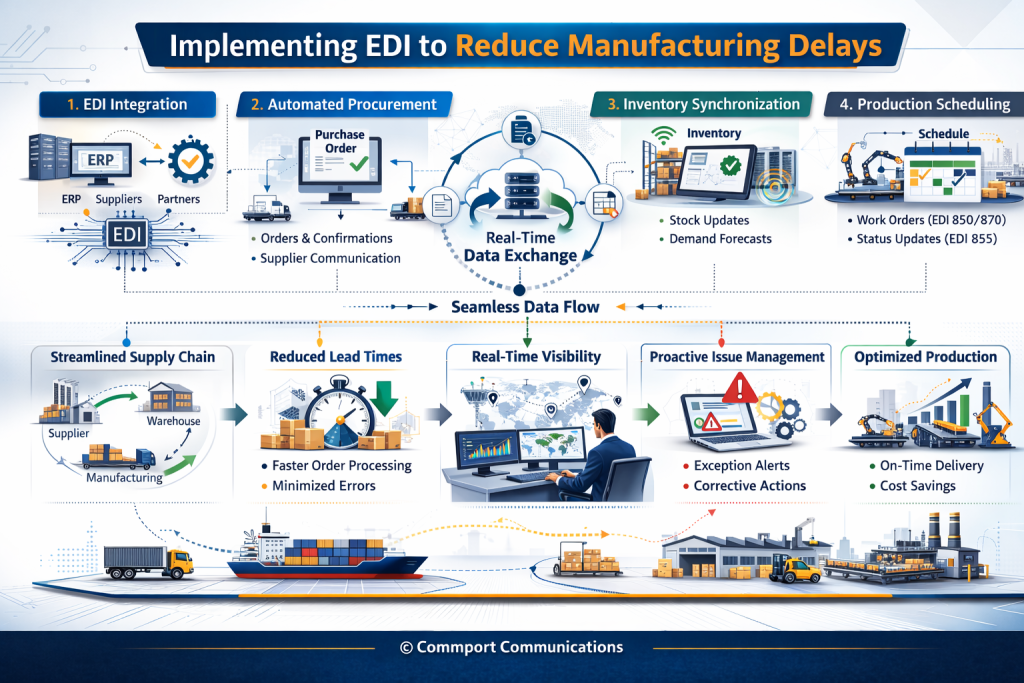
Implementing EDI to Reduce Manufacturing Delays
Successful EDI implementation begins with careful planning and execution. Initially, you’ll need a strategic approach to overcome the 64% of supply chain organizations that typically take 2-4 weeks to onboard just one trading partner.
1. Assess Your Current Supply Chain Processes
Start by defining specific, measurable goals for your EDI implementation, such as reducing response times or minimizing document exchange errors. Identify which business processes would benefit most from automation, whether purchase orders, shipment tracking, or invoicing.
2. Choose the Right EDI Solution
Decide between cloud-based EDI (offering flexibility with minimal upfront investment) or on-premise software (providing greater control but higher maintenance costs). Commport EDI Solutions Help You Streamline Your Supply Chain Operations by Standardizing and Automating all Your Document Transactions. Trusted by 6000+ Happy Customers. Get Started Today!
3. Integrate EDI with Existing Systems
Ensure seamless data flow by integrating EDI with your ERP, warehouse management systems, or other internal platforms. This eliminates silos and enhances data accuracy through modern capabilities like API integration.
4. Train Your Team and Partners
Educate your staff on using EDI effectively—proper training minimizes errors and ensures a smooth transition. Securing buy-in from senior management is crucial; if leadership doesn’t prioritize training, employees won’t either.
5. Monitor and Optimize Performance
Continuously track key performance indicators like acknowledgment receipts, transmission success rates, and error rates. Set up automated alerts for failures or delays to catch and resolve issues quickly.
Conclusion
Supply chain disruptions continue to challenge businesses worldwide, yet EDI presents a powerful solution that directly addresses the root causes of these delays. Throughout this article, we have explored how manual processes, poor visibility, and communication gaps create costly bottlenecks that hamper operational efficiency.
EDI stands as a proven remedy, transforming supply chains through automation and standardization. Companies implementing these systems witness dramatic improvements – faster transaction processing, fewer errors, and enhanced visibility across all operations. Additionally, the 335% three-year ROI demonstrates EDI’s substantial financial benefits beyond simply fixing logistical problems.
The path forward for manufacturers struggling with delays seems clear. First, assess your current processes to identify the most impactful areas for automation. Then, select the right EDI solution that aligns with your business requirements. Subsequently, focus on proper integration with existing systems and thorough training for your team.
Most importantly, remember that EDI implementation represents more than just a technological upgrade. This strategic investment builds stronger, more resilient supply chains capable of weathering disruptions. The competitive advantage gained through faster partner onboarding, reduced errors, and real-time information sharing creates a foundation for sustainable growth.
Companies that embrace EDI today position themselves ahead of the 71% of leaders planning to increase their supply chain software investments. Therefore, the question becomes not whether you can afford to implement EDI, but whether you can afford not to. After all, while supply chain challenges may persist, your business now has the knowledge to overcome them effectively and build stronger relationships with trading partners through streamlined, automated communication.
Commport EDI Solutions - #1 EDI Provider in North America
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) is a system that automates the exchange of standardized business documents between trading partners. It helps in supply chain management by streamlining communication, reducing errors, and providing real-time visibility across operations, ultimately mitigating delays and improving efficiency.
EDI significantly reduces manual data entry errors by automating document exchange and validating data. This automation can lower error rates from around 30% in manual processes to less than 1%, eliminating issues caused by rekeying information and mismatched data formats.
Implementing EDI in manufacturing offers several benefits, including faster partner onboarding (up to 70% quicker), improved order processing speed, enhanced inventory visibility, and accelerated partner communication. It also leads to cost savings, with a minimum 35% reduction in transaction costs.
The implementation time for an EDI system can vary, but it’s important to note that 64% of supply chain organizations typically take 2-4 weeks to onboard just one trading partner. However, with proper planning and execution, companies can significantly reduce this time and start reaping the benefits of EDI more quickly.
When selecting an EDI solution, companies should consider factors such as their specific business needs, integration capabilities with existing systems, scalability, and whether to opt for a cloud-based or on-premise solution. It’s also crucial to evaluate the provider’s support services and the solution’s ability to handle various EDI standards and transaction types.