In this in-depth value added network complete guide you’ll learn everything about VANs from their history, different types, benefits, how to setup guides and more!
Value added networks (VAN) have been around since the early days of EDI in the 1970s and have evolved to keep up with changing technologies and business needs. They have become an integral part of modern supply chain management, logistics, and other operational processes, enabling businesses to exchange transactional data in a standardized and automated manner with their trading partners.

Before we get into the details of this value added network complete guide here are some highlights,
So if you’re ready to go “all in” with value added network (VAN), this guide is for you.
Let’s dive right in.
In this chapter, we will discuss the following topics:
- Definition of Value Added Network
- Importance of VAN
- History of VAN
Let’s dive right in!
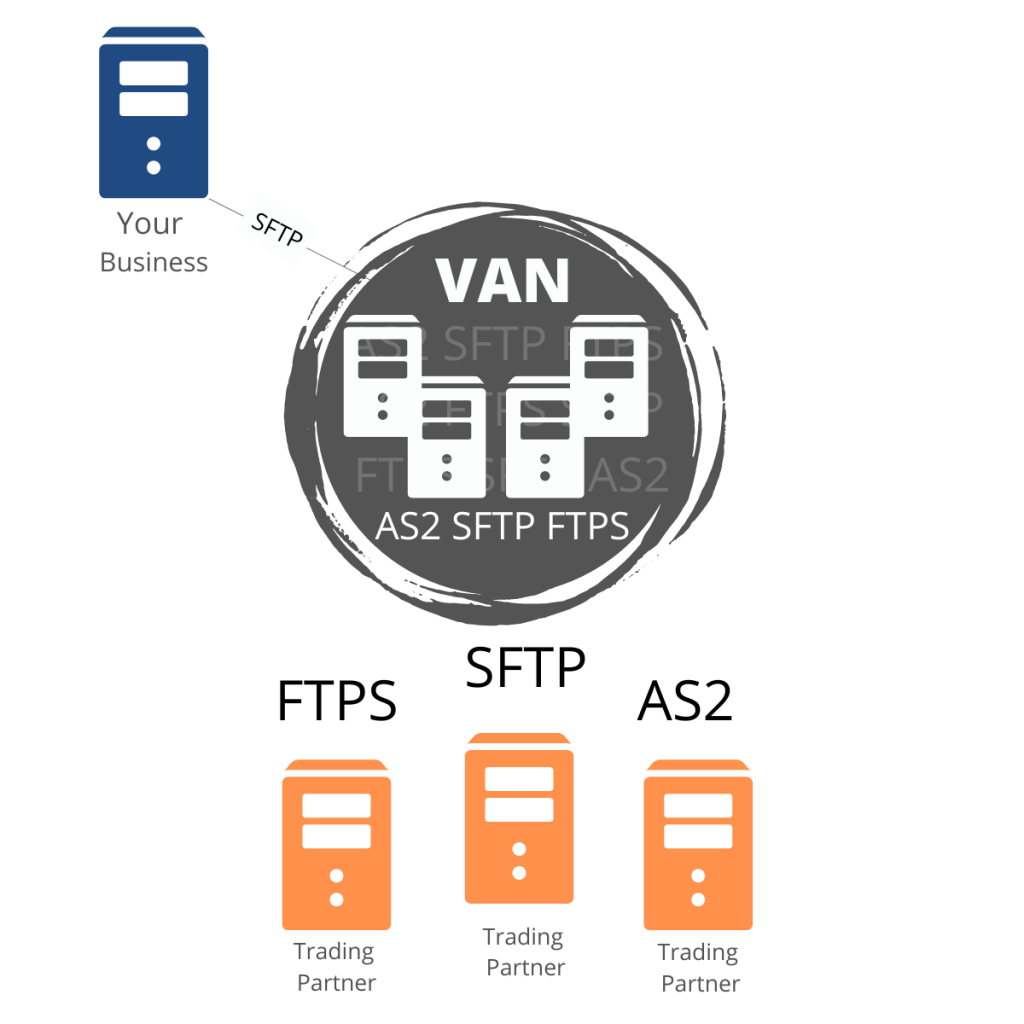
Value Added Networks (VANs) are third-party service providers that facilitate the exchange of electronic data interchange (EDI) transactions between trading partners. They act as intermediaries that receive, validate, translate, and route EDI transactions between businesses, ensuring smooth and secure communication.
VANs provide value-added services such as data validation, data transformation, message routing, and data archiving, among others, to enhance the efficiency and reliability of B2B communication.
It plays a critical role in B2B communication by providing several benefits to businesses. These benefits include increased data accuracy, reduced manual data entry, improved data security through encryption and authentication, enhanced communication reliability, and simplified trading partner management. VANs also offer additional services such as data archiving, auditing, and reporting, which help businesses streamline their data management processes and comply with industry regulations.
It supports different communication protocols and standards, such as X.400, FTP (File Transfer Protocol), AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), and VAN-specific protocols, for transmitting EDI transactions. They also offer different pricing models and support levels, and businesses can choose the VAN service provider that best fits their requirements and budget.
In this in-depth value Added network complete guide we will discuss why VANs are crucial in modern business communication and their significant importance in facilitating efficient and secure B2B (business-to-business) communication.
Here are some key reasons why VANs are essential in modern business communication.
Enables businesses to exchange transactional data with their trading partners in a standardized and automated manner. This streamlines supply chain management processes such as order placement, shipment tracking, and invoice processing, leading to improved efficiency, accuracy, and speed in the supply chain operations.
Provides data validation services that help ensure the accuracy and integrity of data exchanged between trading partners. This reduces the risk of errors, such as incorrect pricing, quantity, or product codes, which can lead to costly disputes, delays, and disruptions in business operations.
It plays a critical role in ensuring the security of data transmitted between trading partners. They use encryption, authentication, and authorization mechanisms to protect sensitive business data from unauthorized access, interception, and tampering, thus safeguarding the confidentiality and integrity of the data.
It provides reliable and scalable communication infrastructure that ensures the timely and consistent exchange of data between trading partners. They manage message routing, delivery, and acknowledgments, ensuring that EDI transactions are sent and received successfully, and provide error handling and notification mechanisms to resolve any issues.
Simplify the management of trading partner connections by providing a centralized platform for managing trading partner profiles, communication protocols, and data mappings. This eliminates the need for businesses to establish and maintain individual connections with each trading partner, reducing complexity and overhead.
The history of Value Added Networks (VANs) can be traced back to the early days of electronic data interchange (EDI) in the 1970s. EDI is the electronic exchange of business documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices, between trading partners in a standardized format. VANs were introduced as intermediaries to facilitate the exchange of EDI transactions between businesses, addressing the need for a reliable and secure communication channel.
In the early years of EDI, businesses used point-to-point connections to exchange EDI transactions, which required direct connections between each trading partner. This approach was complex and costly, as it required businesses to establish and maintain individual connections with each trading partner, leading to a proliferation of point-to-point connections and increased overhead.
VANs emerged as a solution to this challenge by providing a centralized communication platform that could route and manage EDI transactions between trading partners. VANs acted as intermediaries that received, validated, translated, and routed EDI transactions on behalf of businesses, simplifying the communication process and reducing the need for point-to-point connections.
The first VANs were proprietary networks built by large telecommunications companies, such as IBM’s Information Network and GE Information Services’ Value Added Network. These early VANs used proprietary protocols and communication technologies, such as X.25, to transmit EDI transactions. They provided basic services, such as message routing, data validation, and data translation, and operated as closed networks with limited connectivity options.
With the advent of the Internet and the widespread adoption of TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) as the standard for networking, VANs evolved to leverage Internet-based technologies for communication. This led to the development of internet-based VANs or “Web VANs,” which used standard internet protocols, such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol) and HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol), for transmitting EDI transactions.
Web VANs offered greater flexibility, scalability, and connectivity options compared to proprietary VANs, as they could leverage the global reach and ubiquity of the internet. They allowed businesses to exchange EDI transactions with trading partners anywhere in the world using standard internet connections, without the need for expensive dedicated communication lines.
Over time, VANs expanded their service offerings to include value-added services beyond basic message routing and translation. They began offering additional services such as data validation, data transformation, data archiving, auditing, reporting, and trading partner management tools. These value-added services helped businesses streamline their EDI processes, improve data accuracy, ensure data security, and comply with industry regulations.
Today, VANs continue to evolve to keep up with changing technologies and business requirements. They support a wide range of communication protocols and standards, such as AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), FTPS (FTP Secure), and newer technologies like APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) for transmitting EDI transactions. VANs also offer different pricing models, support levels, and integration options with other business systems, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and TMS (Transportation Management System), to provide seamless and integrated B2B communication solutions.
Maximize your business efficiency with the right VAN provider! Grab your free VAN Buyer's Guide and discover the key features and services that will elevate your EDI transactions to the next level.
Make an informed decision today!
In this chapter, we will talk about how VANs work and their role in EDI
We will also be discussing benefits of VAN and comparing VAN with other communication methods.
Let's get started!
VANs act as intermediaries that facilitate the exchange of EDI transactions between businesses by providing a centralized communication platform. Here’s how VAN work and their role in EDI,
Receive EDI transactions from one trading partner and route them to the appropriate recipient. They act as a central hub that manages the flow of messages between trading partners, ensuring that messages are delivered securely and reliably.
Validates the integrity and accuracy of EDI transactions to ensure that they comply with the agreed-upon standards and formats. They also translate EDI messages between different formats or standards used by trading partners, ensuring seamless communication between them.
VANs often offer value-added services beyond basic message routing and translation. These services may include data enrichment, data transformation, data archiving, auditing, reporting, and trading partner management tools, which help businesses streamline their EDI processes and enhance data accuracy and security.
It plays a crucial role in ensuring the security and compliance of EDI transactions. They implement various security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and access controls, to protect EDI data from unauthorized access, tampering, or interception. They also help businesses comply with industry regulations, by providing tools and features to manage data privacy and compliance requirements.
It provides tools and features to manage trading partner relationships efficiently. They offer on boarding and configuration services to establish EDI connections with new trading partners, manage trading partner profiles, and handle communication protocols, formats, and standards specific to each trading partner.
It provides a centralized and standardized platform for exchanging EDI transactions with trading partners, simplifying communication and reducing the complexity of managing multiple connections, formats, and protocols. This simplification can streamline the EDI process, reduce errors, and improve efficiency.
VANs often offer data validation and enrichment services that help ensure the accuracy and integrity of EDI transactions. This can minimize data errors, such as missing or incorrect data, and improve data quality, reducing the need for manual data entry and improving overall business processes.
Typically offer tools and features for managing trading partner relationships, including onboarding, configuration, and profile management. This can streamline the process of establishing and managing EDI connections with trading partners, reducing administrative overhead and improving trading partner collaboration.
Implements various security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and access controls, to protect EDI data from unauthorized access, tampering, or interception. They also help businesses comply with industry regulations, by providing tools and features to manage data privacy and compliance requirements, ensuring that EDI transactions are secure and compliant.
VAN providers often offer value-added services, such as data transformation, data archiving, auditing, reporting, and analytics, which can provide additional insights and visibility into EDI transactions. These services can help businesses optimize their EDI processes, gain valuable business intelligence, and improve decision-making.
VANs are designed to handle large volumes of EDI transactions and provide reliable and scalable communication infrastructure. This ensures that EDI transactions are delivered promptly and reliably to trading partners, even during peak periods of business activity, supporting the growth and scalability of businesses.
Using VANs can be cost-effective compared to setting up and maintaining direct point-to-point EDI connections with multiple trading partners. VANs typically offer subscription-based pricing models, which can be more affordable for businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), compared to the costs associated with setting up and managing in-house EDI infrastructure.
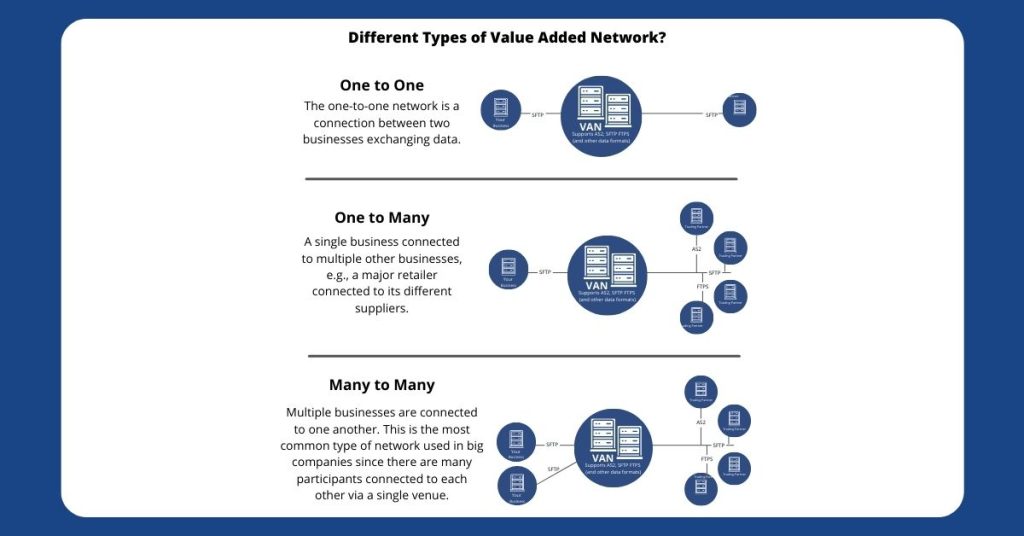
The one-to-one network is a direct point-to-point connection between two businesses to exchange EDI data. In this type of network, there is a direct connection between two nodes, and value is added to the information that is transmitted between them.
Example:
A peer-to-peer network is where two devices are connected directly to each other for the purpose of sharing files or resources. In this case, value is added by enabling the devices to communicate with each other without the need for a central server or intermediary.
As the name says, a single business is connected to multiple businesses to exchange EDI data.
Example:
A single supplier connected to multiple trading partners using a third-party VAN. No matter which communication protocol is used at the trading partner end, VAN can easily connect and transmit the EDI data.
In this type of setup, multiple businesses are connected to one another. This is the most common type of VAN network connection majorly used in the healthcare, finance, and logistics industries as there are many segments connected to each other via a single destination node.
There are various methods available for businesses to exchange data with their trading partners. Let’s compare Value Added Networks (VANs) with some other common communication methods:
In this method, businesses establish direct connections with their trading partners using specific communication protocols, such as AS2, FTP, or SFTP. While direct point-to-point connections provide a direct and secure communication channel, they require individual connections with each trading partner, which can be time-consuming and complex to manage as the number of trading partners increases. VANs, on the other hand, provide a centralized and standardized platform for exchanging data with multiple trading partners, simplifying communication and reducing the complexity of managing multiple connections and protocols.
Some businesses use web portals provided by their trading partners for exchanging EDI transactions. Web portals require manual data entry and uploading of files, which can be time-consuming and error-prone. They also lack real-time data validation and automated processing, which can result in data errors and delays. VANs, on the other hand, provide automated data validation, data transformation, and seamless integration with backend systems, reducing manual effort and improving data accuracy.
EDI software is an in-house solution that allows businesses to process EDI transactions using their own infrastructure. EDI software requires upfront investments in hardware, software, and maintenance, and may require technical expertise for setup and management. VANs, on the other hand, are cloud-based services that provide a managed and scalable solution without the need for upfront investments or extensive technical expertise.
Some businesses use third-party integration platforms, such as iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service), to connect with their trading partners for EDI transactions. These platforms provide integration capabilities for various communication protocols, data validation, data transformation, and backend system integration. However, they may lack the specialized features and expertise that VANs offer for EDI and B2B communication.
VAN service providers offer a comprehensive set of services to facilitate secure, reliable, and efficient EDI and B2B communication between trading partners. Their offerings are designed to streamline business processes, enhance data accuracy, and improve partner connectivity, making them valuable partners for businesses engaged in B2B communication.
It support various communication protocols, such as AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol), VAN-to-VAN, and other custom protocols, to enable secure and reliable data exchange between trading partners.
Provide data validation services to ensure that the exchanged data complies with the required EDI standards, such as ANSI X12, UN/EDIFACT, or other industry-specific standards. They may also offer data transformation services to convert data between different EDI standards or proprietary formats, allowing businesses to seamlessly exchange data with their trading partners regardless of their preferred format.
Provides monitoring and tracking capabilities to allow businesses to track the status of their EDI transactions in real time. This helps businesses to have visibility into the movement of data between trading partners and ensures timely delivery and receipt of EDI transactions.
Prioritizes data security and compliance with industry standards, they implement security measures, such as encryption, authentication, and access controls, to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of exchanged data.
Offering various other additional value-added services to enhance the functionality of EDI transactions. For example, they may provide translation and mapping services to convert EDI transactions into other formats, such as XML or CSV, to integrate with backend systems. They may also offer partner on boarding services to help businesses establish connections with new trading partners quickly and efficiently.
Managed services, meaning that the VAN service provider takes care of the technical aspects of EDI communication, including infrastructure setup, maintenance, and support. This allows businesses to focus on their core operations without having to manage the complexities of EDI communication in-house.
Customer support services to assist businesses with any technical issues, questions, or concerns related to their EDI communication. This includes help desk support, documentation, and training resources to ensure smooth and efficient EDI communication.
Reporting and analytics capabilities to provide businesses with insights into their EDI transactions, such as transaction volume, transaction types, partner performance, and other metrics. This can help businesses monitor their EDI activities, identify trends, and make informed decisions to optimize their B2B communication processes.
Value Added Networks (VANs) support various communication protocols and standards to facilitate electronic data interchange (EDI) and B2B communication between trading partners. Here are some commonly used protocols and standards in VANs:
AS2 is a widely used protocol for secure and reliable EDI communication over the Internet. It uses digital certificates and encryption to ensure data integrity and confidentiality during transmission. AS2 allows for real-time communication, acknowledgments, and error handling, making it a popular choice for B2B communication.
FTP is a standard network protocol used for transferring files over a TCP/IP network. VANs may support FTP as a communication method for exchanging EDI data in a secure and reliable manner. FTP provides options for authentication, encryption, and file integrity verification, making it a widely used protocol for B2B communication.
SFTP is a secure version of FTP that uses SSH (Secure Shell) for authentication and encryption. SFTP provides a secure and reliable method for transferring files over the Internet, making it suitable for EDI communication. VANs may support SFTP as a secure communication method to protect the confidentiality and integrity of EDI data.
VAN-to-VAN communication refers to the direct exchange of EDI data between two VANs. VANs may have their own proprietary protocols and communication methods to enable secure and reliable data exchange between their trading partners. VAN-to-VAN communication can be an efficient and scalable way to exchange EDI data within a VAN community.
In addition to standard protocols and EDI standards, VANs may support custom protocols or formats based on the specific requirements of their trading partners. Custom protocols or formats may be used to exchange data in proprietary formats or to cater to specific business processes or industry requirements. VANs may provide translation and mapping services to convert data between custom protocols and EDI standard
Maximize your business efficiency with the right VAN provider! Grab your free VAN Buyer's Guide and discover the key features and services that will elevate your EDI transactions to the next level.
Make an informed decision today!
In this chapter, we will answer few questions on how to setup a VAN:
- Steps to setup VAN for a business
- Choosing right VAN service provider
- VAN pricing negotiation
- Technical requirements
Let’s begin!
Setting up a VAN requires careful planning, coordination with trading partners, and compliance with relevant protocols and standards. Working closely with your VAN service provider and following best practices for VAN setup and management will help ensure the successful implementation and smooth operation of your B2B communication.
Here’s an overview of the typical process (note: your original setup process may be different based on the service provider you choose):
Define the specific requirements for your B2B communication, including the types of transactions you need to exchange, the trading partners you will be working with, the communication protocols and standards they use, and any other specific needs or compliance requirements.
Select a VAN Service Provider: Research and select a reputable VAN service provider that meets your business requirements. Consider factors such as the VAN’s network coverage, reliability, security features, pricing, customer support, and any additional value-added services they offer.
Once you have selected a VAN service provider, you will need to enter into a contractual agreement with them. This agreement will typically outline the terms and conditions of the VAN service, including pricing, service level agreements (SLAs), data retention policies, and other relevant terms.
Work with the VAN service provider to set up your VAN account. This may involve providing business information, such as your company name, address, contact details, and any specific configuration requirements. The VAN service provider will then provide you with the necessary credentials and access details to start using their VAN services.
Configure your B2B communication settings based on the requirements of your trading partners and the protocols/standards you will be using. This may involve setting up communication protocols (such as AS2, FTP, SFTP) or custom protocols, defining communication parameters (such as encryption, and authentication), and mapping your internal data to the required EDI standards.
Test your VAN setup and B2B communication with your trading partners to ensure that the data is being exchanged accurately and securely. Verify that your EDI transactions are conforming to the required EDI standards and that acknowledgments and error handling are functioning as expected.
Once you have successfully tested and validated your VAN setup, you can deploy it into production for ongoing B2B communication with your trading partners. Monitor and manage your VAN usage, track and resolve any issues or errors, and ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations.
Keep your VAN account up to date with any changes to your business requirements, trading partner configurations, or communication protocols. Stay in touch with your VAN service provider for ongoing support, maintenance, and updates to ensure smooth and uninterrupted B2B communication.
Pricing and contract negotiation are important aspects to consider when selecting a Value Added Network (VAN) service provider. Here are some key considerations to keep in mind
VAN service providers may have different pricing models, such as transaction-based fees, subscription-based fees, or a combination of both. Understand the pricing model offered by the VAN service provider and assess its cost-effectiveness based on your expected transaction volume and frequency. Consider any additional fees for value-added services, data storage, or other charges.
Consider your projected transaction volume and frequency when negotiating pricing with the VAN service provider. Some providers may offer volume-based pricing tiers, where the cost per transaction decreases as the volume increases. Negotiate pricing based on your estimated transaction volume and frequency to ensure that the pricing aligns with your business needs.
Review the contract terms and length offered by the VAN service provider. Consider factors such as contract renewal options, termination clauses, and any penalties or fees associated with early termination. Negotiate contract terms that are favorable and flexible to your business, including the ability to scale up or down as your needs evolve.
Understand the service level agreements (SLAs) offered by the VAN service provider. SLAs typically outline the expected service levels in terms of uptime, response time, and issue resolution time. Negotiate SLAs that align with your business requirements and ensure that they are clearly defined in the contract to hold the provider accountable for their service performance.
Review the contractual obligations of the VAN service provider, such as data retention policies, data ownership, data usage rights, and confidentiality requirements. Ensure that these obligations are in line with your business requirements and compliance obligations. Negotiate any terms that may require adjustments or customization to suit your business needs.
Consider any value-added services offered by the VAN service provider and their associated costs. Negotiate the inclusion of relevant value-added services that can enhance your B2B communication processes, such as data mapping, data validation, or reporting and analytics, based on your business needs.
Understand the billing and payment terms of the VAN service provider. Consider factors such as billing frequency, payment due dates, accepted payment methods, and any late payment fees. Negotiate billing and payment terms that align with your financial processes and cash flow requirements.
Review the contract renewal and termination clauses of the VAN service provider. Consider factors such as automatic contract renewal, the notice period for termination, and any penalties or fees associated with termination. Negotiate contract renewal and termination clauses that provide flexibility and options for your business, based on your anticipated needs and circumstances.
Assess the level of customization and flexibility offered by the VAN service provider. Consider whether they can tailor their services to your specific requirements, such as custom data mapping or integration with your existing systems. Negotiate customization options that can align with your business processes and requirements.
Consider any legal and compliance considerations when negotiating the contract with the VAN service provider. Review the contract for any clauses related to data privacy, data security, confidentiality, and liability. Seek legal advice if needed to ensure that the contract aligns with your legal and compliance obligations.
Negotiating pricing and contract terms with a VAN service provider is an important step in selecting the right provider for your business. Carefully review and assess the pricing, contract terms, service level agreements, contractual obligations, billing and payment terms, and other relevant factors to ensure that the agreement meets your business needs and provides value for your investment.
Implementing a Value Added Network (VAN) requires certain technical requirements to ensure smooth and secure communication. Here are some key technical considerations for VAN implementation:
VANs typically support multiple communication protocols, such as AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure). Understand the communication protocols supported by your VAN service provider and ensure that your systems can communicate using the required protocols.
VANs may support various data formats, such as EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), XML (eXtensible Markup Language), or other proprietary formats. Ensure that your systems can generate and receive data in the required formats for seamless integration with the VAN.
VANs require reliable and secure connectivity between your systems and the VAN service provider’s systems. Assess your existing connectivity options, such as dedicated leased lines, VPN (Virtual Private Network), or Internet-based connections, and ensure that they meet the connectivity requirements of the VAN service provider.
VANs handle sensitive business data, and security is a critical consideration. Ensure that your systems and the VAN service provider’s systems have appropriate security measures in place, such as encryption, authentication, access controls, and auditing, to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data during transit and storage.
VANs may require data mapping and translation between different data formats and standards. Understand the data mapping and translation requirements of the VAN service provider and ensure that your systems can perform the necessary data transformations to meet the VAN’s data format requirements.
VANs need to be integrated with your existing business systems, such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), or other applications, for seamless data exchange. Assess the integration capabilities of the VAN service provider, such as APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), connectors, or other integration methods, and ensure that they align with your integration requirements.
Consider the scalability requirements of your business when implementing a VAN. Ensure that the VAN service provider’s infrastructure and systems can handle the current and future transaction volumes and data processing requirements of your business without performance degradation or disruptions.
VAN implementation requires ongoing monitoring and management to ensure smooth operations. Understand the monitoring and management capabilities offered by the VAN service provider, such as dashboards, alerts, logging, and reporting, to effectively monitor and manage your VAN operations.
Testing and validation are crucial for VAN implementation to ensure that data is exchanged accurately and reliably between your systems and the VAN. Plan for thorough testing and validation of data exchanges, data formats, communication protocols, and other VAN-related processes to identify and resolve any issues before going live.
Ensure that your team is trained in how to use the VAN effectively and efficiently. Evaluate the training and support options provided by the VAN service provider, such as documentation, training materials, user support, and technical support, to ensure that your team can effectively use the VAN for your business needs.
Implementing a VAN requires careful consideration of technical requirements to ensure smooth and secure communication with trading partners. Assess your existing systems and infrastructure against the technical requirements of the VAN service provider to ensure that they align with your business needs and can support reliable and efficient VAN operations.
Maximize your business efficiency with the right VAN provider! Grab your free VAN Buyer's Guide and discover the key features and services that will elevate your EDI transactions to the next level.
Make an informed decision today!
In this chapter we will discuss:
- How to send and receive EDI transactions using VAN
- Use of VAN across many industries
- Relevant examples
- and more
Once you have set up your Value Added Network (VAN) and established a connection with your VAN service provider, you can start sending and receiving Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) transactions using the VAN. Here are the general steps for sending and receiving EDI transactions via VANs:
Prepare your EDI data according to the EDI standards and specifications required by your trading partners. This may involve generating EDI messages using EDI software or converting your business data into EDI format.
Establish a connection to your VAN service provider using the communication protocols and methods agreed upon during the VAN setup process. This may involve using protocols such as FTP (File Transfer Protocol), AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), or other communication methods supported by the VAN service provider.
Transmit the prepared EDI data to the VAN service provider using the agreed-upon communication method. This may involve uploading the EDI data to a designated folder on the VAN’s FTP server, sending the data as an email attachment using AS2, or using other methods supported by the VAN service provider.
The VAN service provider receives the transmitted EDI data and performs VAN-specific processing, such as validating the EDI syntax, translating the EDI data into the appropriate format required by the recipient, and performing data integrity checks.
The VAN routes the EDI data to the appropriate recipient based on the trading partner information provided during the setup process. The VAN may use routing information, such as EDI headers, envelopes, or other VAN-specific routing mechanisms, to ensure that the data is delivered to the correct recipient.
When your trading partner sends an EDI transaction to you via the VAN, the VAN receives and processes the transaction. This may involve VAN-specific processing, such as validating the EDI syntax, performing data integrity checks, and translating the EDI data into the appropriate format for your system.
Once the EDI transaction is successfully processed by the VAN, you may receive a notification, such as an email or a system alert, indicating that you have new EDI data available for retrieval.
Retrieve the EDI data from the VAN using the agreed-upon communication method, such as downloading the data from a designated folder on the VAN’s FTP server or receiving the data as an email attachment using AS2.
Integrate the received EDI data into your business system, such as your ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system, accounting system, or other relevant applications. This may involve using EDI software or other integration tools to convert the EDI data into a format that can be processed by your system.
Process the received EDI data according to your business rules and requirements. Generate acknowledgments, such as EDI functional acknowledgments (997s) or other acknowledgment messages, to inform your trading partners about the status of the received transactions.
It is important to work closely with your VAN service provider to understand their specific processes, protocols, and requirements for sending and receiving EDI transactions. Ensure that you follow the agreed-upon communication methods, data formats, and security measures to ensure smooth and secure EDI transactions via VANs.
- Ensuring data integrity and security in VANs
- Managing VAN connections and user accounts
- Monitoring and troubleshooting VAN communications
- Handling VAN errors and exceptions
- Disaster recovery and business continuity planning for VANs
Let’s dive right into this chapter!
Data integrity and security are critical considerations in the use of Value Added Networks (VANs) for electronic data interchange (EDI) and other business communications. Here are some best practices for ensuring data integrity and security in VANs:
VANs should use encryption techniques, such as SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security), to secure data transmitted over the network. Encryption ensures that data exchanged between parties is protected from interception and unauthorized access.
VANs should have robust access controls in place to restrict access to authorized users only. This includes strong password policies, multi-factor authentication (MFA), and role-based access controls (RBAC) to ensure that only authorized personnel can access and manipulate data within the VAN.
VANs should implement regular data backup procedures and have a robust disaster recovery plan in place to ensure that data is protected from loss due to system failures, natural disasters, or other unforeseen events. Backups should be stored in secure offsite locations to prevent data loss in the event of a physical breach or system failure.
VANs should have auditing and monitoring mechanisms in place to track and monitor data exchanges, user activities, and system events. This helps detect and prevent any unauthorized access or data breaches and enables quick response to any security incidents.
VAN service providers should adhere to industry standards and regulations, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), depending on the industry and type of data being exchanged. VANs should undergo regular security audits and obtain relevant certifications to demonstrate their commitment to data security and compliance.
If a business is using a VAN service provider, it’s important to conduct thorough vendor risk assessments to ensure that the VAN service provider has robust security measures in place to protect the data being exchanged. This includes evaluating their security policies, procedures, infrastructure, and track record in maintaining data integrity and security.
Training employees who have access to the VAN on security best practices, data handling procedures, and the importance of data integrity and security is crucial. This helps prevent human errors, such as accidental data leaks or unauthorized access, which can compromise data integrity and security.
VANs should support data encryption and signing at the transaction level, using industry-standard encryption and signing algorithms. This helps ensure that data transmitted over the VAN is encrypted and signed to protect against unauthorized access, tampering, and data integrity breaches.
Monitoring and troubleshooting Value Added Network (VAN) communications is crucial to ensure smooth and reliable electronic data interchange (EDI) and other business communications. Here are some considerations for monitoring and troubleshooting VAN communications:
VAN service providers typically offer monitoring tools or portals that allow businesses to track the status of their transactions and communications in real-time. These tools may provide visibility into transaction status, message tracking, error notifications, and other relevant information. Monitoring tools can help identify and resolve issues quickly, such as failed transactions, communication errors, or delays.
VANs may generate error messages when there are issues with transactions or communications. These error messages can provide information about the nature of the issue, such as missing or invalid data, incorrect formats, or communication failures. Businesses should have processes in place to handle error messages promptly, investigate the root causes, and take corrective actions to resolve the issues.
VANs may provide transaction validation services to ensure that transactions comply with the relevant standards and protocols. Transaction validation helps identify and correct errors or inconsistencies in the data before the transactions are transmitted. Implementing transaction validation as part of the VAN communication process can help reduce errors and prevent delays in communication.
Proactively monitoring VAN communications involves regularly checking the status of transactions, identifying potential issues, and taking preventive actions. This can include checking for transaction errors, monitoring communication performance, reviewing logs, and conducting periodic health checks of the VAN connections. Proactive monitoring can help businesses identify and address potential issues before they escalate into larger problems.
Having a well-defined troubleshooting process in place can help businesses efficiently identify and resolve issues with VAN communications. This may involve a systematic approach, such as isolating the issue, reviewing logs or error messages, checking communication configurations, validating transaction data, and working with the VAN service provider’s support team for assistance. A clear troubleshooting process can help streamline issue resolution and minimize downtime.
Establishing effective communication channels with the VAN service provider’s support team is important for timely troubleshooting and issue resolution. This may involve setting up designated points of contact, establishing communication protocols, and maintaining regular communication channels for issue reporting, escalation, and resolution. Prompt and effective communication with the VAN service provider can help resolve issues quickly and minimize any disruptions to business communications.
Maintaining documentation of VAN configurations, transaction records, error logs, and troubleshooting activities is important for reference and analysis. Documenting VAN communications can help identify patterns, trends, and recurring issues, which can aid in troubleshooting efforts and continuous improvement of VAN communication processes.
Managing VAN connections and user accounts is an important aspect of effectively utilizing a Value Added Network (VAN) for electronic data interchange (EDI) and other business communications. Here are some considerations for managing VAN connections and user accounts:
Businesses should have a clear process in place for managing VAN connections. This includes establishing guidelines for setting up new connections, modifying existing connections, and terminating connections as needed. It’s important to have a designated point of contact responsible for managing VAN connections and ensuring that the connections are properly configured, tested, and maintained.
Managing user accounts in the VAN involves creating, modifying, and deactivating user accounts based on the roles and responsibilities of the users within the organization. This includes assigning appropriate access levels, permissions, and privileges to users based on their job functions and responsibilities. It’s important to regularly review and update user accounts to ensure that only authorized personnel have access to the VAN.
Implementing strong password policies for VAN user accounts is crucial for security. This includes requiring complex passwords, regular password changes, and prohibiting the sharing of passwords. It’s important to educate users about the importance of creating strong passwords and protecting their passwords from unauthorized access.
Implementing RBAC helps ensure that users have access to only the resources and functionalities necessary for their job roles. This reduces the risk of unauthorized access to sensitive data or functionalities within the VAN. Roles should be periodically reviewed and updated based on changes in job responsibilities or personnel changes.
Regularly monitoring user activities within the VAN and conducting audits helps detect and prevent any unauthorized access or data breaches. Monitoring should include reviewing login activities, transaction activities, and other relevant events to identify any anomalies or suspicious activities.
Providing training and awareness programs for users on VAN connection management and user account management best practices is essential. This includes educating users on proper connection setup procedures, user account management guidelines, password policies, RBAC, and the importance of data security.
It’s important to have a process in place for terminating user accounts when employees leave the organization or when their job roles change. This should include disabling or deleting user accounts promptly to prevent unauthorized access.
Backing up user account information and other relevant data in the VAN is crucial to ensure business continuity in the event of data loss or system failures. Regularly backing up user account information and having a robust data recovery plan in place helps ensure that user accounts can be restored quickly in case of any data loss incidents.
Emerging technologies and innovations in VANs
- Cloud-Based VANs
- Blockchain-Based VANs
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and - Machine Learning
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
- Enhanced Security Features
- Integration with APIs and Web Services
Solution works,
Value Added Networks (VANs) continue to evolve and adapt to the changing landscape of business communication and electronic data interchange (EDI). Emerging technologies and innovations are being leveraged to enhance the capabilities, efficiency, and security of VANs. Here are some examples of emerging technologies and innovations in VANs:
Cloud computing has revolutionized many aspects of business operations, and VANs are no exception. Cloud-based VANs offer the advantage of scalable and flexible communication solutions that can be accessed from anywhere, at any time. They eliminate the need for physical infrastructure and provide greater agility in setting up VAN connections and managing EDI transactions. Cloud-based VANs also offer enhanced security features, such as encryption and access controls, to protect data in transit and at rest.
Security is a critical consideration in VANs, and emerging technologies are being used to enhance security features. This may include advanced encryption algorithms, multi-factor authentication, digital signatures, and other security measures to protect data integrity, confidentiality, and authenticity. VANs are also incorporating advanced threat detection and response mechanisms, such as intrusion detection systems, security information and event management (SIEM) systems, and security analytics, to proactively identify and mitigate potential security risks.
Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) and web services are being used to integrate VANs with other business systems, applications, and platforms. This enables seamless data exchange between VANs and other systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, and e-commerce platforms. API-based integrations allow for real-time data exchange, automated transaction processing, and improved interoperability between different systems.
AI and machine learning technologies are being utilized in VANs to improve transaction processing, data validation, and error detection. AI algorithms can analyze large volumes of data and identify patterns, anomalies, and potential errors in EDI transactions, allowing for proactive error detection and resolution. Machine learning models can also learn from past transaction data to optimize VAN operations, such as routing and prioritizing transactions, and predicting potential issues.
The proliferation of IoT devices in various industries has opened up new possibilities for VANs. IoT devices generate vast amounts of data that can be integrated into VANs to enable real-time monitoring and tracking of goods, assets, and shipments. This can enhance supply chain visibility, improve inventory management, and streamline logistics operations. VANs can also facilitate communication between IoT devices and enable automated transactions and notifications based on IoT data.
VANs play a significant role in modern business communication, enabling EDI transactions, improving communication efficiency, enhancing security, and supporting various industries and applications. Choosing the right VAN service provider, implementing proper technical requirements, ensuring data integrity and security, and staying abreast of emerging technologies are crucial for successful VAN implementation and utilization in business operations.
When selecting a VAN provider, consider factors such as data security, industry expertise, customer support, scalability, pricing, and the provider’s ability to integrate with existing systems. A good VAN provider should offer robust security, reliable uptime, and excellent customer service to support EDI needs.
Point-to-point EDI involves direct connections between trading partners, requiring individual setups for each partner. A VAN, however, serves as an intermediary that connects multiple partners through a single network, simplifying connections and reducing management complexity.
Maximize your business efficiency with the right VAN provider! Grab your free VAN Buyer's Guide and discover the key features and services that will elevate your EDI transactions to the next level.
Make an informed decision today!