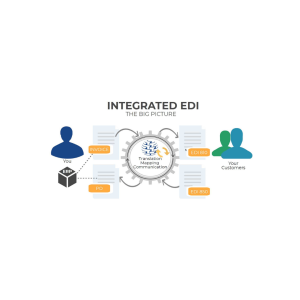
Introduction
Our latest case study has revealed that EDI WMS integration can reduce business transaction costs by at least 35% while speeding up transaction cycles by more than 60%.
We’ve observed that warehouse management system (WMS) integration has consistently remained the top technology solution for third-party logistics warehouses since 2020.
However, without proper integrations, this powerful technology often remains underutilized. By integrating Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) with your warehouse management system, you can eliminate manual data entry, automate document exchange, and significantly improve operational efficiency.
Furthermore, this integration provides real-time visibility into inventory levels, allowing warehouse managers to make informed decisions about stock replenishment and order prioritization. EDI integration can improve data quality by reducing transaction errors by 30-40% and enhancing the order-to-cash cycle time by more than 20%. Additionally, when WMS is integrated with ERP systems, businesses can synchronize inventory data across different platforms, ensuring consistency throughout the organization.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about EDI WMS integration—from basic setup to advanced operations—helping you unlock the full potential of your warehouse operations.
Key Takeaways
- EDI-WMS integration reduces transaction costs by 35% and speeds up processing cycles by 60% while cutting errors by 30-40%
- Five key integration types (ERP, marketplace, shipping, mobile scanning, CRM) create seamless operational workflows across all warehouse touchpoints
- Automated order processing eliminates manual data entry, enabling 100% accuracy in data extraction and faster order-to-cash cycles
- Real-time inventory visibility prevents stockouts and overstocking while enabling better demand forecasting and planning decisions
- Cloud-based EDI solutions provide scalable infrastructure that adapts to seasonal peaks and business growth without major investments
Understanding EDI and WMS in Warehouse Operations
The foundation of efficient warehouse operations rests on two critical technologies that, when combined, create a powerful operational engine for modern distribution centers.
What is WMS and How Does it Support Inventory Control
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is specialized software designed to optimize and control daily warehouse operations—from the moment goods arrive until they leave. WMS serves as the central nervous system of warehouse operations, providing real-time visibility into inventory across all locations.
Through WMS, warehouse managers can streamline typical warehouse logistics practices, including transactions, shipping, receiving, putaway, and picking. Most modern WMS solutions leverage barcode scanning, RFID tagging, and other identification technologies to maintain accurate tracking throughout the inventory lifecycle.
The core inventory control features of a WMS include:
- Real-time inventory tracking and status updates
- Strategic storage optimization based on turnover rates
- Automated cycle counting and inventory reconciliation
- Demand forecasting and replenishment planning
- Order allocation using methods like FIFO and FEFO
The primary strength of a WMS lies in its ability to maintain rigorous control and tracking of stock levels as they change. This capability is essential for preventing stockouts, reducing excess inventory, and enabling accurate forecasting for future needs.
What is EDI, and How Does it Automate Document Exchange
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) refers to the standardized electronic communication between businesses that replaces traditional paper-based document exchange. Essentially, EDI automates the exchange of structured business documents between trading partners using universally understood formats.
Rather than printing, mailing, or manually processing documents, EDI enables businesses to transmit purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other critical documents electronically—eliminating human intervention in processing information. For example, when using EDI, a buyer’s purchase order travels directly to a vendor’s order management system, which then processes it and automatically transmits an invoice back to the buyer.
EDI particularly benefits warehousing through key transaction sets like EDI 940 (Warehouse Shipping Order), EDI 945 (Warehouse Shipping Advice), and EDI 856 (Advance Shipment Notice/Manifest). These standardized documents support precise inventory movement tracking throughout the supply chain.
Why EDI-WMS Integration Matters in Modern Warehousing
The integration of EDI with WMS creates a synergistic effect that drives operational excellence throughout the warehouse. As these systems work together, inventory control gains a higher level of execution while business transactions powering those inventory movements occur instantly through secure data transmission.
This integration enables warehouses to maintain accurate inventory control with real-time processing while simultaneously exchanging documents with suppliers and customers. Subsequently, this integration eliminates the concept of “lost in translation”—confusing inventory statuses or misplaced documents become obsolete as the systems work in unison.
The real-time data exchange between EDI and WMS is vital for maintaining accurate warehouse operations. For instance, the EDI 945 document facilitates inventory management by including essential details such as product identifiers, quantities, shipment times, and tracking numbers.
Ultimately, medium-sized manufacturers and importers increasingly require shipment, replenishment, and inventory information to be automated and updated daily. Therefore, the combined power of EDI-WMS integration provides the foundation for warehouses to scale their operations efficiently while meeting the growing demands of modern supply chain networks.
Core Components of EDI-WMS Integration
Successful EDI WMS integration relies on several key components working together to create a seamless flow of information between systems. Understanding these core elements helps businesses maximize the efficiency of their warehouse operations.
EDI 850, 855, 856, and 810 transaction types
At the heart of EDI WMS integration are standard transaction codes that facilitate precise communication between trading partners. These documents form the backbone of automated warehouse operations:
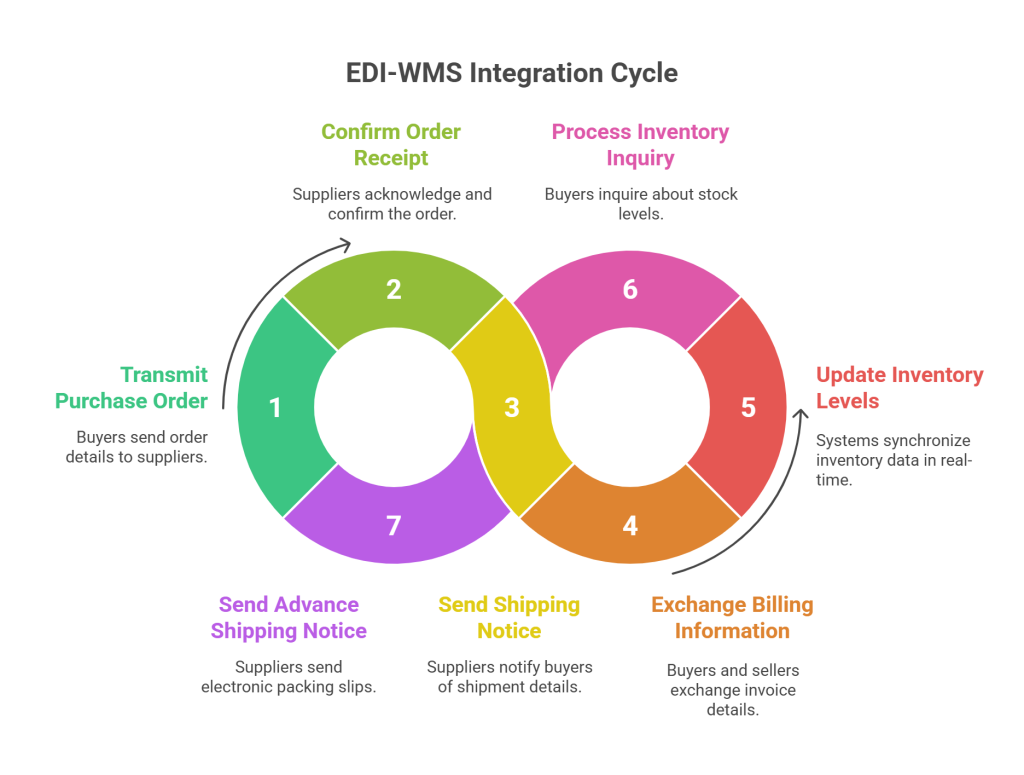
- EDI 850 (Purchase Order): Electronically transmits order details from buyers to suppliers, including item information, quantities, shipping details, and payment terms. This eliminates the need for manual order entry.
- EDI 855 (Purchase Order Acknowledgement): Confirms receipt of a purchase order and outlines acceptance details. This document includes accepted quantities, item specifics, prices, shipping information, and delivery dates.
- EDI 856 (Advance Shipping Notice/ASN): Notifies recipients about pending shipment details before delivery, providing tracking and packing information. This critical document enables efficient supply chain management and proper order preparation.
- EDI 810 (Invoice): Facilitates the exchange of billing information between buyers and sellers, typically sent after goods have shipped. This electronic invoice improves accuracy, speeds up payment cycles, and enhances financial visibility.
These standardized formats ensure accurate and reliable information exchange, leading to better inventory control and efficient warehouse management.
WMS-ERP integration for real-time inventory sync
Despite their different purposes, WMS and ERP systems must work together to provide a complete operational picture. ERP systems manage broad business processes across an organization, whereas WMS focuses specifically on warehouse and distribution operations.
Perhaps the greatest benefit of integrating WMS with ERP is real-time data synchronization. This ensures inventory levels, order statuses, and shipping information are updated in both systems simultaneously to maintain accuracy.
Both systems must be configured to use the same communication standards and security protocols. Validation checks and error-handling procedures are crucial during implementation to prevent data discrepancies.
Consider scalability and flexibility when designing your integration—your system should adapt easily to accommodate new updates, process changes, and additional integrations as your business grows.
EDI inventory feed and ASN processing
The EDI 846 (Inventory Inquiry/Advice) serves as a digital inventory list that companies use to communicate their stock levels. It follows a structured format including beginning segments, date/time references, item identification, quantity information, and transaction totals.
This bi-directional transaction can be sent by either buyers or retailers, often multiple times daily, to maintain accurate inventory information. For retailers, it enables inquiries about product availability to keep e-commerce websites current; for sellers, it provides a mechanism to alert partners about stock levels and forecasted availability.
Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN) processing forms another critical component of EDI-WMS integration. An ASN works as an electronic packing slip sent to customers confirming order shipment. When EDI integration is enabled for ASN processing, a scheduled script typically runs every 15 minutes to identify shipped orders requiring notifications.
ASNs must follow the “4Cs” principle to be effective: Completeness (providing all delivery details), Correctness (ensuring accuracy of shipment information), Confirmation (validating details included), and Communication (sending notices in a timely manner).
Through these core components, EDI WMS integration creates a foundation for automated document exchange, accurate inventory management, and streamlined warehouse operations.
Top 5 EDI-WMS Integration Types Explained
The power of EDI-WMS integration extends through five key connection points in the modern warehouse ecosystem. Each integration type serves a distinct purpose while collectively creating a seamless operational environment.
1. ERP and Accounting System Integration
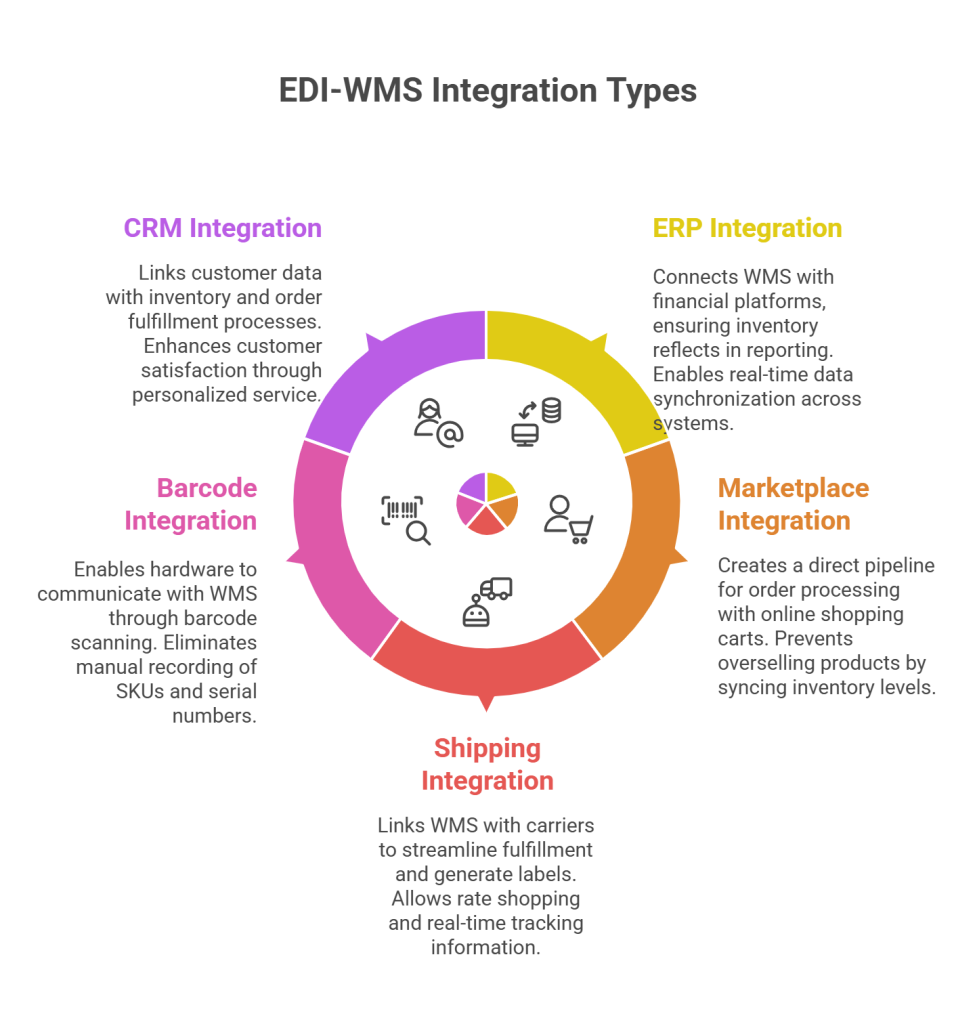
ERP and accounting integrations connect warehouse management systems with broader business financial platforms, ensuring that inventory movements automatically reflect in financial reporting. This integration enables the WMS to capture all billable events—including receiving, storage, picking, packing, and shipping fees—and automatically generate invoices at billing period end.
Accordingly, the WMS-ERP connection facilitates real-time data synchronization, guaranteeing inventory levels and order statuses are updated simultaneously across systems. For businesses using platforms like SAP, NetSuite, or Microsoft Dynamics, this integration eliminates the need to manually update financial records when warehouse activities occur.
2. Marketplace and Shopping Cart Integration
Connecting your WMS with online shopping carts and marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, Shopify, and WooCommerce creates a direct pipeline for order processing. These integrations use REST API connections that allow ecommerce channels and your WMS to communicate bidirectionally.
Indeed, when orders are placed on these platforms, they automatically push through to the WMS with all order details included—eliminating manual entry and associated errors. Moreover, these integrations sync inventory levels between your warehouse and sales platforms, preventing the costly mistake of overselling products.
3. Shipping Carrier Integration
Shipping carrier integrations link your WMS directly with UPS, FedEx, DHL, and other carriers to streamline the fulfillment process. This connection enables automatic generation and printing of shipping labels and necessary documentation that comply with each carrier’s specific requirements.
One significant advantage is rate shopping capability, allowing warehouses to compare rates from multiple carriers in real-time and select the most cost-effective shipping option based on delivery time and price. These integrations also facilitate real-time tracking information fed back into the WMS, enabling warehouse staff and customers to monitor shipment status without leaving the system.
4. Mobile Barcode Scanning Integration
Unlike software connections, mobile barcode scanning integration enables physical hardware to communicate with your WMS. This integration allows your system to recognize scanned barcodes as inputs across various platform fields.
Throughout the receiving, picking, and packing processes, barcode scanning eliminates the need to manually record SKUs, UPCs, or serial numbers—a single scan captures all necessary information. For lot items or serialized inventory, scanning can automatically populate appropriate fields with details like lot numbers, serial numbers, or quantities.
5. CRM and Customer Service Integration
CRM integrations link customer data with inventory and order fulfillment processes, creating a 360-degree view of every customer by syncing orders, communications, and support issues. This comprehensive visibility empowers customer service teams to access order history and real-time status information when addressing inquiries.
Ultimately, this integration enhances customer satisfaction through personalized service while improving operational efficiency. By connecting these systems, businesses can leverage customer data for better marketing, more responsive support, and improved retention strategies.
Operational Benefits of EDI-WMS Integration
Implementing EDI WMS integration delivers measurable operational advantages that directly impact your bottom line. Properly executed integration serves as a catalyst for warehouse efficiency and profitability.
1. Automated Order Processing and Reduced Manual Entry
EDI WMS integration eliminates time-consuming manual data entry, a key source of costly errors in warehouse operations. Consequently, businesses that implement EDI solutions report dramatically improved order processing efficiencies with faster turnaround times. By automating order entry, warehouses guarantee 100% accuracy in data extraction, which naturally prevents costly mistakes such as duplicate orders or incorrect shipments.
Order automation through EDI can process transactions in minutes rather than hours, keeping operations running smoothly even during peak sales periods. This automation allows your team to focus on higher-value tasks instead of repetitive data entry. First, this improves employee satisfaction, plus it enables your business to handle higher order volumes without requiring additional staff.
2. Improved Inventory Accuracy and Real-Time Visibility
Real-time inventory visibility represents one of the most valuable benefits of EDI WMS integration. The system provides instant updates whenever products are received, moved, or shipped, ensuring inventory records remain continuously accurate. This capability prevents stockouts and overstocking while enabling better planning for future needs.
With EDI integration, warehouse managers gain immediate insight into inventory levels, pending orders, and supplier deliveries. This visibility helps anticipate demand fluctuations and adjust orders instantly rather than realizing too late that shelves are empty. Additionally, EDI automates inventory management by keeping stock levels accurate and up-to-date.
3. Faster Order-to-Cash Cycle and Reduced Errors
Primarily, EDI accelerates the entire order-to-cash process by eliminating manual bottlenecks and enabling real-time data exchange between trading partners. This streamlined approach ensures payment-related documents are exchanged instantly, leading to faster cash application and reconciliation.
EDI automation enables automatic generation and delivery of invoices once orders ship, reducing the time between product delivery and payment collection. Notably, this can substantially shorten collection times by automatically handling invoice issuance, sending payment reminders, and processing electronic payments.
4. Regulatory Compliance and Audit Readiness
Compliance and risk management are crucial reasons to implement EDI WMS integration. As privacy legislation evolves worldwide, ensuring your integration system maintains compliance helps avoid financial penalties and reputational damage.
EDI supports compliance with local and international regulations, especially those related to electronic invoicing and tax reporting. Ultimately, this creates auditable records that meet national standards.
Commport EDI Solutions Can Integrate with All Major ERP, TMS and WMS Systems. Our EDI Solutions are Affordable, Scalable and Easy to Use.
Through standardized, secure document exchange, warehouses establish audit readiness while minimizing compliance risks that could otherwise impact operations.
Scalability and Customization in EDI-WMS Systems
Effective growth management requires EDI-WMS systems that can scale with your business while adapting to unique operational requirements. The right integration approach enables seamless expansion without costly infrastructure overhauls.
1. Handling High-volume EDI Inventory Transactions
When managing hundreds of EDI documents monthly, automation becomes essential. Most retailers send EDI 846 (Inventory Inquiry/Advice) inquiries daily or even multiple times throughout the day to maintain accurate e-commerce storefront availability. This bi-directional transaction enables retailers to alert suppliers about current stock levels while allowing sellers to communicate inventory availability and forecasted replenishment dates.
Custom Workflows for Unique Warehouse Needs
Businesses with specialized processes benefit from adaptable EDI-WMS integration. Modern systems allow customization of EDI workflows to suit specific operational requirements. Features like configurable picking methods (batch, wave picking) let warehouses tailor fulfillment to their order volume and type. Furthermore, custom workflows enable efficient stock transfers between locations based on demand patterns.
Cloud-Based Scalability for Growing Operations
Cloud-based EDI solutions eliminate the need for substantial infrastructure investments while offering unparalleled flexibility. As operations expand, cloud EDI allows you to quickly add trading partners, increase transaction volumes, and integrate new systems with minimal effort.
Our EDI Solutions are Affordable, Scalable, and Easy to Use. Trusted by 6000+ Brands and 40+ Years of Industry Experience. Switch to Commport EDI Today!
This scalability proves particularly valuable during seasonal peaks or upon entering new markets, enabling businesses to adapt swiftly without disrupting existing processes.
Conclusion
EDI-WMS integration stands as a transformative solution for warehouse operations, streamlining processes while driving substantial cost savings. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored how this powerful integration eliminates manual data entry, automates document exchange, and provides real-time inventory visibility.
Organizations implementing these integrated systems typically see transaction costs decrease by at least 35% while experiencing 60% faster transaction cycles. Additionally, error rates drop significantly—often by 30-40%—which directly impacts customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
The five integration types we discussed offer flexibility for businesses at various stages of technological adoption. Whether connecting with ERP systems, marketplaces, shipping carriers, mobile barcode scanners, or CRM platforms, each integration type serves a specific purpose while contributing to overall operational excellence.
Scalability remains another significant advantage of modern EDI-WMS systems. Cloud-based solutions eliminate the need for substantial infrastructure investments while providing the flexibility to adapt during seasonal peaks or market expansions. “Trusted by 6000+ Brands and 40+ Years of Industry Experience. Switch to Commport EDI Today!”
Ultimately, EDI-WMS integration transforms warehouse operations from labor-intensive, error-prone processes into streamlined, automated systems that provide accurate, real-time information. Companies embracing this technology position themselves for greater efficiency, improved customer service, and sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive marketplace. The question isn’t whether you should integrate EDI with your WMS—but rather how quickly you can implement this essential technology to start realizing its substantial benefits.
Commport EDI Solutions
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
EDI-WMS integration automates document exchange, reduces manual data entry, and provides real-time inventory visibility. This leads to reduced transaction costs, faster processing cycles, and fewer errors, ultimately improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
The core components include standard EDI transaction types (like 850, 855, 856, and 810), WMS-ERP integration for real-time inventory sync, and EDI inventory feed and ASN processing. These elements work together to create a seamless flow of information between systems.
Yes, EDI-WMS systems are designed to handle high-volume inventory transactions. They can process hundreds of EDI documents daily, including frequent inventory inquiries and updates, ensuring accurate stock levels across all sales channels.
The integration provides real-time updates whenever products are received, moved, or shipped. This constant synchronization ensures inventory records remain accurate, preventing stockouts and overstocking while enabling better demand forecasting and planning.
Absolutely. Modern EDI-WMS systems, especially cloud-based solutions, offer excellent scalability. They allow businesses to easily add trading partners, increase transaction volumes, and integrate new systems as operations expand, without requiring significant infrastructure investments.