Going paperless with Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) involves transitioning from traditional paper-based document exchange to electronic methods. By utilizing standardized formats and automated systems, EDI enables businesses to exchange documents such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices electronically, eliminating the need for printing, mailing, and storing paper documents
What is EDI Automation?
EDI automation refers to the process of automating the exchange, translation, validation, and integration of electronic business documents between trading partners. It involves leveraging EDI technology and integrating it with existing systems to enable seamless, efficient, and accurate data transmission and processing.
EDI automation streamlines the entire lifecycle of document exchange, from document creation and transmission to data validation and integration into internal systems. By automating these processes, businesses can eliminate manual tasks, reduce errors, improve speed, and enhance collaboration with trading partners.
Manual EDI Vs EDI Automation
Manual EDI
EDI Automation
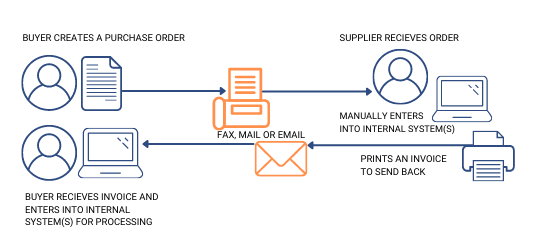
Involves manually translating data from a company’s internal system into the EDI format, sending it to a partner, and then manually processing the received data back into the internal system. This can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
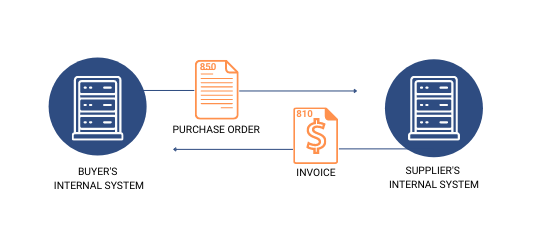
Uses EDI system to automate these tasks. The system translates data, transmits it securely, and integrates it seamlessly with the company’s existing internal systems such as ERP and accounting software, eliminating manual intervention.
EDI Standards
Common EDI Transactions
EDI relies on standardized formats for data exchange. Common EDI standards include:
ANSI X12: Used primarily in North America for various business transactions.
EDIFACT: Widely adopted in Europe and other regions.
XML: A flexible format that allows for custom data structures.
These standards ensure consistency and compatibility across different systems.
Common business documents exchanged through EDI automation include
820 Payment Order/Remittance Advice,
997 Functional Acknowledgement,
855 Purchase Order Acknowledgment and,
846 Inventory updates, which improve sales, accounting, and warehouse departments.

Industry Adoption
Various industries have widely adopted EDI automation to streamline operations and enhance competitiveness., including
- Retail,
- Manufacturing,
- Healthcare,
- Logistics, and
- Banking
Automating End-to-End Business Processes with EDI Step-by-Step Process
To achieve end-to-end automation with EDI, businesses can follow these key steps:
Step 1: System Integration: Integrate EDI technology with internal systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), warehouse management, and accounting systems. This integration allows seamless data flow between systems, ensuring the exchange of accurate and consistent information.
Step 2: Trading Partner Onboarding: Establish EDI connections with trading partners to enable electronic document exchange. Collaborate with trading partners to define document formats, standards, and protocols, ensuring compatibility and smooth data interchange.
Step 3: Document Mapping and Translation: Define mapping rules to transform internal document formats into the standardized EDI format and vice versa. Mapping ensures that data elements are accurately translated, aligned, and validated during the exchange process.
Step 4: Automated Validation and Workflow: Implement automated validation checks to ensure data integrity and compliance with business rules. This includes validating document structures, checking for errors or missing data, and verifying compliance with industry standards.
Step 5: Integration with Internal Systems: Integrate EDI transactions seamlessly into internal systems for further processing. This includes automating order creation, inventory updates, invoicing, shipping notifications, and other relevant processes. The integration enables real-time visibility, reduces manual intervention, and facilitates accurate data flow across the organization.
Benefits of EDI Automation
Implementing EDI automation offers numerous advantages for businesses:
1. Improved Efficiency
EDI automation eliminates the need for manual data entry, document handling, and reconciliation. It streamlines processes, reduces time-consuming tasks, and allows employees to focus on higher-value activities. This leads to increased productivity, optimized resource allocation, and improved overall operational efficiency.
2. Enhanced Accuracy
Manual data entry is prone to errors, which can result in costly mistakes and delays. EDI automation ensures accurate data transmission, validation, and integration, minimizing the risk of human error and data discrepancies. By maintaining data integrity, businesses can improve the reliability of their business processes and build trust with trading partners.
3. Faster Transaction Processing
EDI automation significantly accelerates the speed of document processing. Electronic transmission, real-time data exchange, and automated validation enable businesses to process transactions rapidly. This translates into faster order fulfillment, reduced lead times, and improved customer satisfaction.
4. Streamlined Supply Chain
By automating end-to-end business processes, EDI automation streamlines the entire supply chain. It enables seamless collaboration with suppliers, distributors, and customers, enhancing visibility, reducing cycle times, and optimizing inventory management. This leads to a more efficient supply chain, reduced costs, and improved responsiveness to customer demands.
5. Cost Savings
EDI automation reduces operational costs associated with paper-based document handling, manual data entry, and document reconciliation. By eliminating these manual processes, businesses save on printing, mailing, storage, and administrative overhead. Furthermore, faster transaction processing and improved accuracy result in fewer errors, reducing costs related to order discrepancies, returns, and rework.
Conclusion
EDI automation offers businesses a powerful tool to streamline end-to-end business processes, improve efficiency, and enhance collaboration with trading partners. By automating document exchange, translation, validation, and integration, businesses can achieve increased accuracy, faster transaction processing, cost savings, and a more streamlined supply chain. Embracing EDI automation empowers businesses to optimize their operations, stay ahead of the competition, and deliver superior customer experiences in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.

What are the key features of Commport EDI Solutions?
- Easy B2B integration with any trading partner
- Commport EDI solutions are scalable as your business grows
- Affordable pricing and pay-as-you-go plans available
- Dedicated world-class customer support
- 100% EDI compliance guaranteed
#1 Rated EDI Solutions in Market
Need Help? Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, EDI automation can integrate with existing Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems. Integration with ERP systems allows for seamless exchange of data between different departments within an organization and between trading partners. This integration streamlines business processes, improves data accuracy, and enhances overall efficiency.
EDI automation employs robust security measures to ensure the secure transmission of sensitive business data. These measures may include encryption, digital signatures, secure communication protocols (such as AS2), and access controls. Additionally, many EDI providers undergo regular security audits and compliance certifications to maintain high levels of security and data protection.
Some common challenges associated with EDI automation implementation include:
- Complexity of integration with existing systems and processes.
- Onboarding trading partners onto the EDI system and ensuring compliance with their specific requirements.
- Data mapping and translation between internal formats and EDI standards.
- Maintenance and support of EDI systems and infrastructure.
- Keeping up with evolving EDI standards and technologies. Despite these challenges, careful planning, stakeholder engagement, and leveraging the expertise of EDI solution providers can help overcome implementation hurdles and maximize the benefits of automation.
Yes, EDI automation can be beneficial for small businesses as well. While the initial setup may require some investment in software and infrastructure, the long-term benefits such as efficiency gains, reduced errors, and improved customer relationships can outweigh the costs. Many EDI providers offer scalable solutions that cater to the needs and budget constraints of small businesses.
Getting started with EDI automation involves several steps:
- Assess your business needs and determine the EDI documents and transactions relevant to your operations.
- Select an EDI solution provider or software that meets your requirements and integrates with your existing systems.
- Onboard your trading partners onto the EDI system and establish connectivity and data exchange protocols.
- Develop mappings between your internal data formats and EDI standards to ensure seamless translation and interoperability.
- Test the EDI processes thoroughly and validate data accuracy before full deployment.
- Continuously monitor and optimize your EDI operations to adapt to changing business needs and industry standards.




