EDI 940 Warehouse Shipping Order is a transaction set in Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) that is used for providing shipping instructions to carriers.
This transaction set streamlines the shipping process by providing carriers with all of the necessary information they need to fulfill the shipping order. It eliminates the need for paper-based shipping instructions and helps to reduce errors and delays in the shipping process.
The EDI 940 is an electronic document used to electronically transmit shipping instructions from the shipper to the carrier. This electronic document complies with the ANSI X12 EDI specification.
The EDI 940 transaction set typically includes information such as the shipping order number, ship-to and ship-from locations, requested shipping dates, carrier information, item descriptions and quantities, and other relevant information necessary for the carrier to ship the goods.
Improved accuracy and reliability of data transmission
Increased automation and reduction of manual intervention
Better visibility and communication between trading partners
Improved supply chain management and increased operational efficiency
Warehouse Shipping Order, contains a set of standard data elements that are used to communicate information related to a shipment from a warehouse or distribution center to a transportation carrier.
Here are some of the key data elements included in the EDI 940:
EDI 940 is used to electronically transmit shipping instructions from the shipper to the carrier. The process typically involves the following steps:
Here are some common issues that may arise when using EDI 940:
To prevent these issues, it’s important to have a robust and reliable EDI system in place, with proper data validation and error-checking mechanisms.
Transaction Set Header (ST):
Beginning Segment for Warehouse Shipping Order (W05):
Shipping Order Identification (W06):
Ship-To and Bill-To Information (N1 Loop):
Shipping Instructions (LX Loop):
Carrier Information (TD5):
Transaction Totals (CTT):
Transaction Set Trailer (SE):
EDI 940 is used by manufacturers, wholesalers, retailers, and third-party logistics providers. It is particularly valuable for businesses that manage inventory in warehouses and need to communicate detailed shipping instructions to ensure accurate order fulfillment.
EDI 940 benefits businesses by streamlining the shipping process, reducing manual data entry errors, and improving the accuracy and speed of order fulfillment. It enhances supply chain visibility, facilitates better inventory management, and ensures timely communication between suppliers and warehouses.
Implementing EDI 940 involves setting up EDI software to create, send, receive, and process the document. Businesses must establish EDI partnerships with their trading partners, agree on data standards, and configure their systems to integrate with existing Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and Order Management Systems (OMS).
An EDI 940 document typically includes order details such as product identification, quantities to be shipped, ship-to and bill-to addresses, carrier information, and special shipping instructions. It also contains information about the shipping dates and any relevant references or order numbers.
Common challenges in using EDI 940 include ensuring data accuracy, maintaining data security, managing different EDI standards, and achieving seamless integration with existing systems. Businesses must also handle the technical complexities of EDI software and maintain strong communication with trading partners to ensure smooth data exchange.
Experience the effortless power of Commport’s Integrated EDI solution today!
Say goodbye to complicated and costly software installations, and forget about the need to be an EDI expert or create your own mappings. Our seamless solution adapts effortlessly to your business’s growth, making adding new customers a breeze.
With fast and reliable translation, you can rest assured that your EDI processes are in safe hands, allowing you to focus on what truly matters – your business.
1. Easy integration with any trading partner
2. Commport EDI solutions are scalable as your business grows
3. Affordable pricing and pay-as-you-go plans available
4. Dedicated world-class customer support
5. 100% EDI compliance guaranteed
6. Trusted by 6000+ customers
Take the next step towards efficiency and success with Commport. Get a free quote today!
Discover the transformative impact of our EDI, CPS, and VAN solutions through the powerful testimonials of satisfied clients who have experienced remarkable results with Commport products and services.

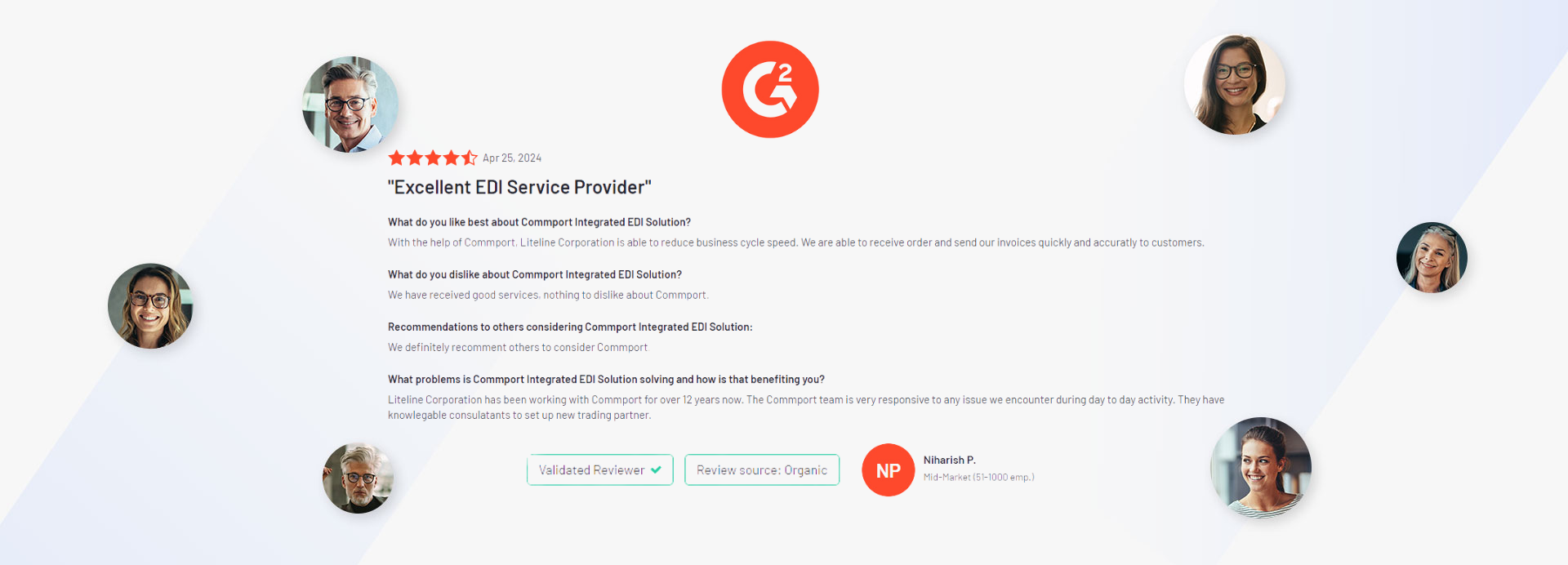

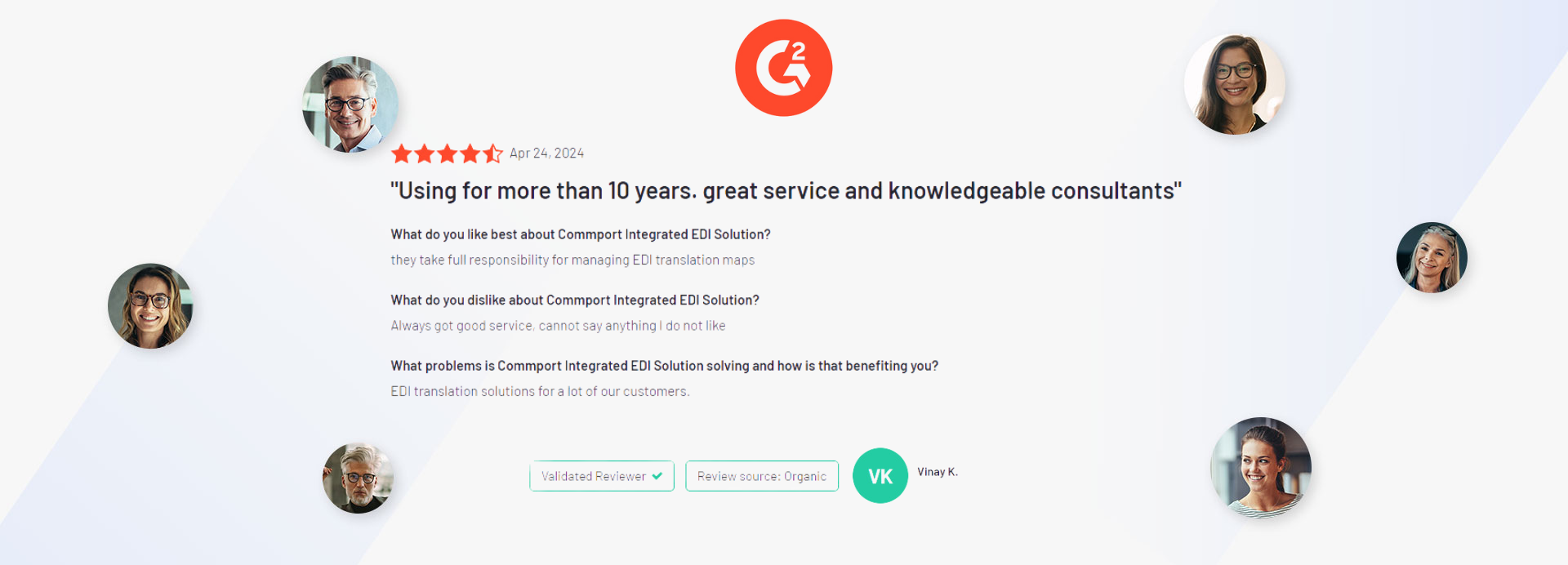

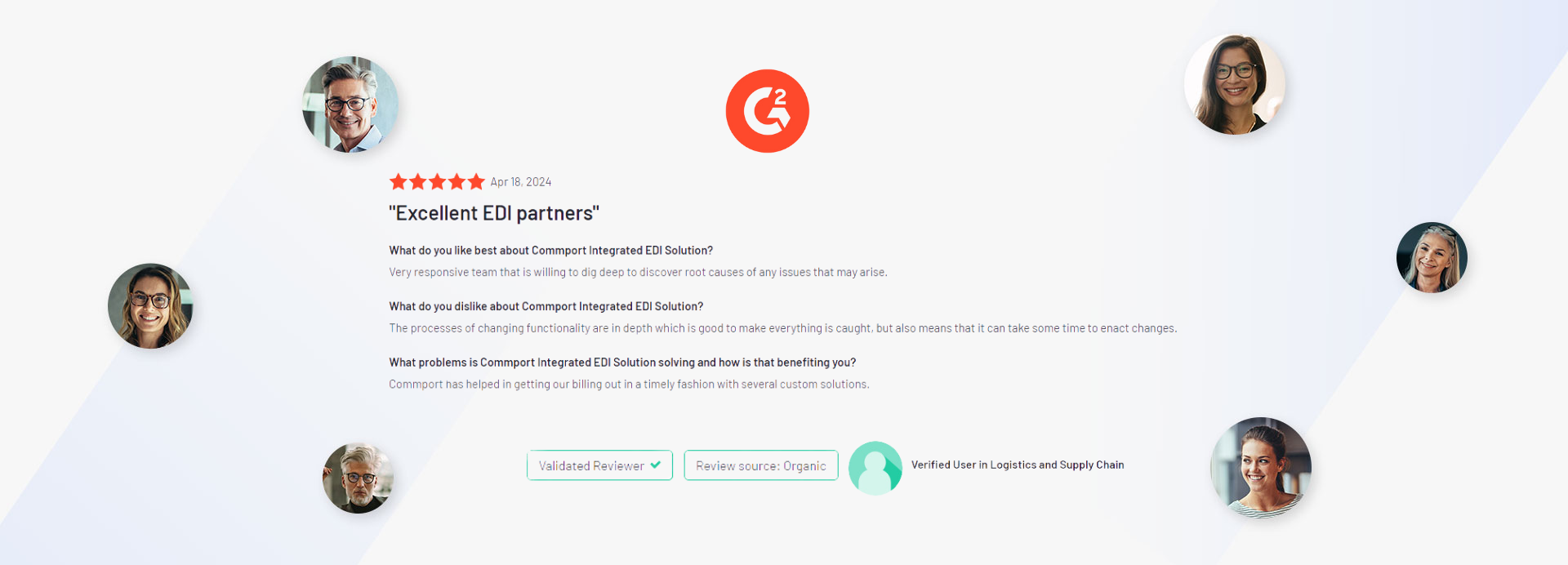

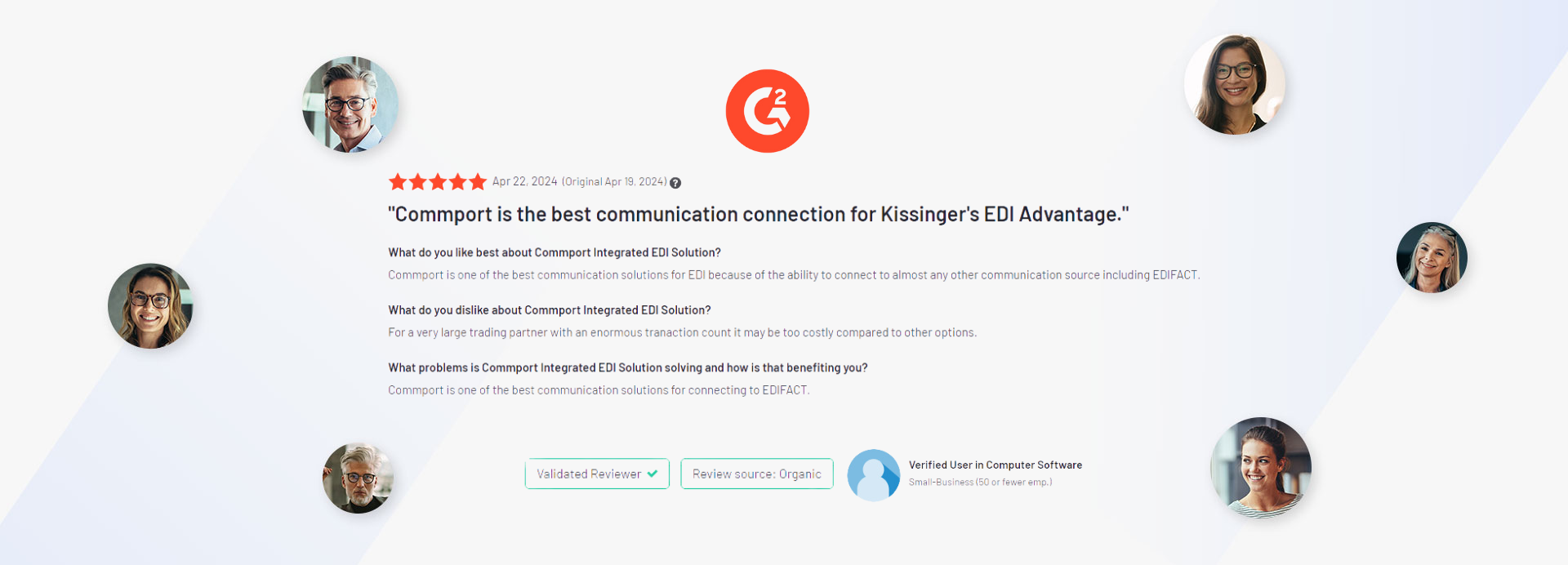
We got the goods to help you utilize your EDI services effectively. We encourage you to explore our available resources below


Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions