Introduction
B2B Data integration refers to the seamless electronic exchange of business documents and information between different companies within a supply chain. This process allows businesses to share important documents, such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping details, in a fast, secure, and standardized way. Furthermore, by converting business documents into standardized formats, EDI enables seamless data exchange and communication with partners, regardless of the systems they use.
In complete integration solutions, Value-Added Networks (VANs) play a critical role. These networks are the gold standard for EDI communication, offering security that meets government standards. In fact, some leading VANs like Commport VAN maintain an impressive 99.99% uptime, ensuring your business communications remain consistently operational. Consequently, the overall aim of combining EDI with VAN connectivity is to enhance operational efficiency by automating and standardizing the exchange of business information, reducing errors, and accelerating transactions in the B2B supply chain processes.
Key Takeaways
- EDI handles 88-95% of all B2B transactions– Making it the dominant standard for electronic business document exchange across industries worldwide.
- VANs provide 99.99% uptime reliability– Offering secure, scalable infrastructure that eliminates the need for individual partner connections.
- Integration reduces costs by 60% and errors by 30-40%– Automating manual processes while accelerating business cycles and improving accuracy.
- Real-time ERP/WMS integration enables complete order-to-cash automation– Connecting internal systems with EDI creates seamless workflows from purchase orders to payment confirmation.
Why EDI Is the Backbone of B2B Data Integration
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) has remained the cornerstone of B2B data integration for decades, with over 60% of businesses using it to conduct business-to-business transactions. Additionally, the global EDI software market is projected to grow from USD 1.98 billion in 2023 to USD 4.52 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 12.5%. These figures clearly demonstrate the enduring importance of EDI in modern business operations.
What is EDI Integration and Why It Matters
B2B EDI integration refers to the process of connecting a company’s internal business systems to an EDI platform, enabling the automated exchange of structured data with partners. Rather than relying on paper-based methods, businesses use standardized electronic formats to exchange information such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notifications.
The value of EDI integration becomes apparent through its tangible benefits. First, it eliminates paper-related expenses, including printing, storage, filing, and postage. Second, it dramatically accelerates business cycles by up to 61%. Third, it significantly reduces transaction errors by at least 30-40%. Moreover, companies that integrated EDI with their ERP systems have reported reducing manual order entry by 90%, virtually eliminating fulfillment errors.
EDI Document Standards: ANSI X12, EDIFACT, UBL
EDI standards are predefined rules for structuring electronic documents, ensuring businesses across different regions and industries can interpret and process data consistently. These standards define the basic set of rules for all EDI documents, depending on location/region and specific industry.
ANSI X12 – Developed by the American National Standards Institute, it dominates North America and is used in retail, healthcare, and logistics industries. There are more than 300 different types of X12 EDI standards, each designated by a different three-digit number.
EDIFACT (Electronic Data Interchange For Administration, Commerce, and Transport) – Created by the United Nations, EDIFACT is widely used in Europe, Asia, and other international markets. It structures data into segments, segments into messages, and messages into an interactive exchange protocol.
UBL (Universal Business Language) – A library of standard XML-based business document formats owned by OASIS and available to businesses for free. As UBL uses an XML structure, it differs from traditional EDI formats and is easier to read.
Most EDI standards include three key components: elements (the smallest part providing submitted values), segments (collections of elements), and transaction sets (collections of segments composing a message).
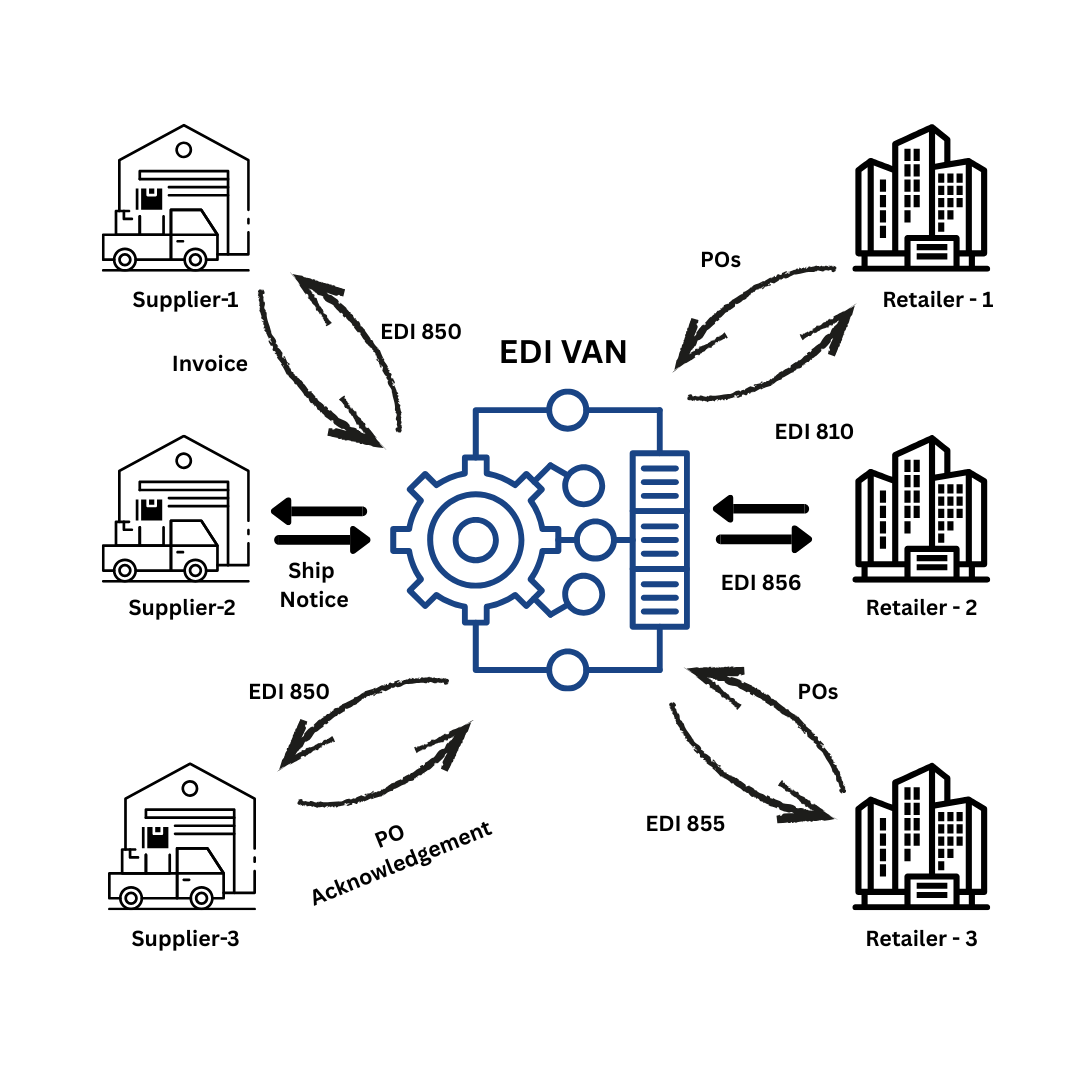
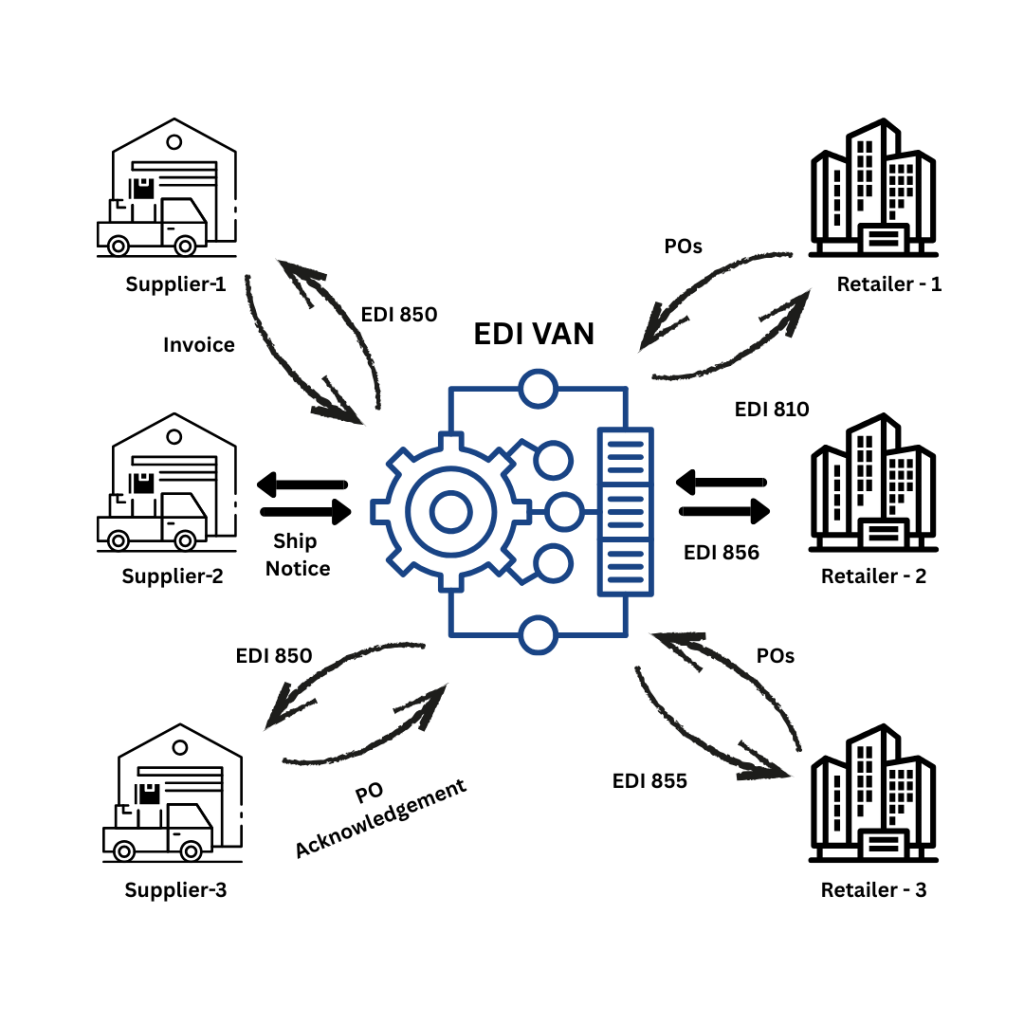
Common EDI Transactions: 850, 810, 856, 855
The most frequently used EDI transaction codes facilitate the entire order-to-cash cycle:
EDI 850 (Purchase Order) – Sent by buyers to request goods from suppliers, it contains information such as order details, product names, quantities, prices, and payment terms.
EDI 810 (Invoice) – An electronic invoice containing invoice details, product information, shipping particulars, and payment information. It’s typically sent in response to a Purchase Order or after an order is fulfilled.
EDI 856 (Advance Ship Notice) – Specifies shipment contents before they reach the partner’s facility, including barcode information, tracking details, delivery date, and time of shipment.
EDI 855 (Purchase Order Acknowledgment) – Confirms receipt of a Purchase Order, eliminating the need for confirmation calls or faxes. It includes information on whether the order was accepted or rejected, along with accepted quantities, pricing, and shipping details
Throughout the supply chain, these standardized transactions form the foundation for automated B2B data exchange, enabling companies to achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and partner satisfaction.
The Role of VANs in Secure and Scalable B2B Communication
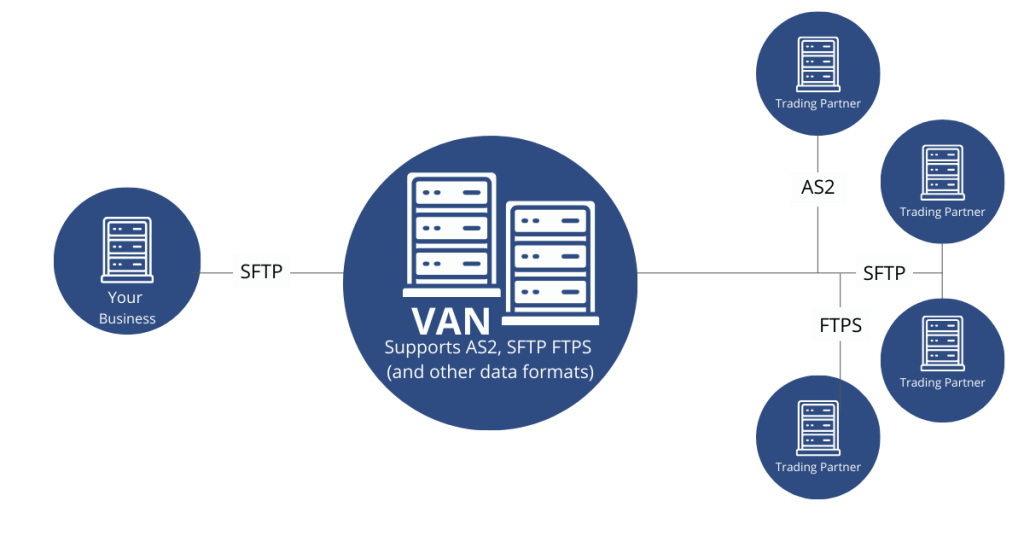
In the complex ecosystem of B2B data integration, Value-Added Networks (VANs) function as a secure highway system connecting trading partners. While EDI provides the language for business document exchange, VANs offer the infrastructure needed to transmit that information reliably and securely.
What is a Value-Added Network (VAN)
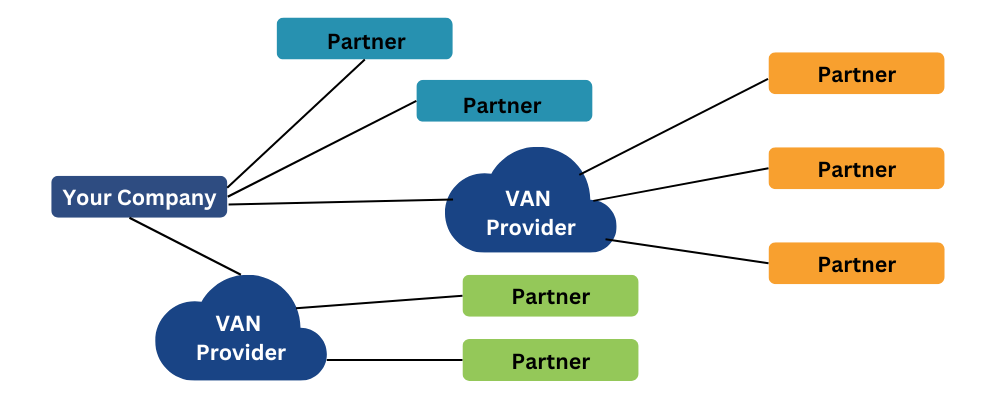
A Value-Added Network is a secure, private network that facilitates the exchange of EDI documents between trading partners. Originally introduced in the 1970s, VANs serve as intermediaries in B2B communication. They operate similarly to a digital post office—each business receives a virtual mailbox where EDI documents are delivered, sorted, and managed. Instead of maintaining individual connections with each partner, companies connect to a single VAN that handles all communications.
The primary function of a VAN is to simplify electronic trading; it enables businesses to use one connection into a network that connects to all their business partners. This centralized approach means incoming documents are managed in a virtual mailbox, which traditionally required manual checking and processing by the receiving party.
Direct EDI vs VAN-Based EDI: Key Differences
The distinction between direct and VAN-based EDI involves several critical factors. In direct EDI, companies establish peer-to-peer connections with each trading partner, which can quickly become an integration nightmare as partner numbers grow. Alternatively, VAN-based EDI provides a managed network with comprehensive security, tracking, and compliance features.
From a cost perspective, VANs typically charge minimal setup costs followed by per-document fees (around 30 cents per document). While this makes them cost-effective for low-volume users, expenses can increase dramatically as transaction volumes grow. Direct EDI involves higher upfront costs but eliminates ongoing transaction fees.
Another crucial difference lies in implementation time. VAN onboarding can take three to six months for new partners, whereas direct connections can be established more quickly once the initial setup is complete.
VAN Protocols: AS2, SFTP, HTTPS
Modern VANs support multiple communication protocols, enabling flexible partner communication:
- AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) – Used for direct B2B exchanges like EDI over HTTP/S, AS2 emphasizes encryption, authentication, and non-repudiation with MDN receipts. Many retailers, including Walmart, have mandated AS2 connections from their suppliers.
- SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) – Offers secure file transfer capabilities often used in EDI communications.
- HTTPS – Provides secure web-based document exchange.
One of the most valuable features of VANs is protocol conversion—if one trading partner uses SFTP to send EDI documents while another uses AS2, the VAN can convert documents between protocols. This eliminates the need for partners to agree on a single communication method.
VAN Uptime and Reliability Metrics
The reliability of VANs stems from their redundant systems and 24/7 monitoring, ensuring high uptime and consistent document delivery. Today’s B2B/EDI VANs are highly reliable, offering connectivity across large networks with fewer delays in business transactions.
VANs provide detailed visibility tools showing delivery status and corresponding workflows. This transparency allows companies to coordinate dependent activities through the system instead of exchanging phone calls and emails.
For businesses where EDI connections represent high-value contracts, VANs offer a highly dependable trading method. They provide complete audit trails, tracking and recording all EDI message transfers and transactions. This comprehensive monitoring ensures partners are immediately notified when messages arrive at their mailboxes.
By acting as trusted intermediaries in B2B communication, VANs continue to play a vital role in providing secure, scalable, and reliable document exchange despite the emergence of newer integration methods.
Download: VAN Buyers Guide
Maximize your business efficiency with the right VAN provider! Grab your free VAN Buyer's Guide and discover the key features and services that will elevate your EDI transactions to the next level.
Make an informed decision today!
Integrating EDI and VAN with Internal Systems
For successful b2b data integration, businesses must connect their EDI and VAN infrastructure with internal systems. This connection forms the critical bridge between external communications and core business operations.
ERP and WMS Integration via APIs and Flat Files
Generally, two primary methods exist for connecting warehouse management systems (WMS) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) with EDI systems. API integration offers the most flexible and real-time option, enabling instant data exchange with minimal latency. Through APIs, businesses automatically update order statuses, monitor stock levels, and improve supply chain visibility.
Alternatively, flat file integration provides a secure approach where data files are uploaded to FTP sites. While this method adds a security layer, it operates as a batch process rather than providing live data transfer. When selecting an integration method, consider that API access allows real-time data retrieval on demand, whereas flat files require waiting for uploads.
Data Mapping and Translation for EDI Formats
EDI mapping refers to matching data structures between systems exchanging EDI documents. This critical process ensures compatibility when trading partners use different standards or versions. Effective mapping requires one system to act as the source and another as the target, with data elements carefully aligned to maintain meaning after translation.
Practically, if a supplier’s ERP generates data in X12 format while its customer uses EDIFACT, mapping aligns elements like buyer, seller, and item codes between standards. This process ensures each system correctly interprets the data, enabling smooth transactions despite format differences.
Using Middleware and iPaaS for Seamless Flow
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) acts as a digital bridge connecting multiple systems through a centralized platform. For EDI integration, iPaaS specializes in transforming data between various formats such as EDIFACT, ANSI X12, and XML.
Currently, solutions like Commport VAN offer compatibility with third-party EDI middleware, connecting businesses to over 1 million pre-existing EDI trading partners globally. Commport EDI and VAN Solutions. #1 B2B Network Solutions Connects With Any Trading Partner and Internal ERP or Other Business Systems for Seamless Data Exchange.
Real-Time Automation of Order-to-Cash Cycle
By connecting critical systems like ERP, CRM, and logistics platforms with EDI solutions, companies establish seamless workflows that eliminate task duplication and reduce human error. This integration enables information to flow automatically between departments, ensuring each order-to-cash phase completes accurately and efficiently.
Effectively, when a customer places an order, the integrated ERP can automatically check inventory while EDI transmits order data to suppliers and carriers. The WMS receives this data for optimal warehouse operations, with advanced shipping notices (EDI 856) alerting customers about incoming shipments. Upon payment receipt, financial systems automatically confirm transactions (EDI 997), completing the cycle.
Operational Benefits of EDI and VAN Connectivity

The tangible operational advantages of implementing integrated EDI and VAN solutions deliver measurable returns across multiple business dimensions. Companies across industries report substantial benefits once these systems are fully deployed.
Reduced Manual Errors and Faster Processing
Manual data entry processes typically introduce human errors that ripple throughout the supply chain. By automating document exchange, EDI eliminates this risk, drastically reducing the likelihood of incorrect shipments, invoice discrepancies, and communication breakdowns. Organizations implementing EDI solutions report saving up to 60% in transaction costs by reducing paper-based processes and manual labor. Notably, high-volume transactions complete instantly through EDI, allowing businesses to shorten processing cycles, reduce lead times, and increase overall supply chain agility. This efficiency ultimately translates into tangible benefits like reduced operational costs and faster transaction cycles.
Improved Supply Chain Visibility and Tracking
EDI integration, especially for logistics operations, provides real-time inventory updates and shipment tracking, enabling smarter inventory decisions. Through this enhanced visibility, businesses can effectively avoid overstocking and stockouts by accurately forecasting demand and synchronizing inventory across locations. Accordingly, VANs facilitate access to real-time visibility, allowing organizations to track transactions at every stage of the process. This comprehensive tracking creates a full audit trail where all EDI messages are recorded, thereby enhancing decision-making processes and boosting overall business agility.
Scalability for Onboarding New Partners
VANs dramatically simplify partner connectivity, enabling businesses to expand their networks without complex integrations. As organizations grow and their data exchange requirements evolve, VANs easily accommodate changing needs, including increases in trading partners and document volumes. Commport EDI and VAN Solutions. #1 B2B Network Solutions Connects With Any Trading Partner and Internal ERP or Other Business Systems for Seamless Data Exchange. Unfortunately, traditional onboarding can be problematic—47% of IT managers report that slow EDI supplier onboarding prevents capturing new revenue opportunities, subsequently, nearly 24% of companies lose $500,000+ annually to integration issues.
Compliance with Industry Standards
VANs ensure adherence to industry-specific standards through advanced encryption, secure transmission protocols, and standardized documentation.
- Enhanced data security through encryption and controlled access
- Better cash flow and revenue cycle management
- Stronger compliance and reduced regulatory risk
GS1 Standards primarily help businesses improve efficiency and quality while lowering costs. The implementation of these standards through EDI enables immediate electronic sharing of standardized, up-to-date product data, providing a common language for trading partners across the supply chain.
Conclusion
B2B data integration stands incomplete without the powerful combination of EDI and VAN connectivity. Throughout this article, we explored how EDI remains the fundamental language of business transactions, standardizing documents across industries while VANs provide the secure infrastructure needed for reliable communications. Together, these technologies form the backbone of modern supply chain operations.
The statistics speak volumes – EDI and XML handle approximately 88-95% of all B2B transactional volumes. This widespread adoption stems from tangible benefits businesses experience after implementation. Companies report dramatic reductions in manual errors, processing times cut by up to 61%, and transaction costs decreased by as much as 60%. Additionally, enhanced supply chain visibility allows for smarter inventory decisions and improved customer satisfaction.
The integration of these systems with internal ERP and WMS platforms creates seamless workflows that automate the entire order-to-cash cycle. This connectivity eliminates data silos and ensures information flows efficiently between departments and trading partners. Consequently, businesses gain agility and responsiveness previously unattainable with manual processes.
The evolution of B2B data integration continues, yet EDI and VANs remain essential components of this landscape. Companies seeking competitive advantage must embrace these technologies to streamline operations, reduce costs, and build stronger trading partner relationships. Undoubtedly, as business requirements grow increasingly complex, the foundation provided by robust EDI and VAN connectivity becomes even more vital for success in the digital economy.
Commmport B2B Solutions
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
While EDI is primarily used for high-volume, standardized transactions between trading partners, B2B eCommerce encompasses a wider range of transactions and offers more flexibility. EDI focuses on the automated exchange of structured business documents, while B2B eCommerce can include additional features and functionalities for online business interactions.
Value-Added Networks (VANs) act as intermediaries in EDI communications, similar to a digital post office. They provide a secure, private network where businesses can exchange EDI documents with all their trading partners through a single connection. VANs offer benefits like protocol conversion, high uptime, and comprehensive tracking of transactions.
EDI offers numerous advantages in B2B transactions, including reduced processing time, fewer errors, enhanced security, and improved supply chain visibility. It automates document exchange, saving time and costs while enabling better connectivity across the supply chain. EDI can reduce transaction costs by up to 60% and cut processing times by as much as 61%.
Integrating EDI with internal systems like ERP and WMS creates seamless workflows that automate the entire order-to-cash cycle. This integration eliminates data silos, reduces manual errors, and ensures efficient information flow between departments and trading partners. It enables real-time updates, faster processing, and improved decision-making based on accurate, up-to-date data.
Several emerging technologies are expanding EDI functionality. Internet of Things (IoT) devices enable real-time shipment monitoring, providing unprecedented supply chain visibility. Blockchain technology creates immutable transaction records, enhancing security and trust. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is being used for predictive exception handling, significantly reducing processing time and improving data accuracy in EDI operations