Introduction
Real-time inventory management using EDI is essential for meeting customer demands in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Modern businesses are moving away from manual processes that significantly hinder growth and operational efficiency. When retailers exchange inventory data automatically through EDI, they gain accurate, real-time information about inventory levels, sales, and customer demand—all crucial elements for making informed decisions and staying competitive.
By implementing real-time inventory management using EDI, companies can track stock levels instantly through automated data sharing across platforms.
EDI automation significantly reduces errors and enhances visibility throughout the inventory lifecycle. Additionally, the EDI 846 document eliminates the need for manual inventory checks, decreasing discrepancies that lead to stock issues or fulfillment delays.
With increasing demand for faster, more accurate deliveries, we’ll show you how EDI inventory automation can transform your supply chain operations. From assessing your current system to implementing real-time inventory feeds, this guide provides the practical steps you need for successful EDI integration.
Key Takeaways
- Manual inventory systems create costly bottlenecks– Human errors, outdated information, and time-consuming processes drain resources and compromise supply chain performance.
- EDI enables real-time inventory visibility– Documents like EDI 846, 850, and 856 automate data exchange between systems, providing instant updates across all platforms.
Just-in-Time inventory management – Originated from Toyota’s production system in the 1970s. The core principle is elegantly simple yet transformative: receive goods only as they are needed in the production process, thereby minimizing inventory holding costs and eliminating waste
- Follow six critical implementation steps– Assess current systems, choose the right provider, map workflows, configure transactions, test thoroughly, and train your team.
- Automation delivers measurable ROI– Companies experience 50% faster order processing, 19% better demand forecasting accuracy, and significant cost reductions through eliminated manual work.
- EDI strengthens supplier relationships– Transparent, automated transactions build trust and enable collaborative planning with real-time order visibility for all partners.
Why Manual Inventory Systems Fall Short
Manual inventory management seems simple on the surface—count your stock, write it down, repeat.
However, this approach creates serious problems that grow exponentially as businesses expand.
Let me explain why these outdated systems hold companies back and how this affects the entire supply chain.
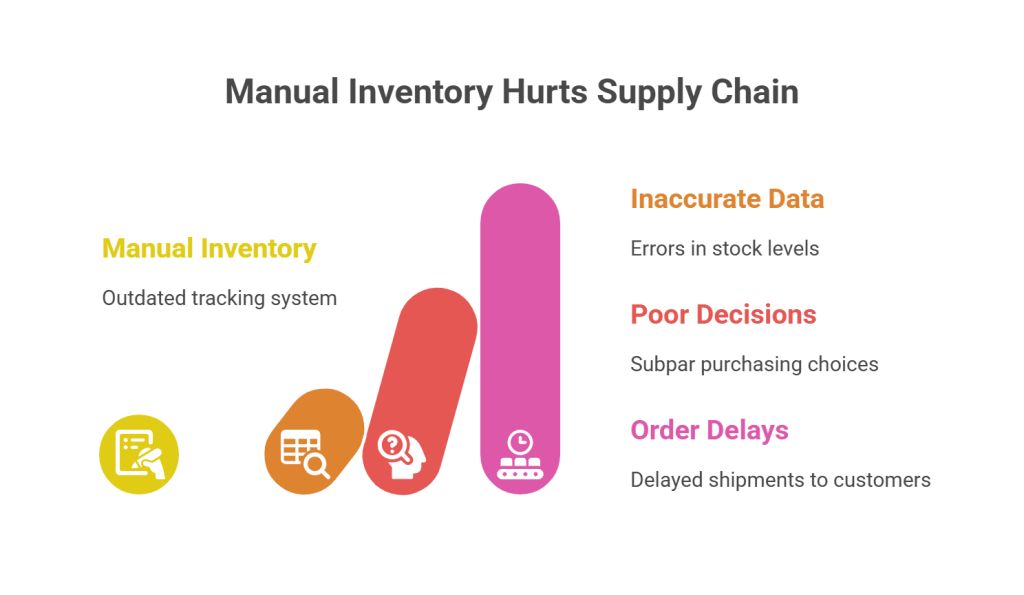
Common Issues with Manual Tracking
The physical nature of manual inventory creates numerous pain points that drain resources and introduce errors:
- Time-consuming processes: Workers must physically count stock, record data by hand, calculate numbers, and transfer results to ledgers or spreadsheets. These tedious tasks pull employees away from more strategic work.
- Human error: Misreading labels, transposing digits, and making data entry mistakes create significant discrepancies between recorded inventory and actual stock levels. These errors multiply throughout your operations, affecting every aspect of inventory management.
- Outdated information: Manual systems provide only periodic snapshots of inventory that become obsolete almost immediately. Without real-time data, you’re essentially flying blind in today’s fast-paced market.
- Spreadsheet limitations: While spreadsheets seem convenient initially, they become burdensome as product portfolios grow. They simply weren’t designed for tracking purchases across multiple warehouses or managing complex manufacturing components.
Impact On Supply Chain Performance
These manual system shortcomings create ripple effects throughout your entire operation:
Manual inventory errors lead to subpar purchasing decisions and inaccurate financial reporting. Consequently, businesses face two equally problematic scenarios: overordering slow-moving items (increasing storage costs and risking obsolescence) or running out of critical materials (losing sales and customers).
Furthermore, without automated EDI inventory management, companies struggle with disconnected systems. This forces manual duplication of data between platforms, increasing error risks and preventing real-time visibility. The result? Your team makes critical decisions based on stale information, compromising supply chain agility.
Moreover, order fulfillment suffers as inventory inaccuracies lead to delayed shipments and unhappy customers. This damages your reputation and directly impacts revenue.
When to Consider Automation
It’s time to implement an EDI inventory system when:
- Manual processes can no longer keep pace with your business demands
- Inventory tasks are becoming increasingly labor-intensive and error-prone
- You need to scale operations across multiple locations
- Stock discrepancies are affecting customer satisfaction
- Employees spend excessive time on administrative inventory tasks rather than strategic work
Essentially, if your team spends countless hours counting stock, struggles with inaccurate spreadsheets, or constantly worries about stockouts, your manual inventory system has become a major drain on resources. Unfortunately, these challenges only compound as your business grows.
Understanding EDI in Inventory Management
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) transforms inventory operations by creating a digital highway for business data. Unlike previous methods that relied on human processing, EDI creates a direct line of communication between computer systems.
What is EDI and how does it work
EDI is the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in standardized electronic formats. EDI technology replaces traditional paper-based methods like mail, fax, and email by enabling systems to communicate directly without human intervention. When two businesses implement EDI, they first agree on specific standards and versions (such as ANSI X12 or EDIFACT) to ensure their systems can interpret the data correctly. Subsequently, EDI translators convert the information into these standardized formats, allowing for seamless data transmission between different platforms.
Key EDI Inventory Documents (EDI 846, 850, 856)
Three primary EDI documents drive effective inventory management:
Three key EDI documents drive effective inventory management:
EDI 846 (Inventory Inquiry/Advice) communicates inventory information between manufacturers, suppliers, and resellers. It contains critical details like inventory location identification, item descriptions, and quantities (including on-hand, committed, on-order, returns, and backorder quantities). This document helps trading partners monitor product availability across multiple locations.
EDI 850 (Purchase Order) represents the digital version of a traditional purchase order, allowing buyers to communicate specific item, quantity, and pricing requirements to suppliers.
EDI 856 (Advance Ship Notice) provides detailed information about upcoming shipments, including contents, packaging, and shipping details—enabling recipients to prepare for incoming inventory and update their records accordingly.
How EDI Supports Real-Time Inventory Updates
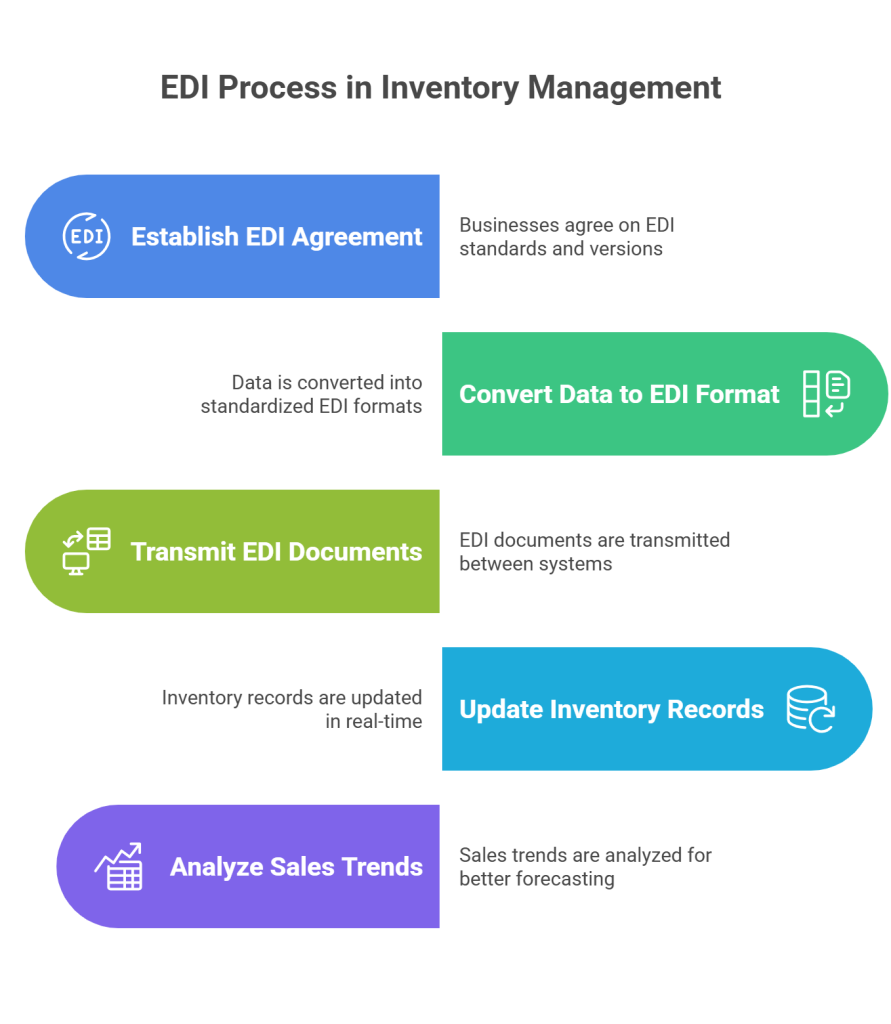
EDI enables instant inventory tracking by automating data exchange between suppliers, warehouses, and sales channels.
Whenever a product is sold—whether online or in-store—EDI immediately updates inventory records across all platforms, dramatically reducing overselling risks.
Furthermore, this real-time visibility allows businesses to make data-driven decisions about replenishment, preventing both stockouts and excess inventory situations.
Companies can therefore analyze sales trends and inventory turnover rates to optimize stock levels and improve demand forecasting.
Understanding Just-in-Time Inventory Management
What is Just in Time Inventory (JIT)?
Receive goods only as they are needed in the production process, thereby minimizing inventory holding costs and eliminating waste
Benefits of JIT Implementation
When properly executed, JIT inventory management delivers substantial advantages:
Reduced carrying costs – Organizations typically reduce inventory carrying costs by 20-30%
Decreased waste – Minimizes obsolescence, damage, and expiration of stored materials
Improved cash flow – Less capital tied up in inventory means more available working capital
Enhanced quality control – Smaller batch sizes make defect identification and correction more manageable
Space optimization – Reduced storage requirements free up valuable warehouse space for value-adding activities
For JIT inventory management to function effectively. EDI systems must seamlessly integrate with ERP and WMS systems.
This integration enables:
Automatic creation of purchase orders based on production schedules
Real-time inventory level monitoring and threshold-based ordering
Production planning based on confirmed material deliveries
Financial systems alignment with inventory movements
Cross-docking operations to move incoming materials directly to production
Precise receiving schedules based on production needs
Optimized put-away locations for materials with imminent production requirements
Accurate inventory counts to support JIT decision-making
Steps to Automate Inventory Using EDI
Implementing EDI for inventory management requires careful planning and execution. Let me walk you through the six essential steps to successfully automate your inventory using EDI.
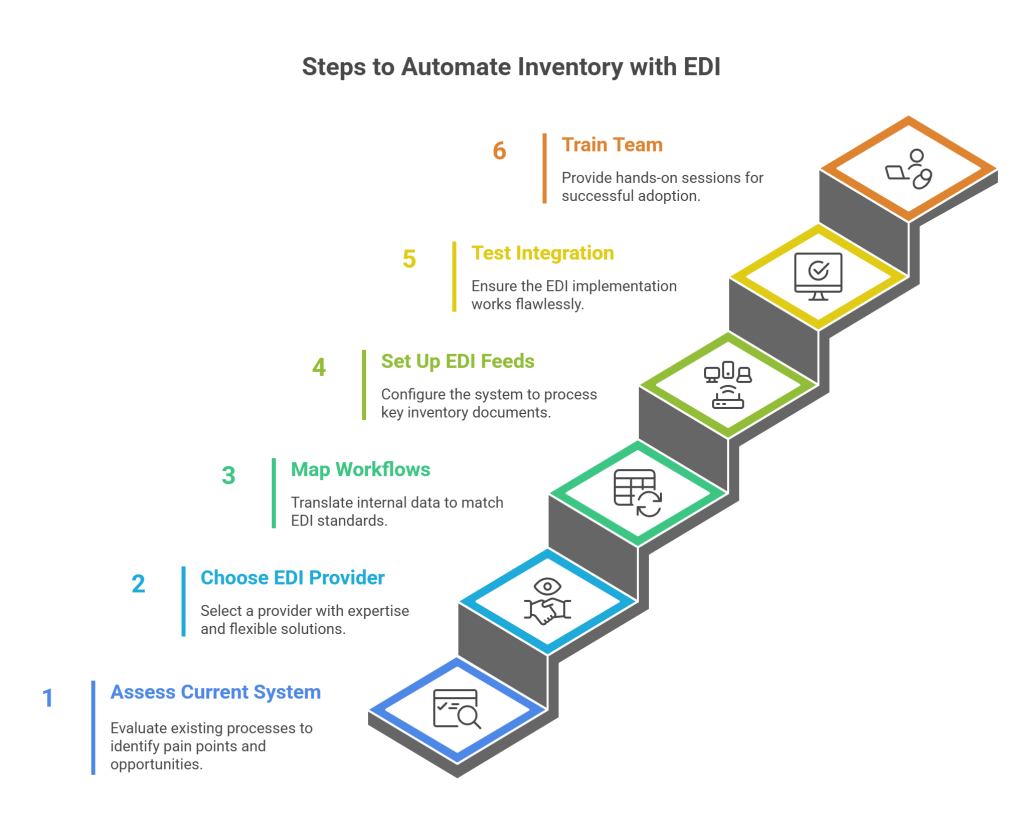
1. Assess Your Current Inventory System
First, thoroughly evaluate your existing inventory processes to identify pain points and automation opportunities. Map out your business operations, noting areas that need streamlined processes or reduced manual work. Analyze your transaction volumes—orders, invoices, shipping notices—and document the specific inventory requirements of your trading partners.
2. Choose an EDI Solution Provider
Select a provider with proven expertise in your industry and a track record of successfully implementing EDI inventory systems. Look for extensive network connections that simplify partner onboarding, secure SaaS solutions, and flexible pricing that accommodates fluctuations in transaction volumes.
3. Map Inventory Workflows to EDI Processes
Before implementation, translate your internal data formats to match EDI standards. Focus specifically on mapping critical inventory data points such as customer information, order data, and product details to standardized EDI formats used by your trading partners.
4. Set up EDI Inventory Feeds and Transactions
Configure your system to process key inventory documents like EDI 846 (Inventory Inquiry/Advice), EDI 850 (Purchase Orders), and EDI 856 (Advance Ship Notices). Establish connections between your EDI solution and internal systems (ERP, WMS, accounting) to enable real-time data exchange.
5. Test and Validate EDI Integration
Comprehensive testing ensures your EDI implementation works flawlessly before going live. Verify connectivity, conduct functional testing of data elements, and validate transaction formatting. Run both proof and final mode tests to identify and resolve any issues with inventory data transmission.
6. Train Your Team on EDI Inventory Controls
Undeniably, proper training ensures successful adoption. Provide hands-on sessions covering EDI standards, document types, and troubleshooting techniques. Document processes clearly and create resources staff can reference when questions arise.
I would highly recommend choosing Commport EDI Solutions for inventory management, as it can streamline your inventory data in real time, and connects to 1000s of trading partners right from our EDI interface. Our EDI Solutions fit any business size and are easy to scale. Integrates with all major ERP systems.
Benefits of EDI Inventory Automation
After implementing EDI for inventory automation, businesses experience five major benefits that transform their operations and bottom line.
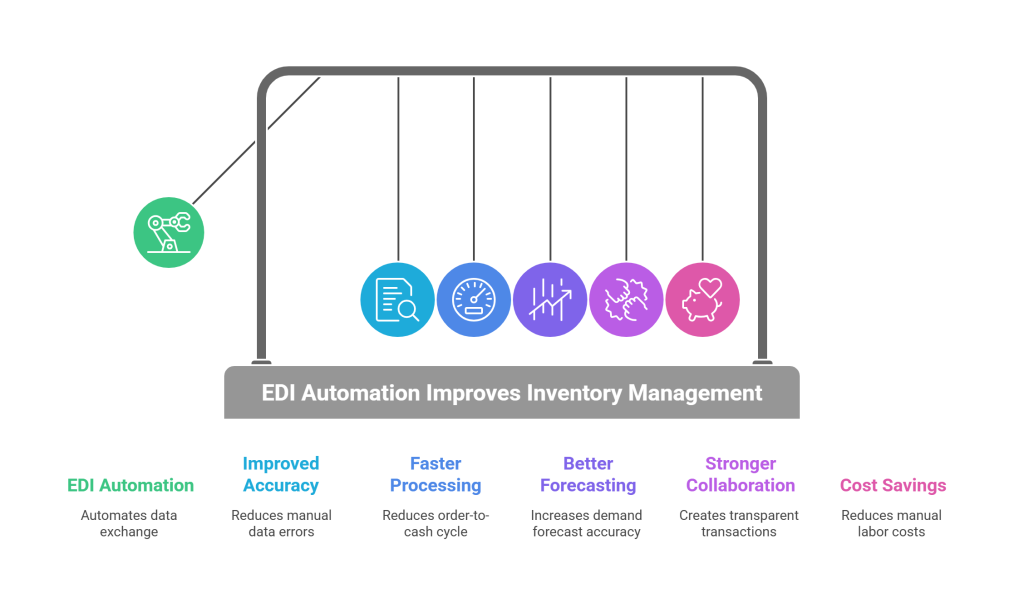
1. Improved Accuracy and Fewer Errors
First and foremost, EDI eliminates manual data entry errors that plague traditional inventory systems. Automated processing of EDI transactions significantly reduces the risk of human error, increasing data reliability. This automation ensures inventory records are accurately managed, minimizing waste and discrepancies between systems.
2. Faster Order Processing and Fulfillment
As a result of automation, order-to-cash cycles can be reduced by as much as 50%. EDI enables companies to process more orders in less time, improving cash flow with faster invoicing. For warehouses, EDI frameworks enable quick turnaround times by rapidly processing product information.
3. Better Demand Forecasting with Real-Time Data
Beyond this, companies realize 19% higher accuracy in demand forecasting with EDI integration. Real-time inventory data provides businesses with insights into customer buying patterns, allowing them to adjust forecasts based on actual demand. This prevents both overproduction and inventory shortages.
4. Stronger Supplier Collaboration
EDI automates order lifecycle visibility through documents like EDI 850 (Purchase Order) and EDI 855 (Purchase Order Acknowledgment). This creates transparent transactions that build trust between partners. Suppliers and buyers share real-time visibility into order progress, with delays triggering immediate alerts.
5. Cost Savings Through Reduced Manual Work
Overall, EDI automation delivers substantial savings:
- Eliminates printing, reproducing, filing, and sending large volumes of documents
- Reduces labor costs through automation of repetitive tasks
- Minimizes chargebacks and penalties from trading partners
Conclusion
EDI inventory automation represents a significant leap forward for companies struggling with outdated manual processes.
Most importantly, EDI creates a digital highway for your inventory data, enabling real-time updates across all systems and trading partners. This visibility transforms decision-making capabilities and allows your business to respond quickly to market changes. As a result, you’ll experience fewer stockouts, reduced overstock situations, and more satisfied customers.
The six-step implementation process we outlined provides a roadmap anyone can follow—from assessing your current system to training your team on new controls. Though the transition requires careful planning, the long-term benefits certainly outweigh the initial investment.
Companies that embrace EDI inventory automation gain substantial advantages over competitors still relying on manual methods. These advantages include dramatically improved accuracy, faster order fulfillment, enhanced demand forecasting, stronger supplier relationships, and significant cost reductions. Consequently, your entire supply chain becomes more agile and responsive.
The business landscape continues to evolve at an unprecedented pace. Accordingly, automated inventory management through EDI has shifted from being merely advantageous to essential for companies seeking sustained growth. You now have the knowledge needed to start this transformation—take the first step toward automating your inventory management with EDI today.
Commport EDI Solutions Help You Automate Your Inventory Process
Need Help? Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) is a system that enables real-time communication and data exchange between businesses. In inventory management, it eliminates manual data entry errors, provides accurate inventory tracking, improves demand forecasting, and enhances supplier collaboration.
EDI automation streamlines the exchange of business documents by automatically transferring data between systems without manual intervention. This improves accuracy, speeds up transactions, reduces human errors, and increases overall operational efficiency in inventory management and supply chain processes.
The key steps include assessing your current inventory system, choosing an EDI solution provider, mapping inventory workflows to EDI processes, setting up EDI inventory feeds and transactions, thoroughly testing the integration, and training your team on the new EDI inventory controls.
The main benefits include improved accuracy with fewer errors, faster order processing and fulfillment, better demand forecasting using real-time data, stronger supplier collaboration, and significant cost savings through reduced manual work.
EDI plays a crucial role in supply chain management by speeding up processes and improving overall movement throughout a business. It enables faster completion of transactions between trading partners at greater volumes, which accelerates payments and improves cash flow. This leads to a more efficient and responsive supply chain.
Implementation timelines vary based on existing systems and complexity, but most businesses can expect 3-6 months from initial assessment to full operational capability, with phased implementation allowing for progressive benefits realization.