Introduction
Did you know that hospital supply chains are uniquely vulnerable to disruptions and delays because of their complex and global nature? When a hospital supply chain falters, critical shortages directly impact the quality of patient care, operational efficiency, and budgetary goals. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, we’ve witnessed firsthand how supply chain failures can cripple healthcare delivery systems across the board.
Hospital supply chain management has become increasingly crucial for maintaining an adequate inventory of life-saving supplies and preventing dangerous stockouts. Research identified 30 key performance indicators across financial, managerial, and clinical categories that affect supply chain performance. Additionally, automated solutions play a pivotal role in transforming healthcare supply chain strategy, from real-time inventory tracking to streamlined procurement processes. Without effective electronic data interchange (EDI) systems, hospitals struggle to achieve the transparency and optimization necessary in today’s healthcare environment.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll examine why hospital supply chains fail without proper EDI implementation and explore data-driven hospital supply chain solutions that can revolutionize operations, improve healthcare supply chain metrics, and establish best practices for long-term success.
Why Hospital Supply Chains Fail Without EDI
Hospital supply chains represent a complex ecosystem where even minor inefficiencies can cascade into major operational problems. The Healthcare Supply Chain Association found that hospitals can save up to 17% – approximately $11 million annually for an average hospital – by improving supply chain management. However, achieving these savings becomes virtually impossible without Healthcare Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) systems.

1. Lack of Real-Time Data Exchange Between Systems
In most healthcare facilities, critical supply chain data remains trapped in disconnected IT systems that cannot communicate effectively with one another. This includes Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), Electronic Health Records (EHR), and Warehouse Management Systems (WMS). Consequently, healthcare procurement systems lack real-time visibility into inventory and logistics, leading to overstocking, stockouts, and difficulty responding to demand changes.
The persistent lack of real-time visibility causes frequent issues like stockouts, product expirations, temperature excursions, delayed shipments, and underutilized assets sitting idle. Furthermore, inadequate demand forecasting forces hospitals to tie up working capital in excessive on-hand stock buffers, creating a financial burden that compounds over time.
According to market research, IV therapy consumables alone account for over 25% of total medical consumables usage in U.S. hospitals. Without real-time data exchange capabilities provided by EDI, hospitals struggle to maintain appropriate inventory levels of these essential supplies.
2. Manual Processes Causing Delays and Errors
Many hospitals still track supplies manually, with approximately 45% of health systems only recently transitioning to cloud technologies for supply chain management. These paper-based clinical workflows and manual processes lead to significant inefficiencies:
- Manual data entry is prone to errors, leading to claim rejections, delays, and increased administrative costs
- When supply chain teams rely on manual processes, data capture depends largely on human intervention
- Staff must spend hours manually counting and recording stock levels, consuming valuable time and increasing error rates
The healthcare supply chain remains plagued by non-value-added manual tasks that burden already strained labor resources and increase costs, non-compliance, errors, and waste. This burden is particularly apparent in procurement, invoicing, payments, and inventory management – areas where EDI automation could provide immediate relief.
3. Disconnected Procurement and Inventory Systems
Perhaps most problematic is the disconnect between procurement and inventory systems. In busy facilities, there are many opportunities for inventory to be recorded incorrectly or go missing – from getting lost in transit from receiving docks to ordering departments, or transferring supplies between locations.
Due to complex supply chain networks where distributors, suppliers, and healthcare organizations must align on continuously changing product and price data, manual updates fall short because of constant data churn. This leads to pricing inaccuracies, rework, and significant time and labor allocated to resolutions throughout supply chains.
Additionally, working with fragmented supply spend information makes it difficult to see whether contracts are optimized for cost savings. Without integrated systems, hospitals struggle to strike the optimal balance between just-in-time inventory and service level requirements, often resulting in both stockouts and overstocks simultaneously.
By implementing EDI-enabled systems, hospitals can transform these disconnected processes into a seamless flow of information, ultimately improving patient care and operational efficiency while reducing the staggering costs associated with supply chain failures
Critical EDI Functions in Hospital Supply Chain Management
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) functions as the backbone of efficient hospital supply chain operations, enabling standardized electronic communication between healthcare facilities and their suppliers. By integrating EDI with supply chain management systems, hospitals optimize inventory control, reduce costs, and maintain EDI compliance with industry regulations.
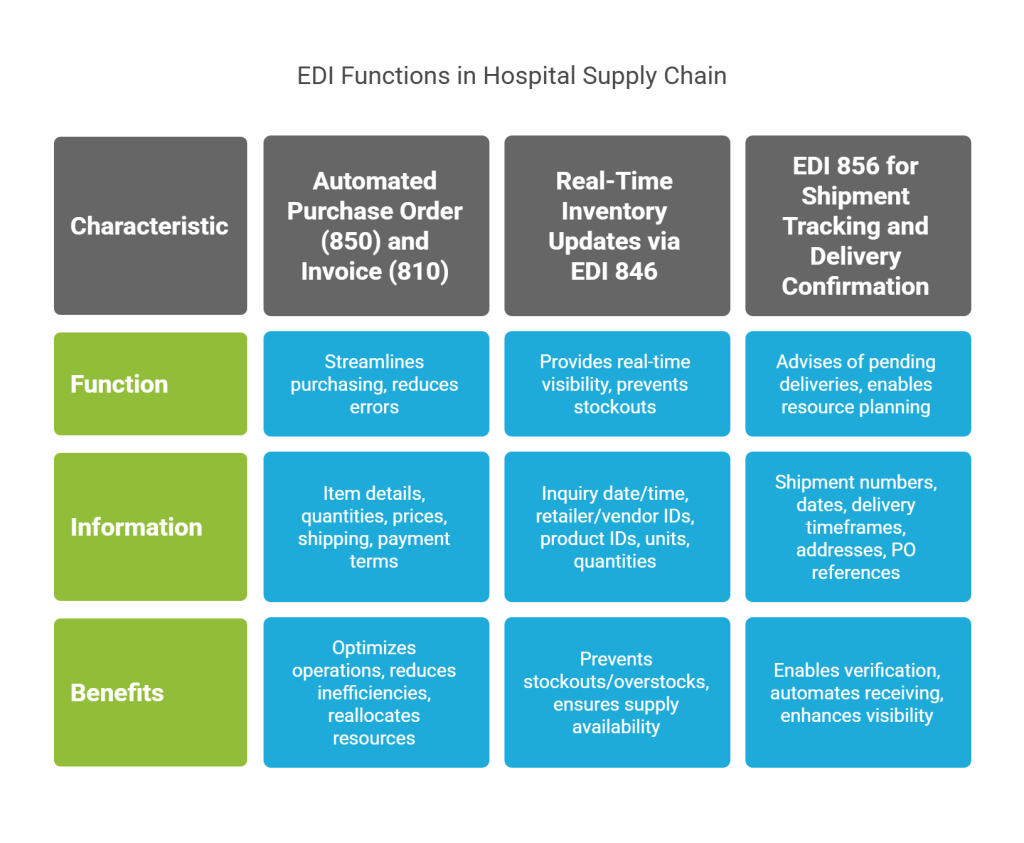
1. Automated Purchase Order (850) and Invoice (810) Processing
The EDI 850 Purchase Order transaction set serves as the critical first step in the ordering process, allowing hospitals to place standardized electronic orders for medical supplies and equipment. This electronic purchase order contains essential information, including item details, quantities, prices, shipping requirements, payment terms, and applicable discounts.
When paired with the EDI 810 Invoice transaction, these EDI documents create a closed-loop procurement system that eliminates paper-based inefficiencies. The EDI 810 electronically delivers detailed invoice information such as:
- Invoice number and date
- Product details, including item numbers and quantities
- Shipping specifications
- Payment terms, including rates and discounts
- Customer identification codes
This automation dramatically streamlines the purchasing process, enabling suppliers to optimize operations and hospitals to receive goods more quickly. Furthermore, medical supply EDI transactions reduce supply chain inefficiencies by minimizing procurement errors that can impact patient care. Through EDI integration, hospitals can reallocate resources previously dedicated to manual processing, sometimes equivalent to a full-time employee, toward more strategic activities like managing exceptions and backorders.
2. Real-Time Inventory Updates via EDI 846
The EDI 846 Inventory Inquiry/Advice transaction enables bidirectional communication about inventory levels between hospitals and suppliers. As a result, healthcare facilities maintain accurate, real-time visibility into product availability, preventing both stockouts and overstock situations.
This transaction is particularly valuable in healthcare settings where patient care depends on critical supplies being available precisely when needed. The EDI 846 provides essential inventory data, including inquiry date/time, retailer and vendor identification, product identifiers (SKUs/UPCs), units of measure, and current inventory quantities.
Notably, the EDI 846 offers hospitals additional critical information such as forecasted restocking dates for out-of-stock items, inventory reporting by location for suppliers with multiple warehouses, and indication of discontinued items. For healthcare facilities managing complex inventory requirements, these real-time updates ensure they can proactively reorder supplies and avoid dangerous stockouts.
3. EDI 856 for Shipment Tracking and Delivery Confirmation
The EDI 856 Advance Shipping Notice (ASN) represents one of the most important yet complicated EDI transactions in hospital supply chain management. Sent before a shipment arrives, this electronic document advises hospitals of pending deliveries, thereby enabling them to plan labor resources and receiving workflows accordingly.
A comprehensive ASN contains detailed information such as shipment numbers, shipping dates, expected delivery timeframes, ship-to/from addresses, purchase order references, item details, quantities, tracking information, packaging configurations, and GS1/UCC128 identification numbers.
For hospitals, EDI 856 implementation delivers substantial operational benefits. It enables receiving departments to verify incoming shipments against expected deliveries, automate receiving processes, and quickly move supplies to appropriate storage locations or point-of-use destinations. Most importantly, with enhanced visibility into order status within the EDI exchange dashboard, hospital purchasing teams can effectively track orders, identify problems like backorders or rejected orders, and intervene promptly to ensure clinicians receive the products they need when they need them.
Top 5 Data-Driven Solutions to Prevent EDI-Related Failures
Successful hospital supply chains depend on reliable data communication. Research shows that 88% of businesses using EDI also use ERP systems, making integration essential for operational efficiency. Let’s explore five proven solutions that can prevent the most common EDI-related failures in hospital supply chains.
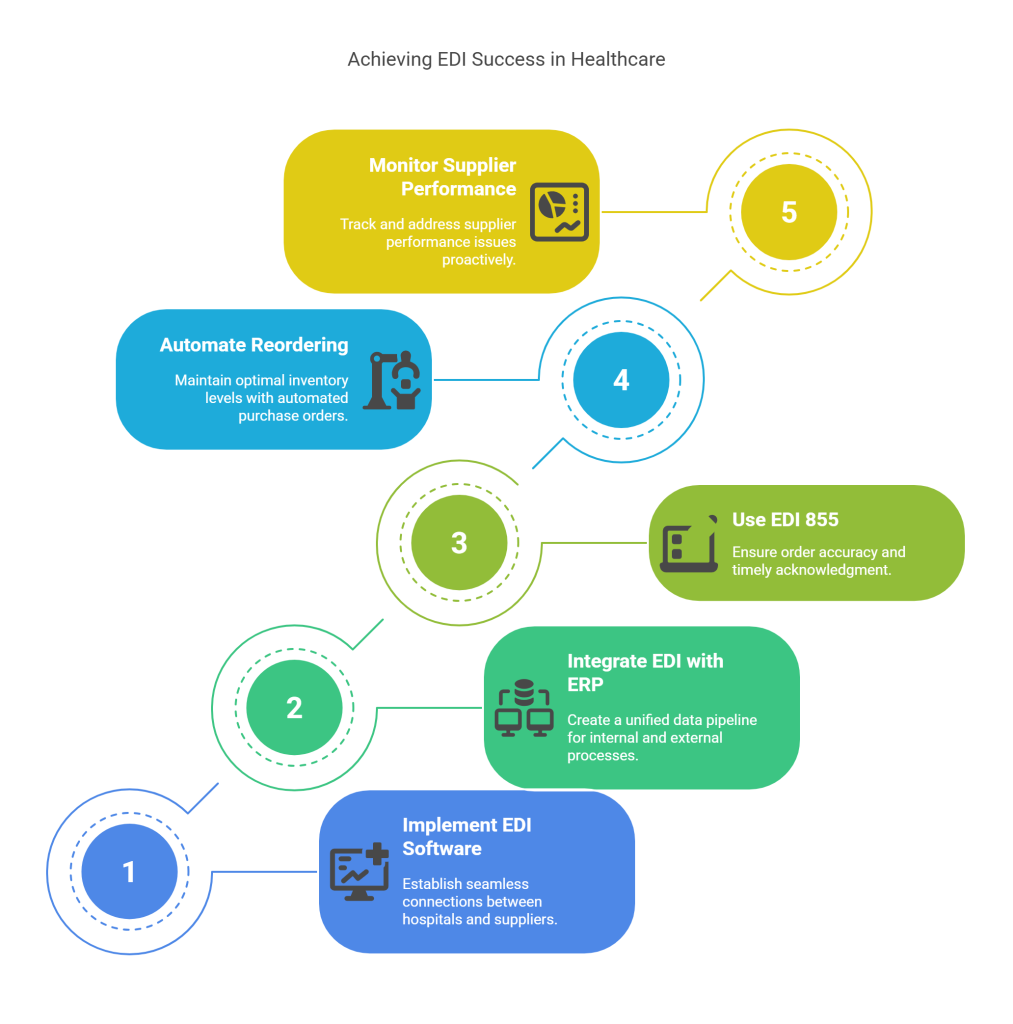
1. Implementing EDI-Enabled Hospital Supply Chain Software
Modern EDI-enabled software creates seamless connections between hospitals and suppliers, eliminating paper-based workflows that cause delays. These specialized systems allow healthcare facilities to transform manual processes across ordering, receiving, and accounts payable into streamlined digital workflows. Moreover, they provide real-time visibility into product availability and shipping status, ensuring clinical departments have the supplies they need when needed.
2. Integrating EDI with ERP and Inventory Systems
EDI and ERP systems are fundamentally data-centric applications that must communicate effectively. Their integration creates a pipeline between internal processes and partner-facing supply chain activities. When properly connected, these systems enable automated data flow that eliminates duplicate entries and accelerates transaction processing. By combining EDI’s front-end connectivity with ERP’s record-keeping capabilities, hospitals gain a single source of truth for all inventory and procurement data.
3. Using EDI 855 for Order Acknowledgment and Accuracy
The EDI 855 Purchase Order Acknowledgment serves as a critical confirmation mechanism between suppliers and hospitals. This transaction set confirms not just receipt but also the processing status of each order. It includes vital details such as accepted quantities, delivery information, and any discrepancies requiring attention, like price differences, out-of-stock items, or delivery date changes. Monitoring the pairing of EDI 850 (Purchase Order) with EDI 855 acknowledgments helps identify potential issues before they impact operations.
4. Automating Reordering with EDI-Triggered Thresholds
EDI enables hospitals to establish automated reordering processes based on predetermined inventory thresholds. When stock levels reach these preset minimums, the system automatically generates and sends EDI 850 purchase orders to suppliers without manual intervention. This capability ensures optimal inventory levels while reducing the workload on procurement staff. Furthermore, these automated systems can adjust reorder quantities based on historical usage patterns and seasonal demand fluctuations.
5. Monitoring Supplier Performance Using EDI Transaction Logs
Proactive monitoring of EDI transactions provides essential visibility into supplier performance. Through real-time dashboards and automated alerts, hospitals can track document flow, identify bottlenecks, and address potential issues before they disrupt operations. Performance metrics such as average acknowledgment response time help identify suppliers who consistently exceed threshold response times, allowing supply chain managers to intervene before delays impact patient care.
Ready to implement these solutions but unsure where to start? Switch to CommCARE, Commport’s Healthcare Supply Chain Solutions, trusted by over 700 healthcare providers to manage and optimize their supply chain. With advanced EDI capabilities designed specifically for healthcare environments, CommCARE helps hospitals eliminate the costly failures that plague 82% of hospital supply chains.
How EDI Enhances Healthcare Supply Chain Metrics
Measurable improvements in key performance indicators demonstrate the true value of EDI implementation in hospital supply chains. By examining specific metrics, healthcare facilities can quantify the return on investment from their EDI systems and identify areas for further optimization.
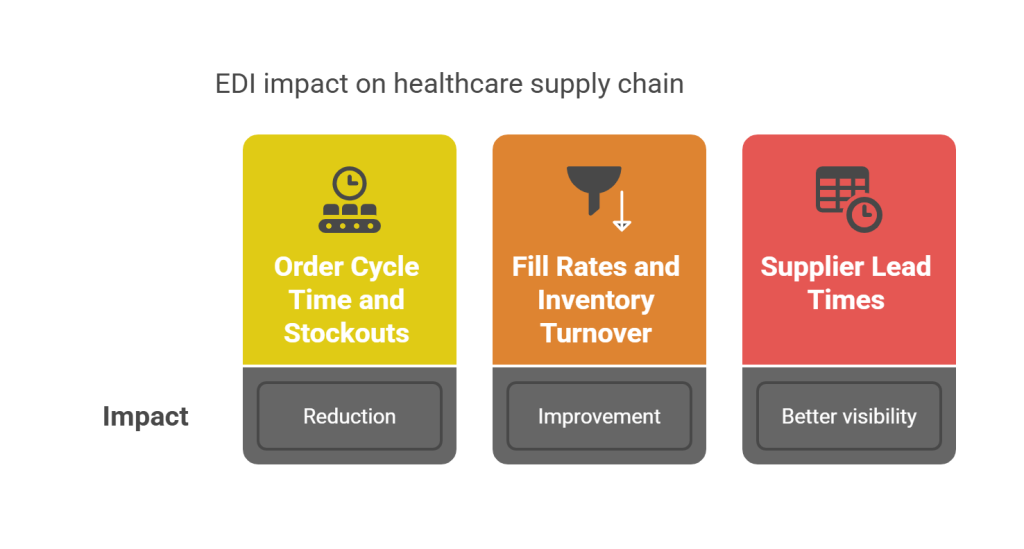
1. Reduction in Order Cycle Time and Stockouts
Hospitals implementing EDI for procurement report significant decreases in processing time—often by as much as 50%—while simultaneously improving accuracy to 99.97%. This dramatic improvement directly impacts the speed at which critical medical supplies move through the supply chain.
In essence, faster order processing translates to shorter lead times between order placement and delivery. Cleveland Clinic’s implementation of automated inventory management systems demonstrated these benefits clearly. First of all, when orders process electronically through EDI, hospitals avoid dangerous stockouts that could otherwise impact patient care.
For instance, EDI enables healthcare organizations to establish automated reordering systems that trigger purchase orders when inventory reaches predetermined thresholds. This proactive approach ensures essential supplies remain available without excessive manual monitoring, ultimately contributing to uninterrupted patient care.
2. Improved Fill Rates and Inventory Turnover
The implementation of EDI creates remarkable improvements in key inventory metrics. One rural hospital increased its EDI purchase order transmission to over 60% within eight months, resulting in:
- Higher fill rates despite reduced on-hand inventory
- Increased inventory turns while maintaining service levels
- Greater trust from clinical leadership in supply chain operations
Healthcare organizations using integrated demand planning approaches reduced inventory costs by 15-20% while maintaining or improving service levels. Even more impressive, Kaiser Permanente implemented segmented inventory strategies that reduced overall inventory value by 15% while increasing service levels for critical items.
3. Better Visibility Into Supplier Lead Times
EDI transactions provide real-time data exchange that enhances visibility throughout the hospital supply chain. Purchase order confirmations typically return within 15 minutes to 2 hours, providing immediate notifications about pricing discrepancies and backorder situations. This transparency allows supply chain managers to proactively address potential disruptions.
Healthcare supply chain teams benefit from complete visibility into product movement, from ordering through delivery. This visibility enables them to track performance metrics like order fulfillment cycle times, supplier performance scores, and recovery time after disruptions.
Overall, EDI enhances healthcare supply chain metrics by providing accurate, real-time data that supports informed decision-making. Supply chain leaders can track treatment outcomes, monitor patient health trends, and optimize resource allocation, fostering better patient care alongside operational efficiency.
Best Practices for EDI Implementation in Hospitals
Implementing an effective EDI system demands strategic planning and meticulous execution. Successful hospital supply chain management hinges on properly executed EDI integration that connects your facility to suppliers while ensuring seamless data flow throughout your operations.
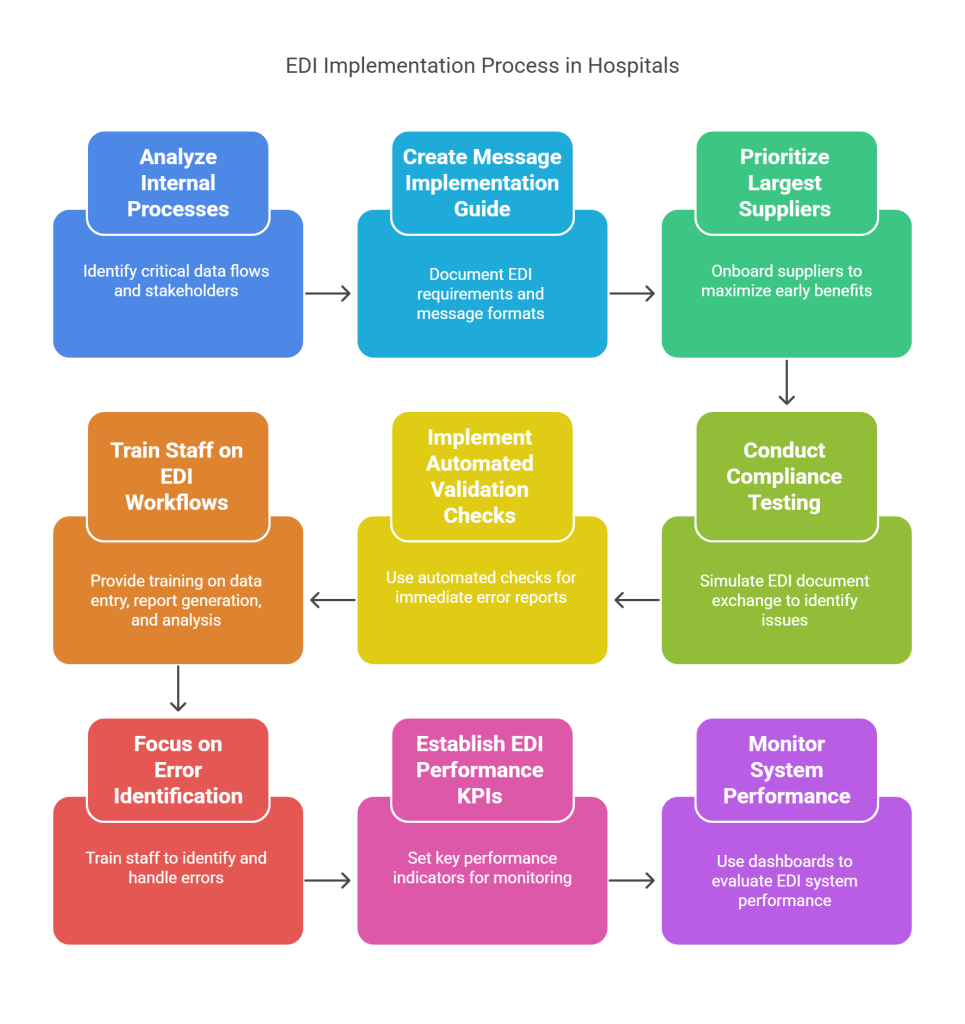
1. Vendor Onboarding and EDI Compliance Testing
Effective vendor onboarding begins with a thorough analysis of internal processes to identify critical data flows and stakeholders involved. Initially, healthcare facilities should create a comprehensive Message Implementation Guide (MIG) that details specific EDI requirements and message formats for trading partners. This documentation serves as a “how-to” guide for vendors connecting to your system. Subsequently, prioritize onboarding your largest suppliers first to maximize early benefits from your EDI implementation.
Thorough compliance testing involves simulating EDI document exchange between your hospital and suppliers to identify issues before implementation. Rather than relying on error-prone manual validation, implement automated validation checks that can immediately return error reports to document issuers. Comprehensive EDI testing verifies that transactions meet specified requirements, including conformance with healthcare standards.
2. Training Staff on EDI Workflows and Exception Handling
Comprehensive training empowers staff to effectively utilize EDI systems for maximum operational benefit. Provide training that covers data entry, report generation, and analysis to ensure users can leverage the system’s full capabilities. Training should extend beyond basic functionality to include specialized technical support for resolving issues that arise during daily operations.
Focus education on error identification and exception handling processes to minimize disruptions. Staff should understand how to manage by exception in real-time, detecting errors before shipment and ensuring the quality and format of all documents. This approach allows team members to concentrate on addressing discrepancies rather than processing routine transactions.
3. Establishing EDI Performance KPIs and Dashboards
Continuous monitoring through well-designed dashboards enables proper evaluation of EDI system performance. Key performance indicators should include:
- Response times for document exchange
- Error rates and resolution timeframes
- Integration effectiveness with other systems
Regular assessment helps identify improvement areas and ensures your EDI platform remains aligned with evolving healthcare sector needs. Through detailed reporting and comprehensive vendor scorecards, your team gains unprecedented visibility into supply chain operations.
Tired of disjointed EDI implementations? Switch to CommCARE, Commport’s Healthcare Supply Chain Solutions, trusted by over 700 healthcare providers to manage and optimize their supply chain. Their specialized expertise ensures your EDI integration delivers maximum operational efficiency while maintaining compliance with healthcare standards.
Conclusion
The evidence speaks for itself. Healthcare organizations implementing comprehensive EDI solutions achieve remarkable improvements across critical metrics – 50% faster order processing times, 99.97% accuracy rates, and 15-20% reduction in inventory costs while maintaining or improving service levels. Additionally, the potential annual savings of $11 million for an average hospital underscores the financial impact of streamlined supply chain operations.
EDI excellence transforms once-fragmented processes into a seamless, data-driven ecosystem. Purchase orders flow automatically based on predetermined inventory thresholds. Real-time updates eliminate dangerous stockouts of critical supplies. Shipment tracking provides unprecedented visibility into the movement of essential medical items.
Healthcare leaders must recognize that EDI implementation represents more than a technological upgrade – it fundamentally changes how hospitals manage resources that directly impact patient care. Consequently, following best practices for vendor onboarding, staff training, and performance monitoring becomes essential for long-term success.
The path forward requires healthcare organizations to embrace data-driven supply chain solutions. After all, the 82% failure rate among hospital supply chains without proper EDI implementation reveals a stark reality – yesterday’s manual methods cannot meet today’s healthcare demands.
CommCARE Health Solutions by Commport
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Aksed Questions
EDI enhances hospital supply chains by enabling real-time data exchange, automating purchase orders and invoices, and providing accurate inventory updates. This leads to faster order processing, reduced errors, and improved visibility across the supply chain, ultimately resulting in better inventory management and cost savings.
The primary challenges in healthcare supply chains include demand volatility, lack of transparency, complex regulations, and the need for cost efficiency. These issues can lead to critical supply shortages, increased operational costs, and potential impacts on patient care if not addressed properly.
Hospital supply chains often fail without EDI due to disconnected systems, manual processes causing delays and errors, and lack of real-time data exchange. These issues lead to inefficiencies, stockouts, overstocking, and difficulty in responding to demand changes, ultimately affecting patient care and operational costs.
Implementing EDI in hospital supply chains can lead to significant benefits, including reduced order cycle times, improved accuracy rates of up to 99.97%, decreased inventory costs by 15-20%, and better visibility into supplier lead times. These improvements contribute to more efficient operations and better patient care.
Successful EDI implementation in hospitals requires thorough vendor onboarding and compliance testing, comprehensive staff training on EDI workflows and exception handling, and establishing clear performance KPIs and dashboards. These practices help ensure smooth integration, effective use of the system, and continuous monitoring for optimal performance.