Introduction
Did you know that ineffective inventory management is costing businesses millions in lost sales and wasted resources? Indeed, in today’s complex supply chains, disconnected systems create a perfect storm of inconsistent data, synchronization delays, and costly errors.
When product information lives in separate silos, the problems multiply quickly. Consider this 67% of Amazon’s sales in 2021 came from third-party sellers, highlighting why accurate inventory management systems for e-commerce are no longer optional. Additionally, businesses struggling with disconnected GDSN and PIM systems face significant challenges with data inconsistency and delayed market updates.
We understand these challenges all too well. That’s why integrating your EDI, GDSN, and PIM into a unified inventory management system creates a powerful solution. By centralizing product data management, you eliminate duplicate entries, streamline collaboration with trading partners, and significantly improve operational efficiency.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through building a foolproof inventory management system that seamlessly connects these critical components. Whether you’re looking for the best inventory management software or trying to improve your existing inventory tracking, this step-by-step approach will help you create a system that scales with your business while maintaining data integrity across all channels.
Understanding the Core Systems
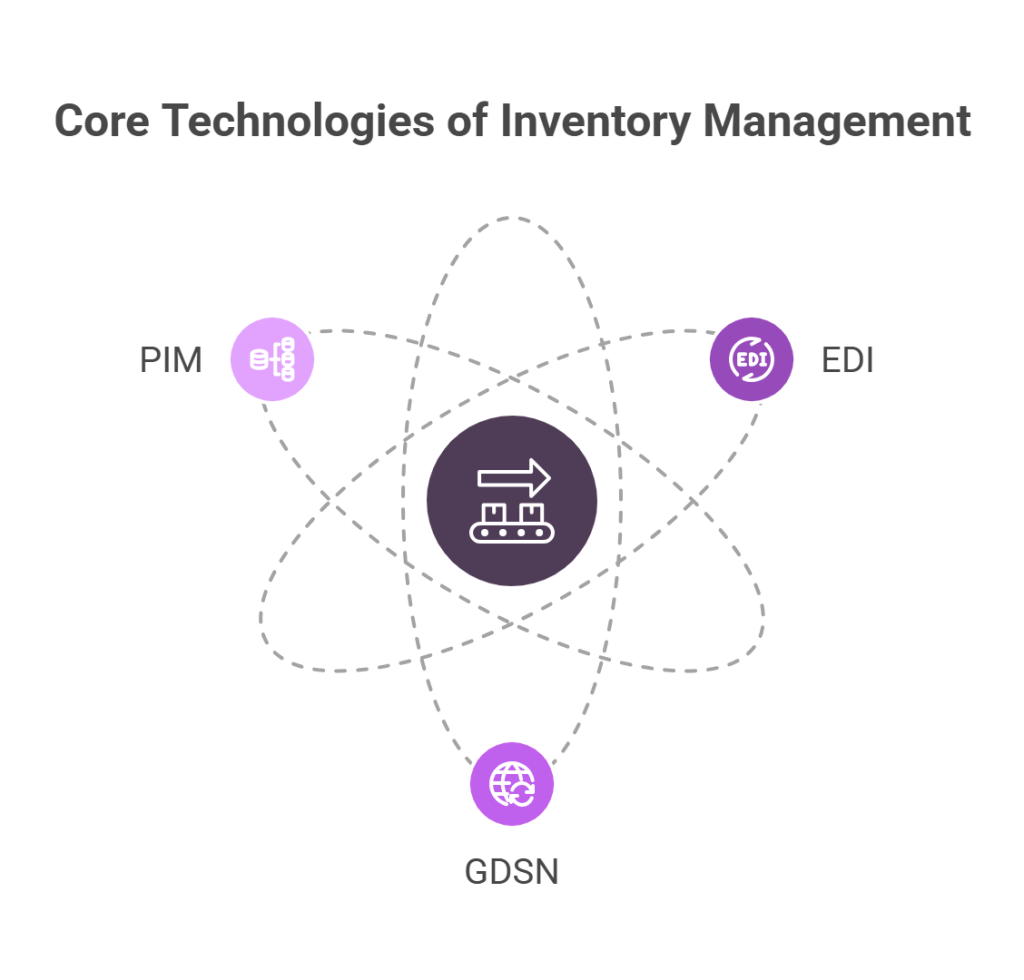
To build a foolproof inventory management system, we must first understand the three core technologies that form its foundation. These interconnected systems work together to create a seamless flow of accurate product information throughout your supply chain.
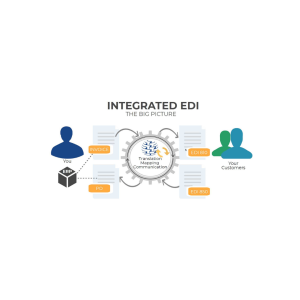
What is EDI and How Does it Support Inventory Data Exchange
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in standardized electronic formats between business partners. This technology eliminates manual data entry, automatically sharing information across platforms for real-time inventory updates.
EDI transforms inventory management by:
- Enabling instant tracking of inventory levels as products are sold online or in-store
- Automating data exchange between suppliers, warehouses, and sales channels
- Supporting better demand planning through accurate, up-to-date inventory data
- Enhancing supply chain visibility to prevent disruptions
The EDI 846 document (Inventory Inquiry/Advice) specifically supports inventory management by containing critical information like item identification numbers, quantities available, and product locations. Through this standardization, EDI reduces errors and delays while improving operational efficiency.
Overview of GDSN and Its Role in Global Product Data Sync
The Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) is an internet-based, interconnected network of interoperable data pools governed by GS1 standards. It serves as the backbone for global product data synchronization, ensuring trading partners worldwide can exchange standardized product information seamlessly.
GDSN operates through a publish-subscribe model between trading partners, with each accessing the network via certified data pools. According to reports, 81% of consumers are willing to switch to brands providing more detailed product information, highlighting GDSN’s importance in today’s market.
The network’s primary function is ensuring high-quality product content is automatically uploaded, maintained, and shared, giving trading partners immediate access to current and complete information. This real-time synchronization eliminates discrepancies in product data across global supply chains, making it particularly valuable for businesses operating internationally.
How PIM Centralizes Product Information
Product Information Management (PIM) systems act as the central source of truth for product data. They enable businesses to collect, manage, and enrich product information before distributing it across multiple sales and marketing channels.
PIM solutions integrate with most e-commerce platforms, CRM systems, and ERP software. This integration capability makes PIM particularly valuable for businesses with constantly changing product catalogs, sales strategies, and marketing messaging.
By centralizing product information, PIM systems:
- Streamline the management of accurate product data throughout multiple channels
- Eliminate redundant data entry, reducing errors and inconsistencies
- Enable product marketing teams to create more engaging content
- Empower sales teams with accurate, up-to-date product information
Furthermore, PIM systems process and de-duplicate shared data simultaneously, organizing product information into catalogs that can be linked to specific channels. This centralized approach helps teams quickly access needed information, increasing productivity by preventing data silos.
While both GDSN and PIM manage product data, they serve distinct purposes – GDSN focuses on global synchronization using standardized formats, whereas PIM emphasizes internal management and distribution across multiple platforms. Consequently, a truly effective inventory management system integrates all three technologies for optimal results.
Why Integration Matters for Inventory Management
Poor inventory management costs businesses nearly USD 2 trillion globally. This staggering figure highlights why companies must address the fundamental challenges that arise when critical systems operate in isolation rather than as an integrated whole.
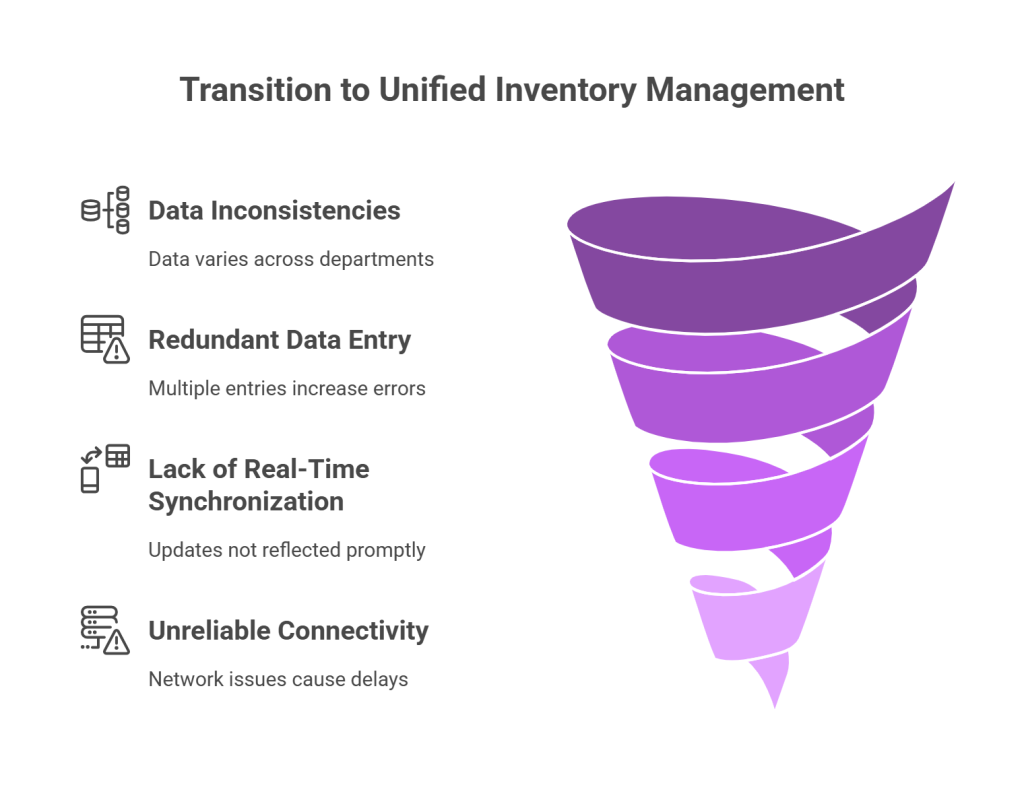
1. Challenges of disconnected systems
When inventory data lives in multiple platforms—warehouse software, sales channels, supplier portals—none synchronizing reliably or updating in real time, the consequences are severe. Fragmented inventory management creates several critical issues:
- Data inconsistencies across departments – When sales have one dataset and finance works with another, the disconnect leads to inefficiency and errors
- Redundant data entry – Maintaining separate data repositories forces businesses to enter the same product information multiple times, increasing error likelihood
- Lack of real-time synchronization – Updates in one system may not reflect in others promptly, causing teams to make decisions based on incomplete information
- Unreliable connectivity – Network problems create dead zones that necessitate re-work, leading to frustration, lost productivity, and reduced inventory accuracy
Manual inventory tracking across different software and spreadsheets is time-consuming, redundant, and error-prone. Moreover, when inventory is difficult to identify or locate in warehouses, it leads to incomplete, inaccurate, or delayed shipments.
2. Impact on Inventory Tracking
For retail and e-commerce operations, disconnected systems create unique challenges. Without real-time tracking, you simply cannot fulfill orders efficiently, plan replenishment accurately, or catch discrepancies before they snowball.
The lack of visibility is one of the most expensive inventory problems in retail and e-commerce. You might know what’s in your main warehouse, but what about returning in transit? Or inventory with third-party logistics partners? These blind spots create significant risks.
Nothing frustrates customers more than completing a purchase only to discover the product is unavailable or backordered. This directly impacts customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. The inability to provide accurate, real-time inventory information across sales channels is a common reason for cart abandonment.
Low-tech, manual inventory processes might work when the inventory is small and there’s only one warehouse. However, as sales volume increases and inventory expands, these inefficient procedures become impossible to scale. This scaling problem is especially acute for growing retail and e-commerce businesses managing multiple sales channels.
3. Benefits of Unified Data Flow
Integrating your inventory management systems creates a single source of truth for product data, eliminating the need for duplicate entry and maintenance. This centralization reduces errors and inconsistencies while providing a platform to manage, update, and distribute product information efficiently.
B2B integration automates repetitive tasks, enabling businesses to improve efficiency and productivity. By eliminating manual data, companies can focus on more value-added activities like strategic decision-making and customer service.
Real-time inventory tracking across all channels helps minimize stockouts and prevent overstocking. This directly impacts your bottom line by reducing storage costs and ensuring you have the right products available when customers want them.
Unified data systems also facilitate improved collaboration with trading partners. By synchronizing product data, businesses can share consistent and standardized information, reducing manual data exchange and improving communication efficiency.
With accurate insights into costs, profits, and other financial indicators, companies can make better decisions to increase profitability. This data-driven approach transforms inventory from a cost center to a strategic asset that drives business growth.
Step-by-Step: Building the Integrated System
Now that we understand the importance of integration, let’s explore the practical steps to build your unified inventory management system. By following this sequential approach, you’ll create a robust foundation that eliminates data silos and streamlines operations.
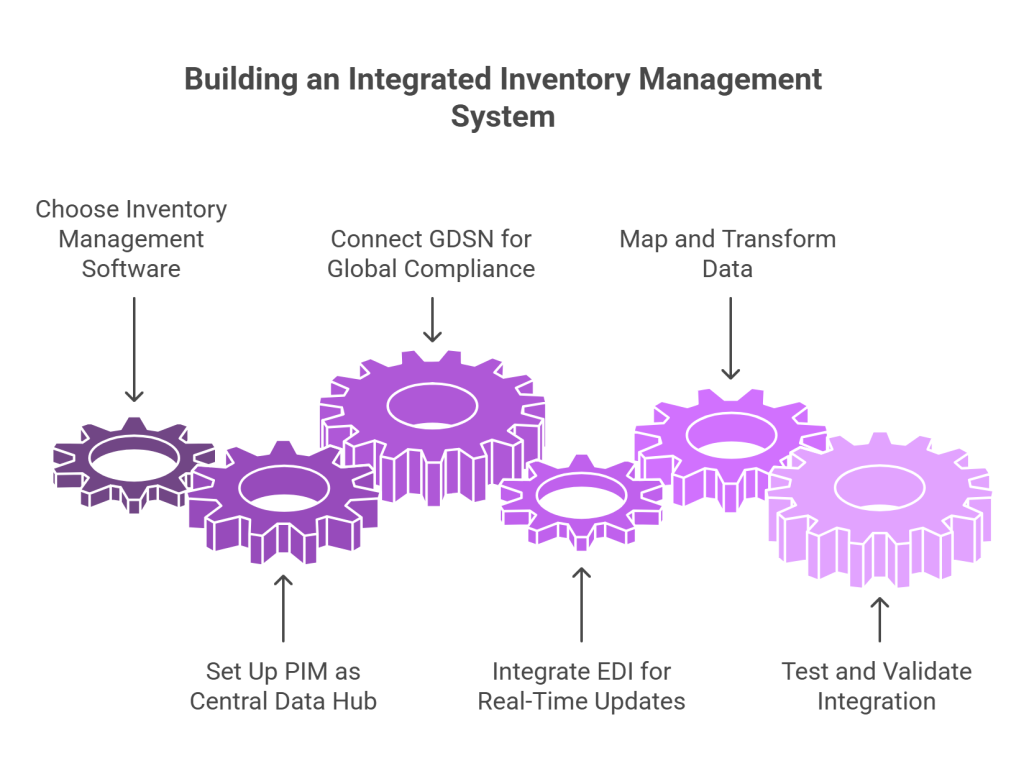
- Choose the right inventory management software
Start by selecting inventory management software that aligns with your business needs. The size and type of your company significantly influence your requirements. Small businesses often need simplicity and cost-effectiveness, while large enterprises require robust features like demand forecasting and multi-location tracking.
Consider these critical factors:
- Scalability to grow with your business
- Integration capabilities with existing systems
- User-friendly interface to minimize training time
- Strong security features and data backup
- Quality customer support and training resources
- Set up your PIM as the central data hub
Next, establish your Product Information Management (PIM) system as the foundation of your integrated solution. PIM serves as your centralized repository for all product information. Modern PIM solutions like Commport PIM enable businesses to consolidate product data from heterogeneous systems, creating a single source of truth.
During setup, configure your PIM to store both structured data (specifications, catalogs) and unstructured content (marketing collateral, images). Implement security controls to ensure appropriate access across departments.
- Connect GDSN for global data compliance
Once your PIM is operational, connect to the Global Data Synchronization Network through a certified GDSN data pool. This connection ensures your product information adheres to global standards and can be shared reliably with trading partners worldwide.
GDSN implementation might seem complex, yet the benefits are substantial. According to GS1 USA, businesses implementing GDSN reported a 25% reduction in data errors and a 30% increase in operational efficiency.
- Integrate EDI for real-time order and stock updates
Following GDSN implementation, integrate Electronic Data Interchange to facilitate automated business document exchange. EDI enables real-time inventory updates by automating data exchange between suppliers, warehouses, and sales channels.
Focus particularly on the EDI 846 (Inventory Inquiry/Advice) document, which contains crucial inventory information like item identification numbers, quantities, and locations. This standardization eliminates manual checks and dramatically reduces processing times.
- Map and transform data across systems
Subsequently, define mapping rules between your systems. Data mapping connects fields from one source to another, reducing potential errors and standardizing your information flow. Create comprehensive mapping documentation that identifies data sources, targets, and their relationships.
- Test and validate the integration
Finally, thoroughly test your integrated system before full deployment. Conduct end-to-end testing to verify that all components work together as intended. Test various scenarios, including order processing, inventory updates, and data synchronization across platforms.
Establish clear validation criteria and document any issues encountered. Only proceed to full implementation after confirming that your inventory management system performs reliably across all integrated components.
Optimizing Inventory Management and Scalability
After integrating the core systems, applying strategic optimizations unlocks the full potential of your inventory management solution. The difference between a functioning system and a truly exceptional one lies in how well it handles real-time updates, multichannel operations, and scalability.
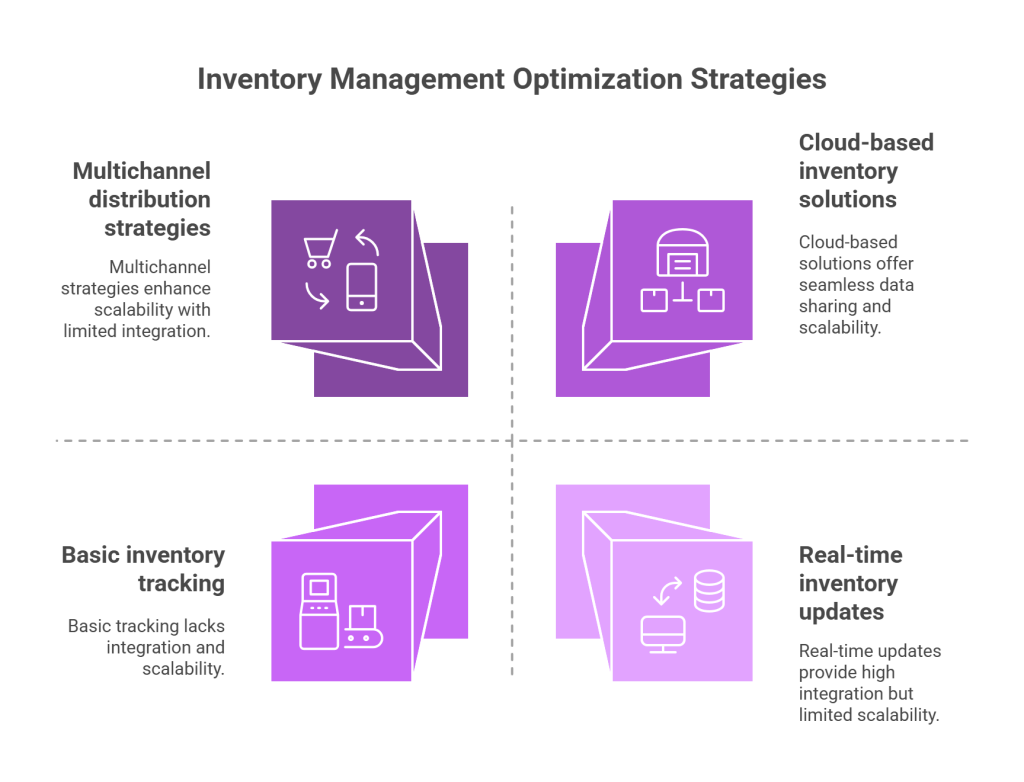
1. Ensuring Real-Time Inventory Updates
Real-time inventory tracking forms the backbone of effective operations. By implementing technology that enables on-demand tracking and management, you gain complete visibility across your supply chain. This level of control improves resilience, enabling you to respond to demand fluctuations and unexpected events without disruption.
Businesses using real-time inventory tracking report significant improvements:
- Up to 25% reduction in stock discrepancies
- 30% improvement in product availability after optimizing safety stock levels
- 15% reduction in inventory carrying costs through just-in-time inventory management
For optimal implementation, establish an inventory management system that connects with all sales channels and distribution centers, consolidating inventory data in one place. This creates a single source of truth for inventory levels, eliminating the confusion of multiple disconnected systems.
2. Handling Multichannel Distribution
Effective multichannel inventory management requires continuous synchronization across all sales platforms. Without real-time updates, you risk overselling, creating frustrated customers, and lost sales.
To optimize multichannel distribution, implement these strategies:
- Set inventory thresholds that automatically reserve inventory for priority channels once stock reaches specific levels
- Distribute inventory strategically across multiple fulfillment centers based on historical data and geographic demand patterns
- Establish consistent return policies across all channels with supporting tracking software
3. Scaling With Automation and Cloud-Based Solutions
Cloud-based inventory solutions offer unparalleled flexibility by hosting data on remote servers accessible through the internet. This creates seamless data sharing across multiple departments and locations, making it possible to manage inventory in a unified way regardless of geographic distribution.
Small and medium businesses using cloud inventory solutions report up to 30% cost savings compared to traditional systems. These savings stem primarily from decreased manual work, reduced errors, and lower IT infrastructure needs.
Key features to prioritize in scalable solutions include multi-location support, barcode/RFID integration, mobile access, real-time reporting, and robust integration capabilities. Furthermore, AI-powered analytics improve demand forecasting, helping prevent both overstocking and stockouts across various sales channels.
Best Practices for Long-Term Success
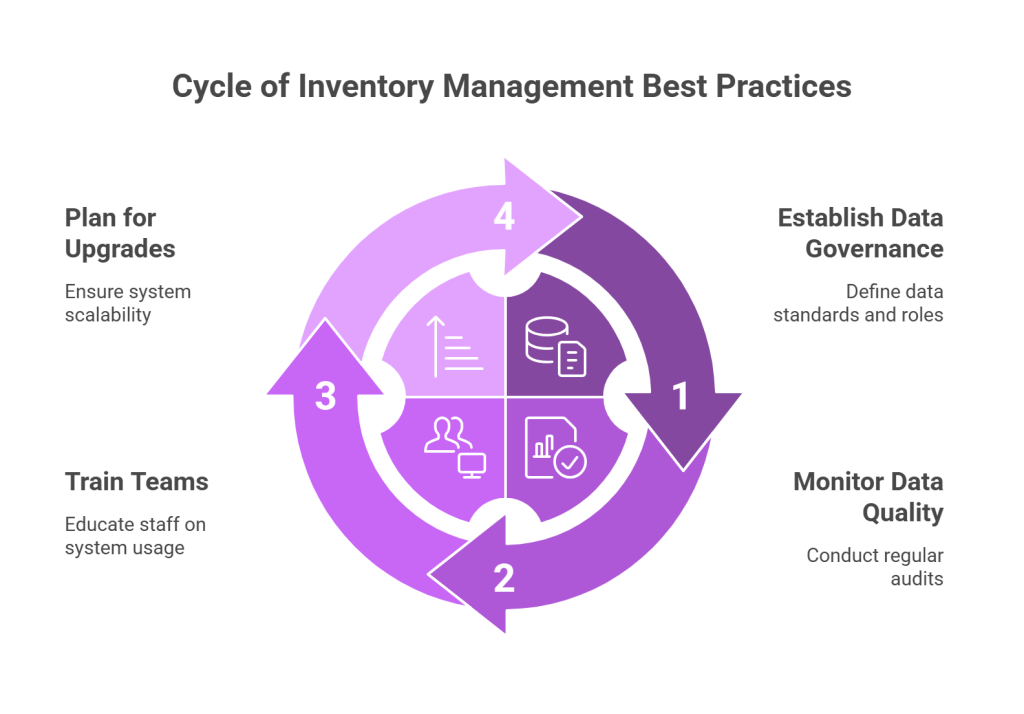
Maintaining your integrated inventory system requires as much attention as building it. Even the best inventory management software requires proper governance, monitoring, and ongoing development to deliver consistent value.
1. Establish Data Governance Policies
Creating robust data governance is the cornerstone of long-term inventory management success. Begin by defining clear data quality standards covering accuracy, completeness, consistency, and relevancy of product information. Then, establish policies that define specific roles and responsibilities for data management.
Effective governance frameworks should include:
- Documented procedures for data collection and categorization
- Clearly defined data ownership across departments
- Policies addressing data quality control, privacy, and compliance
Companies implementing strong data governance report significant improvements in decision-making regarding data optimization and compliance requirements. Regular collaboration between stakeholders and data scientists proves critical for maintaining comprehensive data inventories, with stakeholders providing insights into data importance while technical teams offer expertise in categorization.
Monitor Synchronization and Data Quality
Inaccurate or outdated data undermines real-time updates, creating discrepancies across systems. Therefore, schedule regular audits to identify and rectify quality issues, uncovering patterns in data errors that can guide improvements.
Pay particular attention to inventory reconciliation between your WMS and ERP systems, as out-of-balance inventory can cause numerous problems. Overstated inventory may lead to unfulfillable orders, while inaccurately reflected damaged inventory results in unnecessary vendor orders.
3. Train Teams On System Usage
Ineffective training remains one of the top reasons software implementations fail. Proper staff education minimizes human errors and ensures consistent, reliable data flow throughout your inventory management system.
Initial training should cover basic functionality; nonetheless, don’t stop there. Schedule periodic refresher sessions to reinforce key concepts and address emerging challenges. Likewise, encourage experienced users to mentor colleagues, fostering teamwork and ensuring knowledge sharing.
4. Plan for Future Upgrades and Flexibility
Your inventory management system must evolve alongside your business. Implementing a scalable solution allows your system to handle increased SKUs, seasonal demand changes, and expanding product lines without sacrificing accuracy.
Undeniably, the modern supply chain is too complex not to have a capable planning platform. Prioritize unifying information within a single robust platform so data can be used to its maximum potential. Before selecting vendors for upgrades, identify companies that align with your organization’s goals for sustainability and scalability.
Conclusion
Building a foolproof inventory management system requires thoughtful integration of EDI, GDSN, and PIM technologies. Disconnected systems cost businesses nearly $2 trillion globally, making integration not just beneficial but essential. After implementing an integrated inventory management system, you’ll notice immediate improvements in data consistency, real-time synchronization, and operational efficiency across all sales channels.
Most importantly, this integrated approach creates adaptability in your business operations. Cloud-based solutions offer the flexibility needed for scaling, while automation reduces manual workload and minimizes errors. Additionally, proper data governance ensures long-term success through maintained data quality and regular system monitoring.
Remember that successful implementation depends on choosing the right tools for your specific business needs. We recommend you explore Commport B2B Solutions for Inventory Management to discover how their specialized expertise can help implement the strategies discussed in this guide.
The perfect inventory management system isn’t built overnight, but with careful planning, proper integration, and ongoing optimization, you’ll create a solution that transforms inventory from a challenge into a competitive advantage.
Download: GDSN Buyers Guide
Empower your business with global data synchronization; download our GDSN Buyer's Guide today and take the first step towards streamlined, accurate, and compliant product data management.
Commport B2B Solutions
Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
An integrated inventory management system typically combines Electronic Data Interchange (EDI), Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN), and Product Information Management (PIM). These components work together to create a seamless flow of accurate product information throughout the supply chain.
Integrating these systems creates a single source of truth for product data, eliminating duplicate entries and inconsistencies. It enables real-time inventory tracking across all channels, minimizes stockouts, prevents overstocking, and facilitates improved collaboration with trading partners.
The process involves choosing the right inventory management software, setting up PIM as the central data hub, connecting to GDSN for global data compliance, integrating EDI for real-time updates, mapping data across systems, and thoroughly testing the integration before full deployment.
To optimize for e-commerce, businesses should ensure real-time inventory updates across all sales channels, implement strategies for efficient multichannel distribution, and utilize cloud-based tools and automation for scalability. This approach improves product availability and reduces carrying costs
Key best practices include establishing clear data governance policies, regularly monitoring synchronization and data quality, providing comprehensive training to team members on system usage, and planning for future upgrades to maintain flexibility as the business grows