Introduction
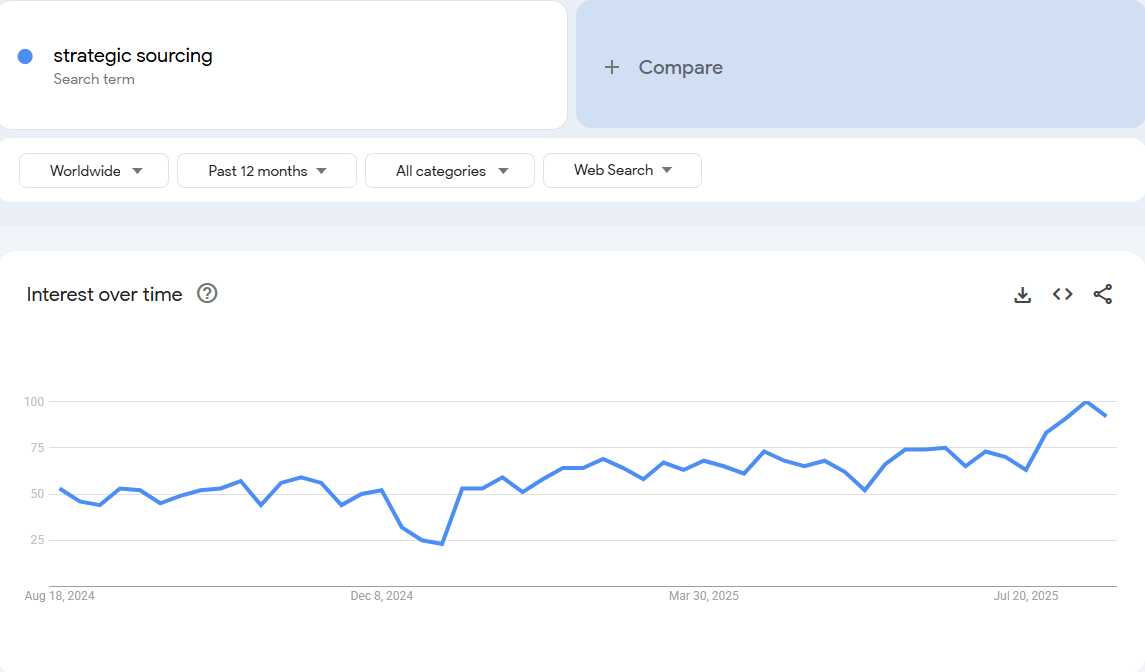
According to Google Trends data, searches for “strategic sourcing” have increased by 367% over the past year, as supply chain tariffs continue to create significant disruptions for businesses worldwide.
Major retailers are now expecting to react in real-time as tariff changes ripple through every link of their supply chain. With expected rates of 10-46% from major import sources, these supply chain tariffs are squeezing profit margins. As trade policies continue to evolve and tensions between major economies persist, businesses are finding themselves caught in a web of uncertainty that threatens their operational efficiency and profitability.
According to a 2025 PwC report, 25% of global companies faced tariff-related fines in 2024 due to inadequate customs processes. Meanwhile, 60% of U.S. companies experienced logistics cost increases of 10% to 15% due to tariffs in the past year. These statistics paint a clear picture of an environment where traditional, rigid supply chain models are no longer sufficient.
The solution lies in transforming your supply chain into an agile, responsive network that can adapt quickly to changing tariff landscapes while maintaining operational excellence. At the heart of this transformation is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) technology
EDI offers a powerful answer to this challenge. It enables fast, structured, and automated data exchange between trading partners, simplifying key transactions from order placement to invoice processing. Additionally, AI-powered cloud-based EDI solutions provide a scalable and intelligent way to remain agile despite unpredictable trade policies.
Key Takeaways
- EDI automation delivers measurable results: Companies report a 30% reduction in lead times, 40% faster customs processing, and a 20% decrease in compliance costs through automated data exchange.
- Real-time visibility enables rapid response: EDI’s computer-to-computer communication provides instant access to critical supply chain data, allowing businesses to pivot quickly when tariff policies change
- Streamlined supplier diversification reduces risk: EDI simplifies onboarding new suppliers and managing multiple partnerships, helping companies avoid over-reliance on single sources during trade disruptions.
- Automated compliance documentation prevents costly errors: Standardized EDI formats ensure accurate tariff documentation and regulatory compliance, eliminating manual processing mistakes that can delay shipments.
- Strategic EDI implementation requires planning but pays dividends: While initial setup involves training and system integration, the long-term benefits of reduced processing times and improved agility far outweigh implementation costs.
Understanding the Impact of Changing Tariffs on Supply Chains
The complex web of global trade is currently experiencing unprecedented disruption as tariff policies shift rapidly. According to recent data, 94% of organizations said securing market access to withstand disruptions will impact them, yet only 11% felt well-equipped to handle these challenges.

Tariffs are essentially taxes imposed on imported or exported goods. While they aim to protect domestic industries, their unpredictability can wreak havoc on global supply chains. Some of the most common impacts include:
- Increased Costs: Businesses may face higher import duties, which can significantly inflate the cost of raw materials or finished goods.
- Supplier Shifts: Companies may be forced to change suppliers or move production facilities to countries with more favorable trade agreements.
- Inventory Challenges: Organizations often stockpile goods to avoid tariff hikes, which can lead to excess inventory and cash flow issues.
- Regulatory Complexity: Complying with tariff rules requires extensive documentation and real-time monitoring.
For instance, during the U.S.-China trade war, tariffs on certain goods reached as high as 25%, forcing companies to rapidly adjust sourcing strategies. Without visibility and automation, many organizations struggled to keep up with these shifting requirements.
How Tariffs Affect Different Supply Chain Players
Tariffs create a ripple effect throughout the entire supply chain ecosystem:
- Manufacturers: Increased tariffs raise costs of imported goods, forcing businesses to either absorb costs or pass them on to consumers, both options leading to reduced profit margins.
- Distributors: Even companies purchasing domestically feel the impact as their suppliers are likely to import materials subject to tariffs, resulting in price increases or quality changes.
- Consumers: When companies pass tariff costs downstream, retail prices increase, potentially reducing demand and market share.
Furthermore, specific industries face disproportionate impacts. For instance, agribusinesses are particularly affected by retaliatory tariffs on products like soybeans and pork.
The Ripple Effect Across Industries
Electronics Industry: Major technology companies have been forced to accelerate supply chain diversification efforts. Apple, heavily reliant on Chinese manufacturing, plans to shift 15% to 20% of its production to India and Vietnam by 2026. However, this transition has created new challenges, including a 10% increase in lead times for some products due to supply chain bottlenecks in Vietnam.
Automotive Sector: The automotive industry faces particular challenges with tariffs on steel and aluminum. Cross-border logistics networks are strained, with cross-border trucking delays rising by 15% as companies attempt to source from alternative suppliers.
Retail Operations: Major retailers like Walmart have had to fundamentally restructure their sourcing strategies. The company reduced Chinese imports by 10% in 2024, shifting to suppliers in Southeast Asia and India. While this strategy helps mitigate tariff costs, it requires sophisticated coordination systems to manage the increased operational complexity.
Agriculture: U.S. agricultural exports have been severely impacted by retaliatory tariffs. U.S. soybean exports to China have dropped 25% since 2023, costing farmers approximately $2 billion annually. This has forced agribusinesses to seek alternative markets while investing heavily in domestic processing capabilities.
The Need for Agility in Today's Global Trade Environment
Agility in the supply chain refers to the ability to respond swiftly and effectively to changes in demand, regulations, or external disruptions. Unlike resilience, which focuses on withstanding shocks, agility emphasizes adaptability and speed.
Define Agile Supply Chains
An agile supply chain represents a fundamental departure from traditional linear models. Instead of rigid, predetermined processes, agile supply chains emphasize flexibility, responsiveness, and adaptability.
At its core, every agile strategy is designed to minimize vulnerability to external factors and reduce the likelihood of serious disruptions. Agile models are particularly well-suited for customized, niche, or trend-driven products like fast fashion or limited-edition electronics, where customer expectations can shift overnight.
An agile strategy is built upon four major components:
- Demand Forecasting: The ability to leverage real-time data to create accurate forecasts is crucial for an agile supply chain to meet demand effectively. This involves analyzing a wide range of variables, from seasonal trends to complex cash flow projections.
- Flexible Inventory Management: An agile approach often means holding strategic safety stocks to act as a buffer against abrupt shifts in demand or supply, such as labor shortages or material disruptions. This is in direct contrast to the lean principle of minimizing stockpiles.
- Digital Centralized Workflows: Agile principles rely on the frictionless communication and sharing of data between different nodes in the supply chain. Centralized digital platforms enable stakeholders to monitor and plan the transport of products and information, creating a single source of truth that can prevent minor problems from escalating into crises.
- Robust Supplier Management Strategy: This component entails building in “fail-safes” to the supply chain, most notably by embracing backup or redundancy suppliers. These contingency vendors are fully onboarded and treated as full participants, ready to take up the slack in a crisis without additional onboarding effort.
Feature | Lean Supply Chain | Agile Supply Chain |
Operational Focus | Efficiency, Cost Reduction | Flexibility, Responsiveness, and Speed |
Inventory Management | Minimal, Just-in-Time (JIT) production | Strategic Buffers, Flexible |
Production Approach | Standardization, High-Volume | Customization, Rapid Design Changes |
Customer Demand | Predictable, Stable | Volatile, Unpredictable |
Lead Times | Longer, Predictable | Shorter, Faster |
Cost Considerations | Minimizing costs is the primary driver | Higher operational costs are accepted for speed and adaptability |
Risk Management | Centralized and optimized for efficiency | Decentralized, built on redundancy and foresight |
The current trade landscape demands unprecedented flexibility. As pointed out by industry experts, “The pandemic taught us we need to allow flexibility in our supply chains, maybe at the cost of pennies”.
An agile supply chain enables companies to:
- Swiftly adjust procurement and transportation strategies
- Access real-time data for proactive decision-making
- Implement flexible inventory solutions to handle demand fluctuations
Nevertheless, achieving this agility requires both technological capabilities and strategic planning. Companies that adopted proactive approaches have shown greater resilience, with many diversifying supplier bases (63%) and increasing nearshoring efforts (57%).
What is EDI Technology and How Does it Work
EDI technology stands as the backbone of modern supply chain management, enabling businesses to respond rapidly to changing market conditions, including tariff fluctuations. This standardized system transforms how companies exchange critical business documents across borders and regulatory environments.

EDI’s value is magnified in the modern era of tariff volatility. For international trade, it provides a structured framework to automate complex customs and trade compliance processes. EDI allows for the electronic submission of essential customs declarations (CUSDEC), cargo reports (CARGO), and invoices (INVOIC) in a standardized, secure format. This automation is vital for navigating the constantly shifting landscape of tariffs, HTS codes, and trade compliance, reducing paperwork and processing times. Without EDI, the ripple effects of tariffs would become an insurmountable tsunami of manual data entry, errors, and invoice rejections. The case study of SMR, an automotive company, demonstrates this perfectly; by moving to an in-house EDI solution, they gained complete ownership of their processes, which resulted in an “increased agility” and “significant cost savings of more than 50%”. This shows that EDI is not a legacy system but a strategic asset that provides the fundamental plumbing for modern supply chain agility.
The benefits of EDI can be understood through a mathematical lens.
Benefits=i=1∑n(Automation+Accuracy+Visibility)
where n is the number of trading partners, Automation represents the benefits of automating data exchange, Accuracy represents the reduction of errors, and visibility represents the improvements in supply chain transparency. This formula illustrates how the benefits compound with each trading partner added to the network.
Definition and Basic Functions of EDI
EDI is the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in standardized electronic formats between trading partners. Unlike traditional methods involving paper, fax, or even email that require human intervention, EDI creates direct system-to-system communication. Essentially, EDI automates and streamlines critical processes, including inventory management, logistics, and communication with suppliers and customers.
The core function of EDI involves converting documents like purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notifications into structured, standardized data formats that computer systems can process automatically. This eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and accelerates transaction processing.
Key EDI Standards and Formats
Several established EDI standards govern document exchange across different regions and industries:
- ANSI X12: Predominantly used in North America, covering retail, manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics
- UN/EDIFACT: The international standard widely adopted across Europe and globally
- TRADACOMS: Originally used in UK retail sector
- EANCOM: A subset of EDIFACT developed for retail and product identification
These standards ensure consistency and compatibility, allowing different systems to interpret data correctly. Switch to Commport EDI Solutions Today. Companies have saved thousands of dollars by eliminating chargebacks from trading partners and achieving 100% EDI compliance with our EDI solutions.
Here’s how EDI supports agility amid changing tariffs:
- Speed of Communication: Instead of manual data entry, EDI transmits information instantly between partners.
- Error Reduction: Automated data exchange eliminates costly mistakes that often occur during tariff compliance checks.
- Regulatory Compliance: Customs documents and tariff codes can be automatically validated before submission.
- Integration with ERP & TMS: EDI works seamlessly with enterprise systems, ensuring tariff updates are reflected across procurement, finance, and logistics functions.
- Scalability: Whether trading with 10 partners or 1,000, EDI makes it easy to onboard and manage data exchanges quickly.
- Automated Product Classification: EDI systems can automatically classify products according to appropriate tariff codes, reducing the risk of misclassification errors that can result in penalties or delays.
- Real-Time Cost Calculation: By integrating tariff data with supply chain information, EDI systems can automatically calculate landed costs, enabling rapid assessment of sourcing alternatives when tariff conditions change.
- Documentation Automation: EDI automates the generation and transmission of customs documentation, ensuring compliance with evolving trade regulations while reducing administrative overhead.
- Audit Trail Management: Comprehensive tracking and documentation capabilities ensure that all tariff-related decisions and transactions are properly recorded for compliance purposes
For companies facing tariff uncertainty, this means fewer delays, faster decision-making, and a more cost-efficient operation.
How EDI Differs From Other Data Exchange Methods
Primarily, EDI differs from alternatives like APIs through its standardized formats and strict validation rules. While APIs offer real-time interactivity, EDI provides robust partner compliance and scalability for high-volume transactions. Moreover, EDI formats reduce errors through structured mapping and validation.
The Role of EDI in Modern Supply Chains
Throughout the supply chain, EDI enables real-time visibility that helps businesses react quickly to changing market demands—including tariff changes. For inventory management, EDI supports real-time stock updates, helping control inventory levels and plan for restocking. Additionally, in logistics, EDI automates shipment notifications and delivery confirmations, enabling effective tracking and improving transportation efficiency.
By implementing EDI, companies typically experience reduced lead times, improved decision-making, and significant cost savings—critical advantages when navigating unpredictable tariff environments.
Implementing EDI for Tariff Management
Implementing an EDI solution specifically for tariff management begins with careful planning and clear objectives. Initially, businesses should identify what tariff-related documents need automation and which trading partners require connections.

1. Setting up EDI for automated tariff documentation
To automate tariff documentation, configure your EDI system to handle customs forms, shipping notices, and invoices with tariff codes. A logistics provider implementing EDI reported a 40% reduction in processing times for customs documentation, enabling faster clearance and delivery of goods. Seamlessly connect with any trading partner and ERP systems. Book a free demo today.
2. Integrating EDI with existing systems
Successful EDI implementation requires integrating with existing enterprise resource planning (ERP) and transportation management systems (TMS). This integration ensures data flows automatically between internal systems and external trading partners, minimizing manual entry and reducing errors.
3. Training your team on EDI processes
Comprehensive training is vital for team adoption. Provide hands-on training sessions, user guides, and online resources to familiarize employees with EDI processes. Several organizations offer structured learning paths from foundational to advanced levels.
4. Common implementation challenges and solutions
Primary challenges include system compatibility issues, data quality concerns, and security considerations. Address these by choosing the right EDI solution compatible with your specific needs, implementing robust security measures including encryption, and ensuring data is clean and accurate.
5. Cost considerations for EDI adoption
EDI implementation costs vary based on whether you manage it in-house or use a third-party provider. Although initial setup requires investment in software, hardware, and potentially third-party consultants, many businesses recover these costs through enhanced efficiency.
Strategies for Supply Chain Agility Using EDI
EDI technology empowers businesses with four key strategies to maintain supply chain agility amid fluctuating tariff environments. These strategic approaches transform how companies respond to unpredictable trade policies.
1. Real-time data sharing for faster decision-making
EDI accelerates information flow throughout the supply chain, enabling instantaneous communication when tariff changes occur. This real-time visibility helps reduce lead times and improve inventory management. Companies leveraging EDI automation report 50-60% reductions in order-to-shipment cycles, allowing rapid response to market disruptions. Through standardized data exchange, businesses gain the insights needed to make informed decisions quickly regardless of changing trade conditions.
2. Diversifying suppliers with streamlined onboarding
A supplier enablement platform with EDI capabilities significantly simplifies the diversification process:
- Streamlines compliance and legal checks through centralized documentation
- Accelerates vendor onboarding, getting products to market faster
- Provides analytics on key performance indicators like on-time fulfillment
- Enables ongoing monitoring of supplier performance metrics
3. Automating compliance documentation
EDI standardizes and automates documentation, ensuring compliance with ever-changing tariff regulations. Proper EDI implementation validates data against trading partner requirements, simultaneously reducing errors while maintaining security through encryption. Regular monitoring ensures systems remain compliant as standards evolve.
4. Creating flexible routing options
Finally, EDI creates adaptable supply chains by standardizing interfaces between systems and partners. This interoperability simplifies implementing alternative sourcing strategies or modifying fulfillment processes. Many modern EDI solutions incorporate configurable business rules that automatically trigger contingency workflows based on predefined conditions, ensuring appropriate actions are initiated promptly when tariff disruptions occur.
Conclusion
Changing tariffs create significant challenges for supply chains worldwide, yet EDI technology offers a powerful solution to remain agile during these uncertain times. Throughout this article, we’ve seen how tariffs affect every link in the supply chain from manufacturers to consumers, causing price volatility and documentation complexity while straining supplier relationships.
EDI technology stands as a critical tool for businesses facing these challenges. Most importantly, this standardized system enables computer-to-computer exchange of business documents, eliminating manual processes and reducing errors that commonly occur during tariff-related documentation. Companies implementing EDI have experienced remarkable improvements – faster customs clearance, reduced processing times, and significant cost savings.
Setting up EDI specifically for tariff management requires careful planning and integration with existing systems. Therefore, proper training and addressing implementation challenges become essential steps toward success. While initial costs exist, the long-term benefits far outweigh these investments.
The strategic value of EDI becomes clear when examining its four key capabilities. First, real-time data sharing enables faster decision-making when tariff policies change. Second, streamlined supplier onboarding simplifies diversification efforts. Third, automated compliance documentation ensures adherence to evolving regulations. Finally, flexible routing options create adaptable supply chains that can quickly pivot when disruptions occur.
As supply chain tariffs continue to fluctuate, businesses must adapt or risk falling behind. EDI technology provides the foundation for this adaptation through standardized, automated data exchange. Companies embracing this technology will find themselves better positioned to navigate trade uncertainties, protect profit margins, and maintain competitive advantage despite unpredictable tariff environments.
Undoubtedly, the future of global trade demands agility. EDI delivers exactly that – transforming how businesses respond to tariff changes and creating resilient supply chains ready for whatever comes next.
Commport EDI Solutions
Need Help? Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
To increase supply chain agility, companies should focus on data independence, implement time-saving automation, utilize real-time insights for better customer service, improve internal and external communication, and seek tailored support services. These strategies help businesses adapt quickly to changing market conditions and tariff fluctuations.
EDI technology significantly enhances supply chain efficiency by automating document exchange, which drastically reduces transaction processing times from days to minutes. It also minimizes human errors in data entry, improving the accuracy of orders and invoices, leading to smoother operations and cost savings.
Tariff changes affect various supply chain players differently. Manufacturers face increased costs for imported goods, distributors may experience price hikes from suppliers, and consumers might see higher retail prices. These impacts can lead to reduced profit margins, strained supplier relationships, and potential shifts in market demand.
Companies can leverage EDI to manage tariff challenges by implementing real-time data sharing for faster decision-making, streamlining supplier diversification, automating compliance documentation, and creating flexible routing options. These strategies enable businesses to respond quickly to tariff changes and maintain supply chain agility.
While implementing EDI involves initial investments in software, hardware, and potentially third-party consultants, many businesses recover these costs through enhanced efficiency. Companies have reported significant benefits, including 30% reduction in lead times, 40% faster customs processing, and 20% decrease in compliance-related costs, demonstrating the potential for substantial returns on investment.