Introduction
Did you know that 50% of businesses spend more than 8 to 12 hours each week on invoicing and supplier payments? That’s at least 500 hours annually wasted on manual document processing when EDI tools could be handling this work automatically.
Additionally, 88% of companies admitted to losing orders, while 74% reported increased revenue losses due to integration issues, with some losing over a million dollars.
We understand these challenges because we’ve seen them firsthand. EDI purchase orders, advanced shipping notices, and EDI invoices create a seamless flow that eliminates these problems. For instance, an advanced shipping notice provides detailed information about incoming shipments, increasing supply chain visibility and allowing better planning.
In this article, we’ll break down how EDI tools work to simplify document exchange, explain the core components of EDI order processing, and show you how implementing these solutions can transform your business operations. Let’s explore how the right EDI integration tools can help you stop losing orders and start saving hundreds of hours each year.
The Problem with Manual Document Exchange
Manual document exchange remains a significant bottleneck for businesses across industries. Paper-based processes that once seemed adequate now create substantial challenges as transaction volumes grow and business relationships become more complex.
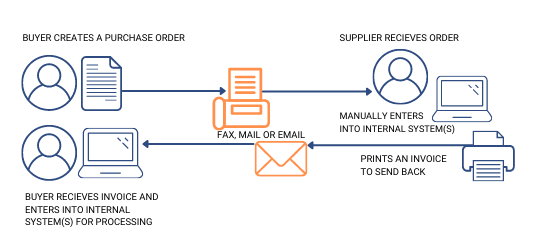
Delays and Errors in Traditional Processes
The inefficiency of manual document processing is staggering. Companies typically spend over five days a month on tasks like invoice processing alone. This time consumption extends across all document types, from purchase orders to shipping notices, creating delays that ripple throughout the supply chain.
Error rates present another major concern. Manual data entry errors range from 18% to 40% in general business scenarios. Even in specialized fields with higher accuracy standards, error rates still hover between 0.04% and 3.6%. These seemingly small percentages can have cascading effects:
- Misdirected documents failing to reach intended recipients
- Incorrect pricing or quantities on purchase orders
- Mismatched invoices create payment delays
- Shipping errors resulting from inaccurate documentation
Moreover, physical document management creates its own set of problems. Once a paper document is mailed out, it cannot be changed or tracked. Finding specific information in physical filing systems becomes time-consuming and inefficient, hampering productivity and delaying responses to customer inquiries.
Security and compliance risks also increase with manual document handling. Documents containing sensitive information can be misplaced, damaged, or accessed by unauthorized personnel. Furthermore, inconsistent filing systems make it difficult to track document versions, leading to confusion about which document represents the current state of an agreement.
Why Automation is Essential for Scaling
As businesses grow, document processing challenges multiply exponentially. Scaling operations means handling more customers, more extensive operations, and increasingly complex processes. Manual document exchange becomes unsustainable at scale for several critical reasons.
- The cost implications are substantial. The typical data entry employee earns approximately $35,000 per year in the United States. With dual entry for accuracy verification, costs double while still maintaining significant error risks. EDI tools eliminate these redundancies through automated verification.
- Time efficiency becomes crucial for competitive advantage. Manual document processing occupies over 40% of employee work hours. In contrast, EDI order processing can handle multiple documents within seconds rather than hours or days. This acceleration enables businesses to process higher volumes without proportional increases in workforce.
- Automation drastically improves accuracy. EDI purchase order systems can maintain consistent data structures across departments, eliminating the inconsistencies that plague manual systems. Automated document processing can achieve up to 99%+ accuracy with smart data validation, compared to the error-prone manual alternative.
- Customer satisfaction improves significantly with automation. In a recent survey, nearly 80% of employees reported that automation gave them more time to deepen relationships with customers and stakeholders. Rather than spending hours on data entry, staff can focus on resolving customer issues and building stronger business relationships.
- Importantly, the C-suite faces mounting pressure to deliver results amid inflation, supply chain disruptions, and market volatility. Implementing EDI invoicing and other EDI tools allows businesses to trim costs and boost efficiency, precisely what leadership teams need in challenging economic conditions.
Understanding the Key EDI Documents and Their Process
Electronic data interchange (EDI) forms the backbone of modern business transactions. Understanding the standard document types and their functions is essential before implementing any EDI tools in your business operations.
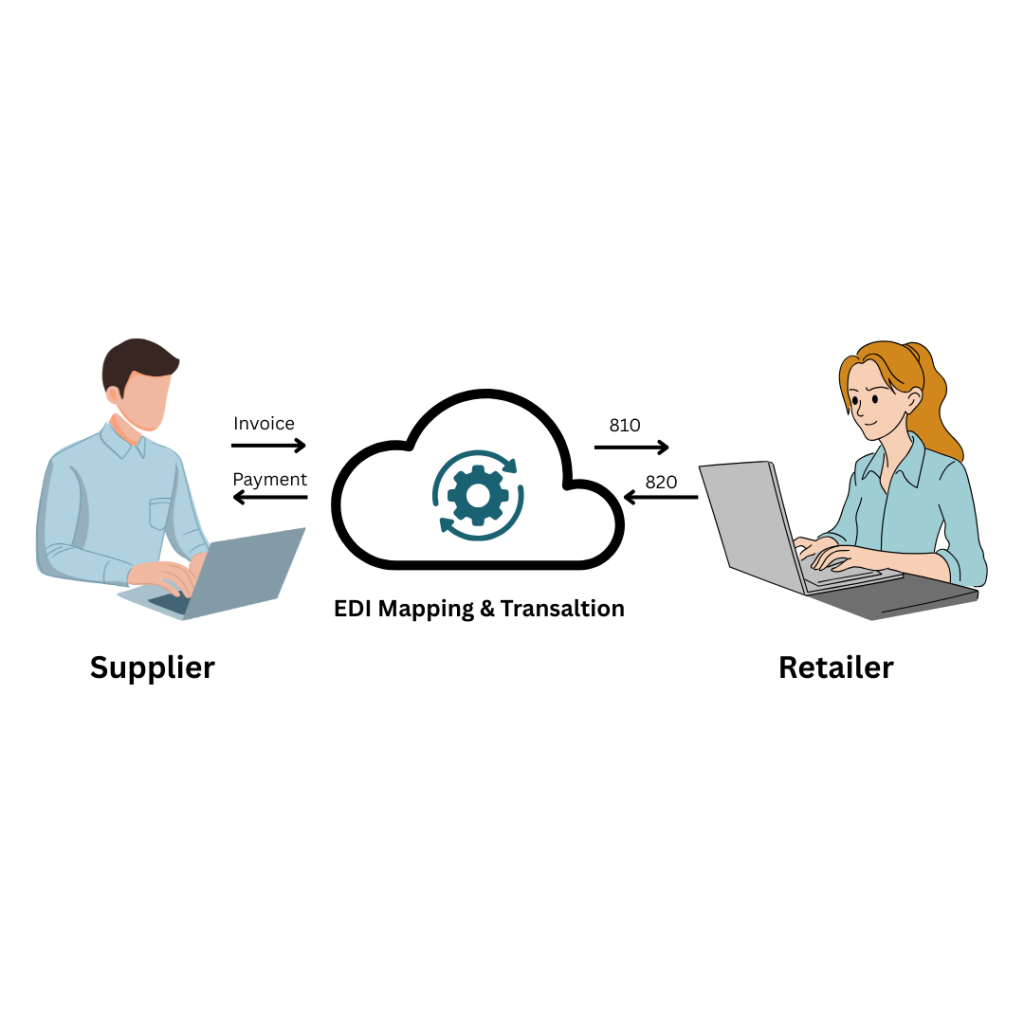

What is EDI Ordering and Invoicing?
EDI ordering and invoicing represent standardized electronic business documents that replace traditional paper-based transactions between trading partners. Each document in the EDI ecosystem is called a “transaction set” – a structured collection of data formatted according to specific standards such as ANSI X12 (North America) or EDIFACT (international).
Essentially, these transaction sets consist of three key components: data elements (individual pieces of information like company name or price), segments (logical groups of related data elements), and envelopes (wrappers that secure the transmission). This structured approach ensures that receiving computer systems can correctly interpret where to find specific information without manual intervention.
Unlike paper documents or emails that require human processing, EDI ordering and invoicing allow information to flow directly from one computer application to another. For instance, when an EDI translator receives a purchase order, it instantly recognizes order numbers, buyer information, item details, and pricing automatically.
Overview of EDI PO, ASN, and invoice flows
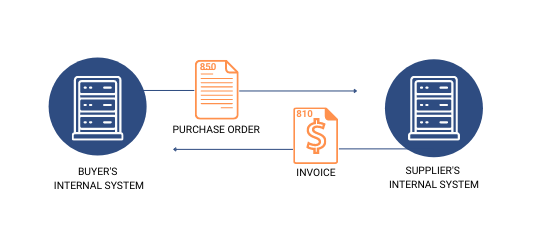
The typical EDI document flow begins with a purchase order (PO) and concludes with payment processing:
- The buyer initiates the process by sending an EDI 850 Purchase Order to the supplier, detailing products, quantities, pricing, and delivery requirements.
- The supplier responds with an EDI 855 Order Acknowledgement, confirming product availability and expected shipping dates.
- Before shipment, the supplier sends an EDI 856 Advanced Shipping Notice (ASN) containing carton-level details and tracking information.
- After shipping, the supplier submits an EDI 810 Invoice requesting payment.
- The buyer’s system automatically matches the invoice against the original PO and ASN for verification.
- Once approved, payment processing occurs, sometimes accompanied by an EDI 820 Remittance Advice.
This standardized flow eliminates manual data entry at each step, drastically reducing errors and accelerating the entire order-to-payment cycle. Additionally, this process enables Evaluated Receipt Settlement (ERS) – a streamlined “pay-on-receipt” approach that eliminates invoice processing entirely by generating payment based on the original PO upon goods receipt.
Understanding these core EDI documents and their relationships forms the foundation for implementing effective EDI tools that can transform your business document exchange processes.
Types of EDI Tools and What They Do
Successful electronic document exchange depends on having the right specialized tools for each task. EDI tools come in various forms, each designed to address specific aspects of the electronic data interchange process.
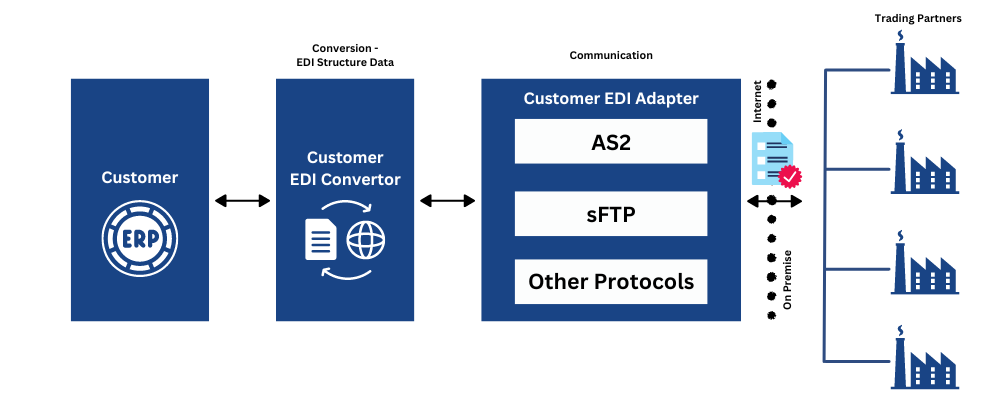
1. EDI Integration Tools
EDI integration tools connect EDI systems with internal business applications like ERP, customer relationship management, accounting software, and inventory management systems. These solutions handle two critical functions: facilitating external communication with trading partners and ensuring internal systems stay synchronized.
For external communication, these tools automate the exchange of standardized EDI documents across your supply chain. Whether sending purchase orders or receiving invoices, integration tools ensure documents are transmitted accurately in the correct format required by each partner. Internally, they ensure received EDI documents flow directly into backend systems, minimizing delays and reducing human errors.
Key features to look for include:
- Compatibility with multiple EDI standards (ASC X12, EDIFACT, TRADACOMS)
- Support for various communication protocols (HTTP, FTP, SFTP, AS2)
- Robust security features with data encryption and authentication
- Real-time data exchange capabilities
Switch to Commport Integrated EDI Solution, North America’s leading EDI provider. They offer comprehensive EDI services, including integration, mapping, translation, and testing—everything needed for seamless document exchange.
2. EDI Mapping Tools
EDI mapping is the process of transforming data from one format to another so recipients’ systems can process it correctly. This critical function enables communication between different systems speaking different “languages.”
“EDI mapping is essential for accurate electronic data exchange between businesses, translating documents like purchase orders and invoices into compatible formats,” explains a leading industry expert.
These specialized tools support both direct and indirect (canonical) mapping methods. Direct mapping creates a specific connection between two formats, while indirect mapping uses an intermediate data model—an abstraction layer—to simplify EDI integration. This two-step approach reduces complexity by avoiding custom 1:1 mappings for every partner.
Sample Any to Any Mapping Includes
- EDI to XML and Vice Versa
- EDI to JSON and Vice Versa
- EDI to Flat File and Vice Versa
- Flat file to flat file conversion (XML, CSV, JSON, iDOC, and Many More)
Other EDI Document Management Systems/Tools
- EDI Order Management System
- EDI Inventory Management System
- EDI Procurement Management System
- EDI Warehouse and Shipping Management System
- EDI Accounting Management System
EDI Order Management System
An EDI Order Management System automates the exchange of purchase orders, order acknowledgments, and shipping notices between trading partners. It streamlines the entire order lifecycle, reduces manual data entry, eliminates errors, and speeds up order processing—ensuring timely fulfillment and improved customer satisfaction.
EDI Inventory Management System
The EDI Inventory Management System enables real-time communication of inventory levels, stock status, and demand forecasts between suppliers and buyers. By automating inventory updates and alerts, businesses can optimize stock levels, prevent overstocking or stockouts, and enhance supply chain efficiency.
EDI Procurement Management System
An EDI Procurement Management System facilitates the seamless exchange of procurement-related documents such as RFQs, purchase orders, and invoices. This system helps organizations manage vendor relationships, improve sourcing accuracy, reduce procurement cycle times, and achieve cost savings through process automation.
EDI Warehouse and Shipping Management System
This system integrates EDI with warehouse operations and shipping processes to automate tasks like pick-and-pack instructions, shipping notices, and freight details. It enhances warehouse efficiency, ensures accurate shipment tracking, and supports timely deliveries with minimal manual intervention.
EDI Accounting Management System
An EDI Accounting Management System automates the exchange of financial documents such as invoices, remittance advices, and payment confirmations. It improves the accuracy and speed of financial transactions, supports compliance, and enhances visibility into accounts receivable and payable.
How to Implement EDI Tools in Your Workflow
Implementing EDI tools requires a methodical approach to ensure seamless document exchange between trading partners. Following a structured implementation plan helps minimize disruptions while maximizing the benefits of automation.
Step 1: Data Collection and Preparation
The foundation of successful EDI implementation begins with a thorough assessment and data preparation:
- Analyze current business processes to identify opportunities for automating manual processes and replacing traditional document handling methods. Look specifically for redundant data entry points and error-prone manual steps.
- Develop an organizational structure that includes an EDI coordinator, steering committee, senior management sponsor, and dedicated EDI team. This structure ensures proper oversight and accountability throughout implementation.
- Conduct a strategic review to determine which business cycles will benefit most from EDI automation. Evaluate which areas are most ready for EDI, which will cost least to implement, and which will deliver the greatest savings.
- Assess your trading partners’ EDI capabilities through an EDI survey. This helps ensure that your chosen EDI system will be supported across your business partner network.
Step 2: Data Translation and Mapping
After collecting and preparing your data, the next critical phase involves establishing translation rules:
- Analyze data structure of incoming and outgoing files to understand both your internal formats and your trading partners’ requirements.
- Create mapping specifications that define how each data element in your source format corresponds to elements in the target format, including data types, lengths, and any necessary transformations.
- Select appropriate mapping methods – either direct mapping (1:1 translation) or canonical/indirect mapping (using an abstraction layer). Indirect mapping simplifies maintenance when dealing with numerous trading partners.
Step 3: Document Transmission and Tracking
The final implementation phase ensures documents flow correctly between systems:
- Choose a communications model based on your business needs: direct connections with partners, EDI network services, a hybrid approach, or outsourcing to a managed EDI services provider.
- Test the system thoroughly before full deployment by simulating real-life business transactions. This identifies discrepancies in document type or data format that could cause implementation issues.
- Monitor EDI acknowledgments (EDI 997) within specified timeframes after sending each transaction to verify successful delivery and processing.
Switch to Commport EDI Solutions, North America’s leading EDI provider. They offer both integrated and cloud-based EDI solutions with comprehensive EDI services, including EDI integration, mapping, translation, and testing – everything needed for successful EDI implementation.
Measuring the Impact of EDI Tools on Your Business
After implementing EDI tools, measuring their impact becomes essential for validating your investment and identifying further optimization opportunities. The right metrics reveal how these digital solutions transform your business operations.
Tracking Order Accuracy and Speed
Implementing EDI order processing dramatically improves accuracy by eliminating human errors associated with manual data entry. Companies typically see error rates drop significantly, as EDI minimizes the risks of transcription mistakes or missing information. One major benefit is faster delivery to customers—some estimates indicate EDI can result in 30% faster delivery time.
The precision gained through EDI purchase orders creates cascading benefits throughout your supply chain. Automated validation processes ensure data integrity, consequently improving inventory management accuracy. Real-time data exchange enables better visibility into order status, allowing for proactive issue resolution instead of reactive problem-solving.
Reducing Invoice Processing Time
The financial impact of EDI invoicing is substantial. Traditional invoice processing costs approximately $21.00 per invoice when handled manually. This breaks down to roughly $10.00 for scanning and indexing, $8.00 for approval routing, and $3.00 for accounting system entry.
Conversely, implementing EDI tools can reduce processing costs to approximately $1.00 per invoice or less. This represents an astounding 85% cost reduction. Furthermore, the time savings are equally impressive—EDI processing can save up to 61% of the time needed for manual order processing.
Improving Supplier and Customer Relationships
Perhaps the most valuable yet difficult-to-quantify benefit comes from strengthened business relationships. EDI tools provide unprecedented visibility into transaction status—from submission through payment—enabling both buyers and suppliers to track processes in real time.
This transparency eliminates the need for constant communication about order status or payment timing. Indeed, businesses report that automation gives employees more time to deepen relationships with customers and stakeholders. Rather than spending hours on data entry, your team can focus on strategic supplier management and customer service improvements.
The consistency and reliability that EDI tools bring to business transactions build trust between trading partners, laying the foundation for long-term collaborative relationships that drive mutual growth.
Conclusion
Implementing EDI tools represents a transformative step for businesses struggling with manual document processing challenges. Throughout this article, we’ve seen how automated document exchange eliminates the costly inefficiencies of traditional methods. Undoubtedly, the 500+ hours annually wasted on manual processing can be reclaimed through proper EDI implementation.
EDI purchase orders, advanced shipping notices, and invoices work together to create a seamless document flow that drastically reduces errors. Additionally, the right EDI tools cut invoice processing costs by up to 85% – from $21 per invoice down to approximately $1. This cost reduction alone justifies the investment for most organizations.
The benefits extend far beyond mere cost savings, however. Faster order processing, improved accuracy, and enhanced visibility across your supply chain create a competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced business environment. Consequently, your team spends less time on data entry and more time strengthening customer and supplier relationships.
Switch to Commport EDI Solutions if you’re looking for comprehensive EDI services, including integration, mapping, translation, and EDI testing. Their expertise ensures a smooth transition from manual to automated document processing.
Remember, successful EDI implementation follows a clear roadmap: thorough data preparation, careful mapping, and reliable transmission protocols. Following these steps ensures your business captures all the efficiency benefits while minimizing disruption during the transition period.
The digital transformation of document exchange isn’t just about technology adoption—it fundamentally changes how businesses operate. Therefore, measuring the impact through concrete metrics like processing speed, error reduction, and cost savings becomes essential for validating your investment.
EDI tools have evolved from nice-to-have technology to essential business infrastructure. Companies still relying on manual document exchange face significant competitive disadvantages in speed, accuracy, and cost-efficiency. The question isn’t whether your business should implement EDI tools, but rather how quickly you can deploy them to start realizing these substantial benefits.
Commport EDI Solutions
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
EDI tools are software solutions that automate the exchange of business documents between trading partners. They simplify document processing, reduce errors, cut costs, and speed up transactions, ultimately improving efficiency and accuracy in business operations.
Businesses can save over 500 hours annually on manual document processing by using EDI tools. Additionally, EDI can reduce invoice processing costs from $21 per invoice to approximately $1, representing an 85% cost reduction.
The main EDI documents include the 850 (Purchase Order), 855 (Purchase Order Acknowledgement), 810 (Invoice), 856 (Advance Shipping Notice), 820 (Payment Order/Remittance Advice), and 997 (Functional Acknowledgment).
EDI significantly reduces human errors associated with manual data entry, leading to improved order accuracy. It also enables faster processing and real-time data exchange, which can result in up to 30% faster delivery times to customers.
Implementing EDI tools involves three main steps: 1) Data collection and preparation, including analyzing current processes and assessing trading partners’ capabilities; 2) Data translation and mapping, which involves creating mapping specifications for different data formats; and 3) Document transmission and tracking, including choosing a communications model and thorough system testing.