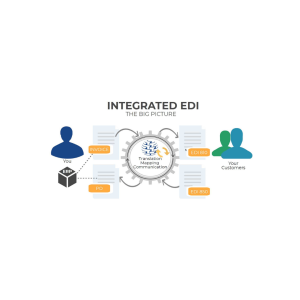
Introduction
Define EDI Compliance
EDI compliance refers to a business’s capacity to accurately send and receive EDI transactions according to the requirements of its EDI trading partners. Each document must adhere to a specific EDI format to ensure the successful exchange of EDI documents.
Key Takeaways
- EDI compliance means adhering to trading partner requirements when exchanging electronic transactions. Major retailers mandate EDI trading, making compliance essential for maintaining partnerships and protecting revenue streams.
- Non-compliance results in chargebacks—financial penalties ranging from hundreds to thousands of dollars per violation. These avoidable costs are imposed when vendors fail to meet specific requirements like accurate shipping notices or timely delivery.
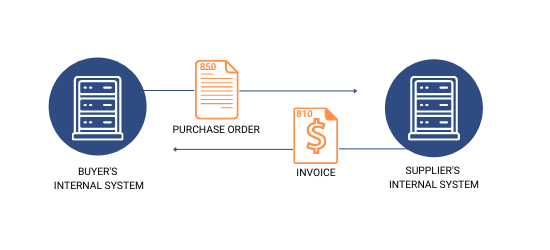
- Most retailers require six essential EDI documents: EDI 810 (Invoice), EDI 850 (Purchase Order), EDI 856 (Ship Notice/Manifest), EDI 855 (Purchase Order Acknowledgement), EDI 846 (Inventory Status), and EDI 860 (P/O Change).
- Key EDI standards include ANSI X12 (North America), EDIFACT (international), and TRADACOMS (UK retail). Following these standards ensures effective communication across different regions and industries.
- Becoming EDI compliant involves identifying trading partner requirements, selecting an appropriate solution, implementing and testing the system, training your team, and establishing ongoing monitoring protocols.
Why Do Businesses Need to be EDI Compliant?
Today, you would be hard-pressed to find a major retailer that does not make EDI trading a requirement to do business with them. The importance of becoming and maintaining EDI compliance can not be understated, especially given how much it benefits your bottom line.
Being EDI capable means your business can use EDI to transmit your basic business documents, like Purchase Orders and Invoices, to your trading partners.
EDI implementation issues can be costly and time-consuming. The cost of being non-compliant comes in the form of EDI chargebacks.
What are EDI Chargebacks?
EDI Chargebacks (also known as ‘Expense Offsets’) are financial penalties for non-compliance with your customer’s requirements. Customers issue EDI chargebacks because vendor non-compliance disrupts operations and creates an additional expense for the customer.
Every customer-supplier relationship agreement is different, EDI chargebacks can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars per violation, which can add up very quickly, causing huge and avoidable loss of revenue on an annual basis. If you’re late or miss a delivery, packages are labeled wrong, or a shipment is damaged or incomplete, expect to receive an EDI chargeback.
Most Common EDI Chargebacks
The EDI 856 Advance Shipping Notice is one of the most common EDI documents to receive a chargeback. Most major retailers consider the EDI 856 a crucial component of EDI compliance. The EDI 856 is used to communicate the tracking and packing information of a shipment.
Furthermore, to the ASN errors, such as incorrect barcodes or shipping labels, other common reasons that a customer may charge their vendor include:
- Missing or late delivery
- Invoice errors, such as sending duplicates or incorrect invoice totals
- Delivery to the wrong location
- Using the wrong shipping carrier
- Failure to meet proper packing specifications
EDI Compliance Requirements
Many companies have requirements for EDI trading partner setup and maintenance, both of which are important in keeping compliant. These requirements include, but are not limited to, the ability to exchange the basic EDI document set, a timeline for testing, and specific connection requirements.
Here is a list of a couple of basic EDI documents that most retailers will require to be compliant:
Key Regulations and Standards in EDI Compliance
Several key regulations and standards govern EDI compliance, depending on the industry and geographic location. Understanding these is crucial for businesses aiming to achieve and maintain compliance. Common standards include ANSI X12, EDIFACT, and TRADACOMS, each serving different industries and regions.
ANSI X12: Predominantly used in North America, this standard is widely adopted across various sectors, including retail, healthcare, and transportation. It defines the format for electronic documents, ensuring consistent data exchange.
EDIFACT: Used internationally, especially in Europe, EDIFACT is a standardized language for EDI that facilitates global trade. Its universal approach allows companies to engage with international partners without compatibility issues.
TRADACOMS: Primarily used in the UK retail sector, TRADACOMS is an older standard but remains relevant for certain industries and trading communities.
Compliance with these EDI standards ensures that businesses can communicate effectively with partners across different regions and sectors. Furthermore, industries such as healthcare may have additional regulations that mandate specific data privacy and security measures.
How to Become EDI Compliant
There are a few important steps in the process to becoming EDI compliant.
View our Getting Started With EDI
A 5-Step Process
1. Identify Requirements
You first need to understand the requirements of your specific trading partner. Most trading partners will have resources on their websites that detail the full set of requirements and expectations
.
2. Select an EDI Solution
There are 3 main types of EDI solutions:
Internet EDI/ Web EDI – EDI web forms (such as Commport’s Internet EDI) – these solutions are hosted on the internet and are ideal for users who have a low volume of transactions or trading partners.
Integrated EDI Solution – Managed EDI (such as Commport’s Integrated EDI) – these solutions enable transaction integration. They rely on the solution provider to manage the EDI standards which allows the user to focus on their
business and system requirements.
Software and Services – These solutions rely on “edi translation software” which is often purchased and maintained on-premise. They rely on the user to be able to perform their own application and data mapping between the EDI translation software and their business system. Users that pursue an on-premise EDI translation software approach will also still require an EDI Services provider (Value Added Network or VAN) for communications otherwise, they will also need to adopt some communications infrastructure to manage their relationships with their trading partners.
3. Implementation and Testing
Once you have selected a solution and a provider, work with that provider to implement the solution. Your next step is EDI testing, you must test your EDI solution to ensure that the documents can be exchanged successfully in the proper format with your trading partner(s).
4. Train Your Team
Ensure that your team is well-versed in EDI practices and compliance requirements. Provide training and resources to help them understand the importance of EDI and how to use the systems effectively.
5. Monitor and Maintain
Once your systems are operational, continuously monitor them to ensure ongoing compliance. Regularly update and maintain your systems to adapt to changing standards and regulations.
Conclusion
EDI compliance means, ensuring seamless electronic communication and collaboration within supply chains. Adhering to EDI standards and requirements is essential for organizations to efficiently exchange business documents, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain positive relationships with trading partners.
Need Help? Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
EDI Compliance refers to the adherence to Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) standards and requirements, ensuring that businesses can exchange electronic documents seamlessly with their trading partners in a standardized and efficient manner.
EDI Compliance is crucial for businesses as it streamlines communication, reduces errors in data exchange, accelerates business processes, and enhances overall operational efficiency. It also helps maintain consistency in transactions with various trading partners.
Yes, there are industry-specific standards for EDI Compliance, such as EDIFACT, ANSI X12, and others. These standards define the format and structure of electronic documents to ensure consistency and compatibility between trading partners.
Achieving EDI Compliance involves implementing EDI software or solutions that adhere to industry standards, collaborating with trading partners to ensure mutual compliance, and staying informed about updates and changes in EDI standards.
Non-compliance with EDI standards can lead to communication errors, delays in business processes, increased operational costs, and strained relationships with trading partners. It is essential for businesses to prioritize and maintain EDI Compliance to avoid these issues.