Introduction
A Global Location Number (GLN) is a 13-digit identifier, part of the GS1 system, used to uniquely identify locations in the supply chain. It can be used to represent a physical location like a warehouse, a legal entity like a company, or a specific function within a company.
GLNs improve efficiency by streamlining communication and enabling accurate identification of locations, regardless of size or nature of the business.
Key Takeaways
GLNs provide universal identification – As part of the GS1 standards system, GLNs offer a globally unique 13-digit identifier for locations and legal entities, eliminating confusion and standardizing location identification across supply chains.
Enhanced operational efficiency – By implementing GLNs, businesses can streamline processes, reduce manual data entry, minimize errors, and achieve significant cost savings through improved inventory management and logistics operations.
Critical for supply chain visibility – GLNs enable precise tracking of goods throughout the supply chain, facilitating better demand forecasting, improved planning, and creating transparent, agile supply networks that can quickly adapt to market changes.
Essential for GDSN functionality – GLNs play six key roles within the Global Data Synchronization Network, from identifying trading partners to supporting audit trails, making them indispensable for effective product data synchronization.
Industry-wide applications – The versatility of GLNs makes them valuable across multiple sectors, including retail, healthcare, and manufacturing, where they support everything from inventory management to patient safety protocols.
What is a GLN used for?
GLNs are used to identify parties to business transactions, functional groups within a company, or real, physical “places” that might ship, receive, process, or hold inventories.
- Legal Entities: whole companies; subsidiaries or divisions within a company; health system corporation; etc.
- Functional Entities: specific departments within a legal entity, such as an accounting department, purchasing department, hospital pharmacy, etc.
- Physical Locations: manufacturing facility, distribution center, warehouse, dock door, hospital wing, bin location, retail store, etc.
- Digital Locations: an electronic or non-physical address such as an EDI gateway or ERP system
The GLN is a required component for using the Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) and various types of e-commerce transactions. This global identification system of GS1 helps ensure that the GLN placed in a barcode or Electronic Product Code (EPC) is the same information contained in the corresponding electronic documents processed between trading partners.
The Importance of GLN in Business Operations
The significance of GLN numbers in business operations cannot be overstated. At its core, a GLN helps to streamline processes by ensuring accurate data exchange and location identification. This functionality is crucial in avoiding errors, reducing costs, and improving the overall efficiency of operations.
For instance, in the supply chain process, knowing precisely where products are located at any given time is fundamental. A GLN allows businesses to track inventory accurately, ensuring that goods are available where and when they are needed. This leads to improved inventory management, reduces the risk of stockouts, and optimizes storage space utilization.
Moreover, the GLN is essential for businesses that interact with multiple partners, suppliers, and customers. It allows for seamless integration of systems, enabling automated data exchange and reducing the need for manual data entry. This not only saves time but also minimizes the risk of human error, enhancing the reliability of business operations.
How GLN Enhances Supply Chain Efficiency
The role of GLN in enhancing supply chain efficiency is profound. Supply chains are complex networks with numerous entities, each needing precise identification to function smoothly. GLNs provide a standardized method for identifying these entities, which contributes significantly to supply chain transparency and efficiency.
One of the primary ways in which a GLN improves supply chain efficiency is through better visibility. With each location assigned a unique GLN, businesses can precisely track the movement of goods through the supply chain. This visibility allows for better demand forecasting, improved planning, and more efficient logistics operations.
Furthermore, GLNs facilitate better collaboration between supply chain partners. By using a common language for location identification, businesses can more easily coordinate their activities, share information, and respond to changes in demand or supply. This collaboration is essential for maintaining a responsive and agile supply chain that can quickly adapt to market changes.
Benefits of Using GLNs
There are several benefits of using the GLN to identify parties, functional groups, and physical locations:
- Improved visibility: GLNs allow businesses to track where products are located throughout the supply chain.
- Streamlined communication: They ensure clear identification of locations, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
- Enhanced data accuracy: GLNs provide a standardized way to identify locations, leading to more accurate data collection and analysis.
- Simplified processes: They can streamline tasks like order processing, invoicing, and logistics management.
Where are GLNs used & Which Industries Benefit From It?
Data carriers
GLNs in barcodes can help to route products to their destination or capture where they came from. Use of EPC®/RFID and readers identified with GLNs can support automatically capturing the movement of goods without the need for line-of-sight scanning or other manual intervention.
Systems and communications
Sharing information relating to parties and locations using GLN within GS1 standards like EDI and EPCIS will enhance transactional data and physical event data.
List of Industries
Retail
The retail industry is one of the primary beneficiaries of GLNs. With numerous locations, including warehouses, distribution centers, and stores, accurate location identification is essential. GLNs help retailers manage inventory, optimize supply chains, and improve customer satisfaction by ensuring products are available when and where they are needed.
Healthcare
In healthcare, GLNs play a crucial role in enhancing patient safety and improving operational efficiency. By accurately identifying locations such as hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies, healthcare providers can ensure the right medications and supplies are delivered promptly. This accuracy is vital for maintaining high standards of patient care and reducing errors in the supply chain.
Manufacturing
Manufacturers benefit from GLNs by improving production processes and supply chain management. With precise location identification, manufacturers can optimize logistics, manage raw materials and finished goods, and reduce lead times. This efficiency leads to cost savings and improved competitiveness in the global market.
The Key Roles of GLNs in GDSN
What is GDSN?
The Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) is the world’s largest product data network.
GDSN makes it possible for any company, in any market, to share high-quality product information seamlessly. Because companies of all sizes need the same thing—timely and reliable product information—to ultimately benefit consumers and patients.
With GDSN, high-quality product content is uploaded, maintained, and shared automatically, ensuring trading partners have immediate access to the most current and complete information needed to exchange products on both local and global markets.
GLN’s Key Role Within GDSN:
Identify Trading Partners
GLNs are used to uniquely identify each party (supplier, retailer, distributor, etc.) involved in a GDSN data exchange.
Ensures there’s no ambiguity about who is sending or receiving data.
Define Ownership and Responsibilities
GLNs define who owns the data (Data Source), who is authorized to receive it (Data Recipient), and which GDSN-certified Data Pool is used.
Example: A supplier’s GLN is associated with product data submitted into the GDSN.
Data Pool Registration and Synchronization
Each organization registers their GLN with their GDSN-certified Data Pool.
Synchronization of product data (like price, dimensions, descriptions) is routed and managed using GLNs.
Location-Specific Data
When product data is dependent on location (e.g., regional packaging, language, or pricing), GLNs are used to define the applicable location.
This allows data recipients to receive tailored product information relevant to their specific location.
Audit and Compliance
GLNs help track where data originated from and where it was sent, supporting data accuracy, validation, and audit trails.
Transactional Efficiency
GLNs reduce errors in data exchange by eliminating confusion about location identifiers.
This enhances automation and reliability in supply chain operations.
How to Obtain a GLN Number
Obtaining a GLN number is a straightforward process, but it requires an understanding of the GS1 system. The first step is to join GS1, a global organization that manages the standards for GLNs and other identifiers. Membership provides access to the tools and resources needed to implement GLNs in your business.
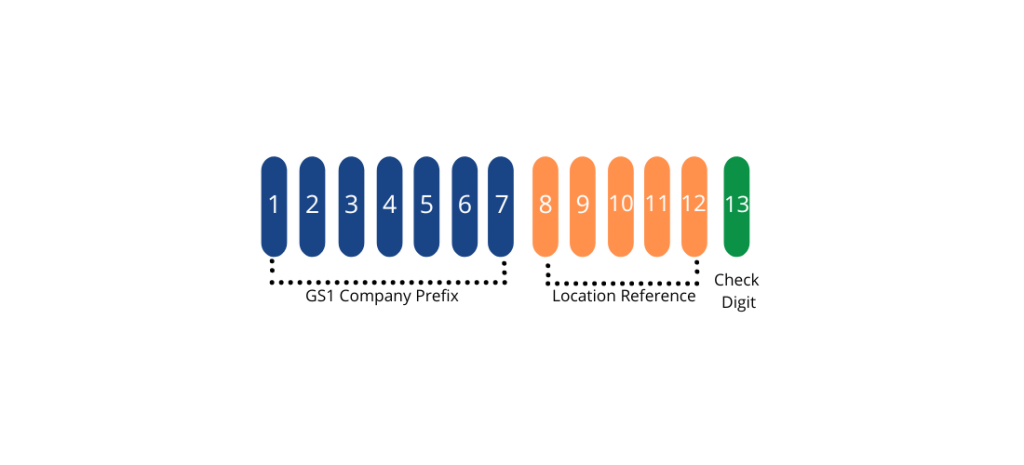
Once you are a member, you can start assigning GLNs to your locations. This involves using the GS1 Company Prefix, which you receive upon registration, to create unique GLNs for each of your locations. This prefix is combined with a location reference and a check digit to form the complete GLN.
It’s important to maintain accurate records of your GLNs to ensure they are used effectively across your organization. Keeping an updated database of GLNs helps in managing changes, such as opening new locations or closing old ones, ensuring that your business operations remain smooth and efficient.
About GS1
GS1 is a neutral, not-for-profit, international organization developing and maintaining standards including barcodes. GS1 standards, services and solutions are designed to improve the efficiency, safety and visibility of supply chains across physical and digital channels in a wide variety of sectors.
Sources: GS1.org
Conclusion
A Global Location Number (GLN) is a unique identifier assigned to a physical location or legal entity in the supply chain. It plays a crucial role in facilitating efficient and accurate communication between businesses by providing a standardized way to identify and track entities across the global marketplace. The use of GLNs enhances supply chain visibility, reduces errors, and promotes seamless interoperability in various industries.
Download: GDSN Buyers Guide
Empower your business with global data synchronization; download our GDSN Buyer's Guide today and take the first step towards streamlined, accurate, and compliant product data management.
Frequently Asked Questions
A Global Location Number (GLN) is a globally unique identifier assigned to a specific location or legal entity. It is crucial in business for accurate and standardized identification of entities within the supply chain, promoting efficiency, reducing errors, and improving communication between trading partners.
While barcodes and QR codes encode information about products, GLNs are unique identifiers for locations or entities. GLNs provide a standardized and globally recognized format for identifying physical or legal entities, facilitating efficient communication in the supply chain.
GLNs are typically assigned by a GS1 Member Organization in each country. Businesses can obtain a GLN by becoming a member of GS1 and registering their company. Once registered, they can allocate GLNs to their different locations or legal entities.
GLNs are versatile and can be used across various industries, including retail, healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing. Their standardized format ensures interoperability, making them applicable in diverse business scenarios for accurate and efficient identification.
GLNs enhance supply chain management by providing a standardized and unique identifier for each location or legal entity. This improves visibility, traceability, and accuracy in supply chain processes, leading to reduced errors, streamlined communication, and overall operational efficiency.