Introduction
As supply chains grow increasingly complex, the demand for faster, more efficient processes has intensified.
By automating workflows like
- Inventory management,
- Order processing, and
- Shipping,
Businesses can streamline operations, reduce manual intervention, and maintain visibility across the entire supply chain.
Key Takeaways
- Start with strategic planning: Evaluate current workflows, set measurable goals, and identify high-impact opportunities before selecting technology platforms to ensure maximum ROI.
- Focus on integration over isolation: Choose ERP, WMS, and TMS systems that work as an integrated ecosystem rather than standalone solutions for seamless operations.
- Prioritize quick wins first: Target high-volume, repetitive processes like order fulfillment and inventory tracking to achieve 20-30% cost reductions within 3-6 months.
- Invest in change management: Provide comprehensive training (typically 200 hours) and use structured approaches like ADKAR to ensure employee adoption and success.
- Monitor and optimize continuously: Establish KPI dashboards post-deployment to track performance metrics and make data-driven refinements that compound benefits over time.
What is Supply Chain Automation?
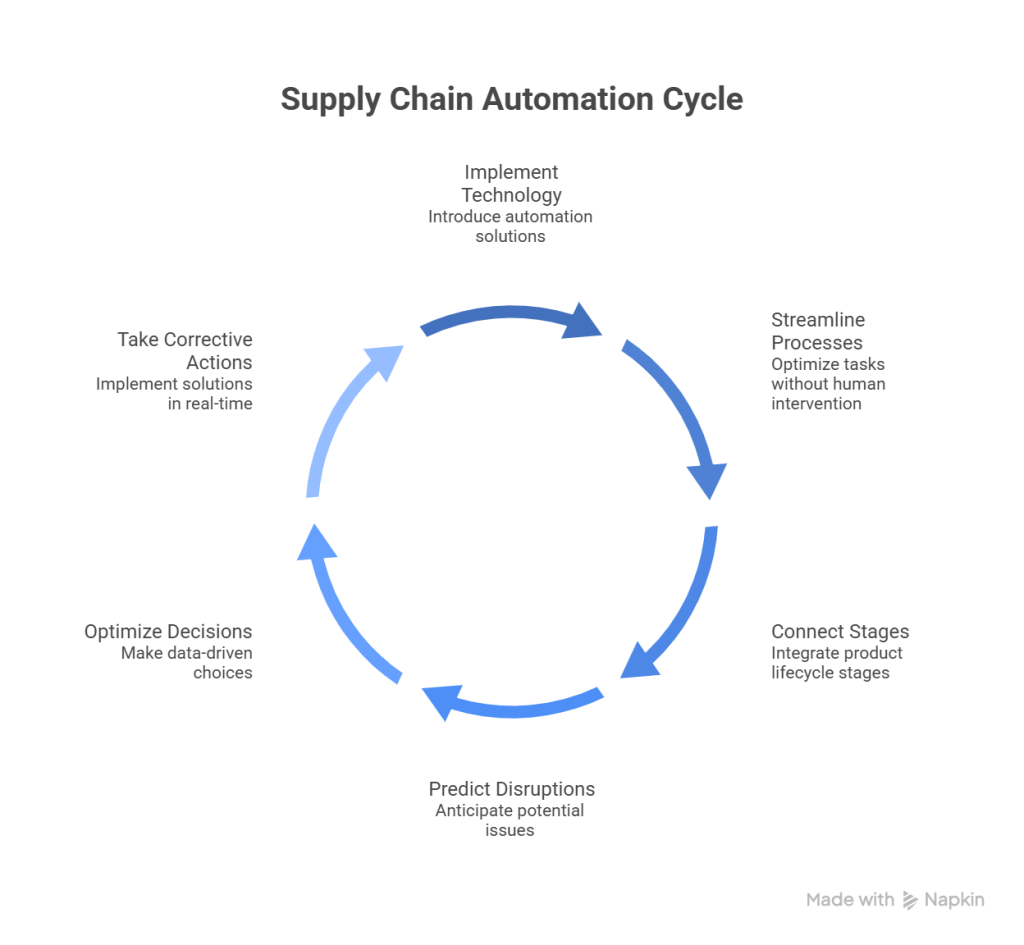
Supply chain automation refers to the implementation of technology solutions that streamline and optimize processes across the supply chain without human intervention. Rather than relying on manual workflows, businesses can now automate various supply-related tasks, including procurement, inventory management, warehouse operations, and logistics.
The fundamental purpose of supply chain automation is to connect different stages of the product lifecycle through specialized software. For instance, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems integrate purchasing, sales, and inventory into a unified process that automatically checks inventory levels, triggers warehouse shipments, and updates product status for stakeholders across the organization.
Modern supply chain automation transcends mere efficiency improvements. It creates responsive, data-driven operations that can predict disruptions, optimize decisions, and take corrective actions in real-time. This represents a significant shift from traditional approaches that relied heavily on reactive decision-making.
Why Manual Processes are No Longer Scalable
Businesses dependent on manual supply chain workflows face significant scalability challenges. Manual operations frequently result in inventory shortages, delayed shipments, process errors, and other serious risks that incur substantial time and financial costs. According to studies, automated systems typically operate with an accuracy rate of 99.96% to 99.99%, with error rates of just 0.04%.
Additionally, manual processes create coordination bottlenecks. When companies rely on manual systems to coordinate materials from multiple global suppliers, orders frequently get lost, preventing timely deliveries. Furthermore, in manual environments, teams predominantly operate in reactive mode—constantly addressing delayed shipments, supplier shortages, or unexpected production halts with little opportunity for strategic planning.
Manual planning processes tend to be inherently rigid and inflexible. Once established, plans rarely adapt to daily fluctuations or unexpected changes. Modifying any aspect typically involves lengthy email threads, multiple approval layers, and time-consuming meetings, significantly hampering responsiveness.
How EDI and VAN Solutions Helps With Supply Chain Automation
Supply chains depend on fast, accurate information flow just as much as the physical movement of goods. When purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and inventory updates are handled manually, delays and errors quickly pile up. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) solves this by allowing businesses to exchange standardized documents directly between systems, without emails, paper, or rekeying data. Orders move faster, confirmations happen automatically, and downstream processes like picking, packing, and billing can begin immediately.
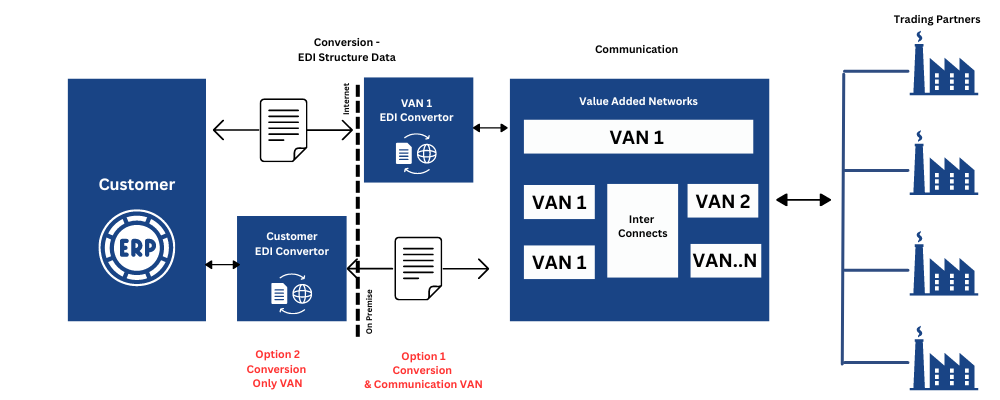
By removing manual data entry, EDI significantly reduces errors that lead to incorrect shipments, pricing disputes, and inventory issues. It also improves visibility across the supply chain. Advance shipping notices let warehouses prepare before goods arrive, while real-time inventory and order updates help teams plan more accurately. The result is smoother coordination between partners and lower operating costs driven by fewer corrections, less labor, and faster cycle times.
A Value-Added Network (VAN) strengthens this automation by acting as a secure intermediary for EDI transactions. Instead of building and maintaining separate connections with every trading partner, companies connect once to the VAN. The VAN validates, routes, tracks, and secures EDI documents, ensuring reliable delivery even when systems are temporarily unavailable. It also provides monitoring tools and audit trails that support compliance and troubleshooting.
Together, EDI and VAN create an automated, scalable foundation for modern supply chains. EDI standardizes the data, while the VAN ensures it moves securely and reliably between partners. This combination enables end-to-end automation, faster partner onboarding, and consistent information flow across complex networks. In an environment where speed, accuracy, and resilience matter more than ever, EDI and VAN are essential blocks for supply chain automation.
How GDSN and PIM Datapool Solutions Help with Supply Chain Automation
Supply chain automation depends on more than moving orders and shipments quickly. It also relies on having accurate, consistent product data across every system and trading partner. When product information is incomplete or mismatched, even the most automated processes break down. This is where GDSN and PIM datapool solutions play a critical role.

GDSN, or the Global Data Synchronization Network, is a global framework that allows companies to share standardized product data with their trading partners. Through certified datapools, suppliers publish product information such as dimensions, weights, ingredients, pricing attributes, and regulatory details. Retailers subscribe to that data, ensuring both sides are always working from the same, validated information. This eliminates manual data entry, spreadsheets, and constant back-and-forth to fix discrepancies.
PIM, or Product Information Management, serves as the internal source of truth for product data. A PIM system centralizes product attributes, images, descriptions, and compliance details, making it easier to manage and enrich data before sharing it externally. When integrated with a GDSN datapool, the PIM ensures that high-quality, approved product data flows automatically into the network. Updates such as packaging changes or new product launches can be published once and synchronized everywhere.
Together, GDSN and PIM datapool solutions automate one of the most error-prone areas of the supply chain: product data management. Accurate data supports smoother ordering, faster item setup, fewer invoice disputes, and more efficient logistics planning. By replacing manual updates with continuous synchronization, these solutions reduce delays, improve partner trust, and create a more resilient, automated supply chain from product creation to point of sale.
How Supply Chain Analytics Solutions Help with Supply Chain Automation
Supply chain automation isn’t just about moving data faster. It’s about making smarter decisions with that data. Even highly automated supply chains can struggle if teams lack visibility into what’s happening across orders, inventory, transportation, and suppliers. Supply chain analytics solutions turn raw data into actionable insights, enabling automation that is not only faster but also more intelligent and responsive.

Supply chain analytics platforms collect data from multiple sources, including ERP systems, WMS, TMS, EDI transactions, and IoT devices. By consolidating this information into a single view, they provide real-time visibility across the entire supply chain. Dashboards, alerts, and performance metrics help teams spot delays, inventory risks, or demand shifts early, allowing automated workflows to trigger corrective actions such as replenishment, rerouting, or supplier notifications.
Advanced analytics take automation a step further by using predictive and prescriptive models. Instead of reacting to problems after they occur, these solutions forecast demand, identify potential disruptions, and recommend optimal responses. For example, analytics can predict stockouts, optimize safety stock levels, or suggest alternative transportation routes before delays impact customers. This reduces manual intervention and improves service levels while controlling costs.
By embedding analytics into automated processes, organizations move from rule-based execution to data-driven decision-making. Automated planning, continuous monitoring, and intelligent exception management help supply chains operate with greater speed, accuracy, and resilience. In a complex and constantly changing environment, supply chain analytics solutions provide the insight needed to automate confidently and adapt in real time.
The Role of AI, RPA, and IoT in Modern Supply Chains
Artificial Intelligence has become instrumental in transforming supply chain operations. AI systems process vast data volumes, predict trends, and perform complex tasks in real-time, enabling better data-driven decisions and operational efficiency. In advanced manufacturing, AI-powered visual inspection has proven more effective than human inspection, particularly for components like silicon in equipment.
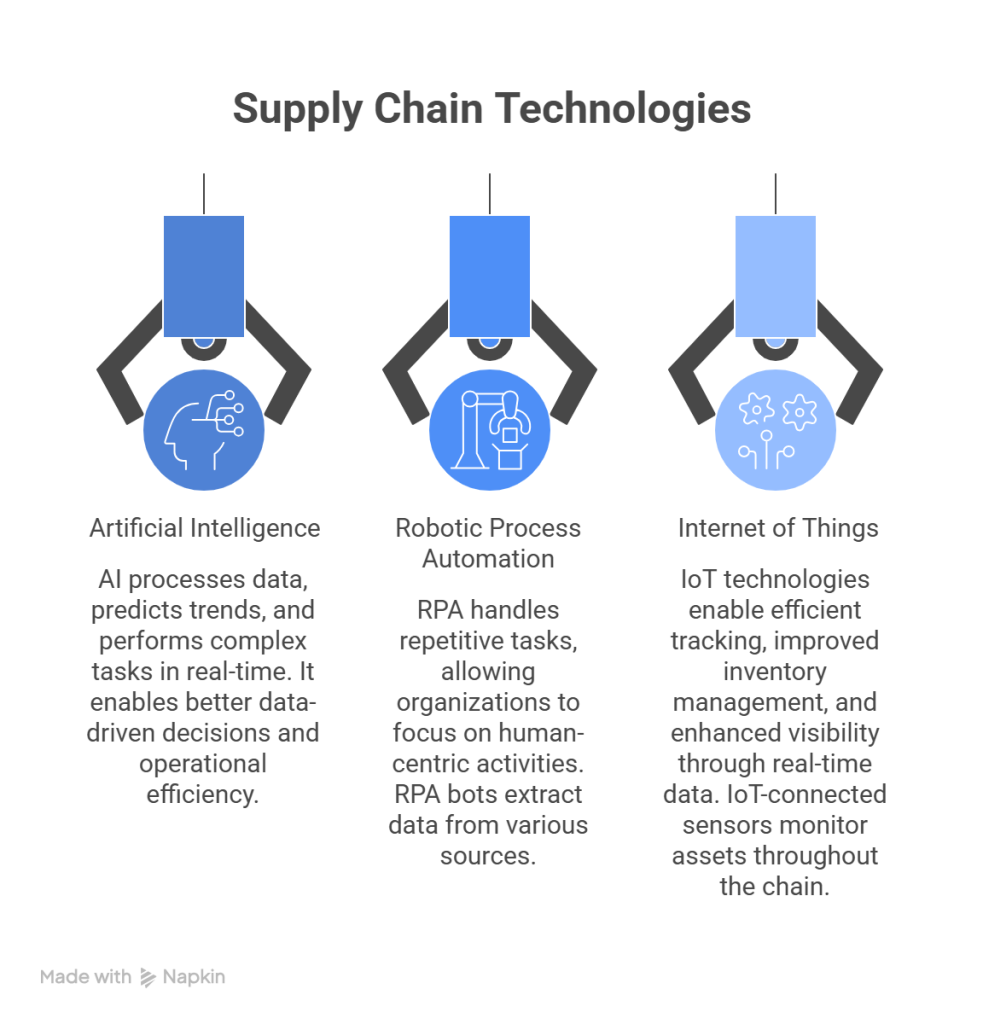
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) serves as a digital acceleration catalyst by handling repetitive tasks so organizations can focus on human-centric activities. RPA bots can extract data from various sources like project management software, emails, and scanned documents. According to industry reports, companies implementing RPA report approximately 30% in operational expense savings.
Internet of Things (IoT) technologies have fundamentally changed supply chain management by enabling more efficient tracking, improved inventory management, and enhanced visibility through real-time data. IoT-connected sensors close the control loop in smart supply chain management by monitoring assets throughout the chain. These sensors can assess numerous variables, including temperature and vibration, that affect raw materials quality.
Together, these technologies create an interconnected ecosystem that transforms planning from reactive to predictive systems that can detect disruptions, simulate outcomes, and respond in real-time with minimal human input. Looking forward, these technologies will continue to evolve, with autonomous, self-learning machines potentially managing broader supply chain processes seamlessly.
Key Benefits of Supply Chain Management Automation
Implementing automation across supply chains delivers a substantial return on investment that significantly impacts bottom-line performance. Companies deploying these technologies report measurable gains in efficiency, accuracy, and customer experience that drive competitive advantage.

1. Reduced Operational Costs Through RPA
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) creates an immediate financial impact by addressing core operational inefficiencies. A well-executed RPA deployment can generate savings exceeding $100 million while handling work previously requiring 1,000+ employees. Organizations implementing RPA typically experience 20-30% reduction in operational costs within the first year, with some achieving up to 50% savings in specific processes like invoice processing.
The financial case for RPA becomes even more compelling when examining labor metrics. Private sector workers average $43.78 per hour in compensation costs, meaning even one employee can cost over $100,000 annually. Meanwhile, companies relying on manual processes spend 15% more on labor than those with automated systems. For retail businesses, RPA implementation can potentially save approximately $340 billion annually across the sector.
Notably, RPA delivers rapid payback periods that accelerate adoption. Most organizations see returns within 3-6 months when focusing first on high-volume, repetitive tasks. One logistics provider, Raben Group, deployed over 200 RPA automations that saved 78,815 employee workdays and over €6 million in a single year.
2. Improved Inventory Accuracy with Real-Time Tracking Using EDI
Real-time inventory tracking eliminates the chronic problems of stockouts and overstock situations that plague manual systems. Automated inventory management delivers precise stock usage data that enables just-in-time ordering, reducing carrying costs and freeing capital for other business priorities.
The accuracy improvements are substantial—automated warehouse systems achieve inventory accuracy rates of 99.99%, virtually eliminating costly errors. This precision matters financially since fixing a single data entry mistake costs between $50 and $200, while inventory discrepancies cost up to $1,000 per SKU.
Moreover, automated systems provide comprehensive visibility across all locations and channels through a centralized system. This transparency allows organizations to monitor stock levels, movements, and trends in real-time, enabling quick responses to supply chain disruptions or changes in demand. Mobile-integrated RPA enables immediate updates to inventory levels as goods are received, moved, or sold—improving accuracy while reducing both stockout and overstock risks.
3. Faster Order Fulfillment Using Warehouse Robotics
Warehouse automation technologies dramatically accelerate fulfillment capabilities. Organizations implementing robotics solutions boost throughput by up to 40% while driving inventory accuracy to 99.99%. The Locus autonomous warehouse solution improves productivity 2-3x and reduces labor costs by half. Similarly, companies using AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots) handle repetitive transport tasks while increasing worker productivity by up to 40%.
The financial impact of this accelerated fulfillment extends beyond direct labor savings. Companies report 50% faster cycle times and payback periods of 6-24 months for modular automation pilots. One fast-moving consumer goods company consolidated slower-moving products into three mega-distribution centers and improved inventory turnover, ultimately supporting a $500 million capital investment with a 40% ROI.
4. Enhanced Customer Satisfaction via Automated Updates
Automation directly improves customer experience by providing real-time visibility throughout the order lifecycle. With automated systems, businesses can provide accurate delivery estimates and avoid disappointing customers with out-of-stock items, building trust and loyalty.
Automated order processing manages high volumes without requiring additional resources, validates orders for accuracy, and applies custom requirements—significantly reducing handling times while improving on-time delivery rates. This visibility translates into tangible business results, with leading consumer-focused businesses unlocking 20-50% improvement in service levels while generating 25-50% reduction in fulfillment costs.
Planning for Automation: Laying the Right Foundation
A successful supply chain automation journey begins long before implementation. Proper planning creates the essential groundwork for long-term success, ensuring that automation investments deliver maximum value.
1. Evaluating Current Supply Chain Workflows
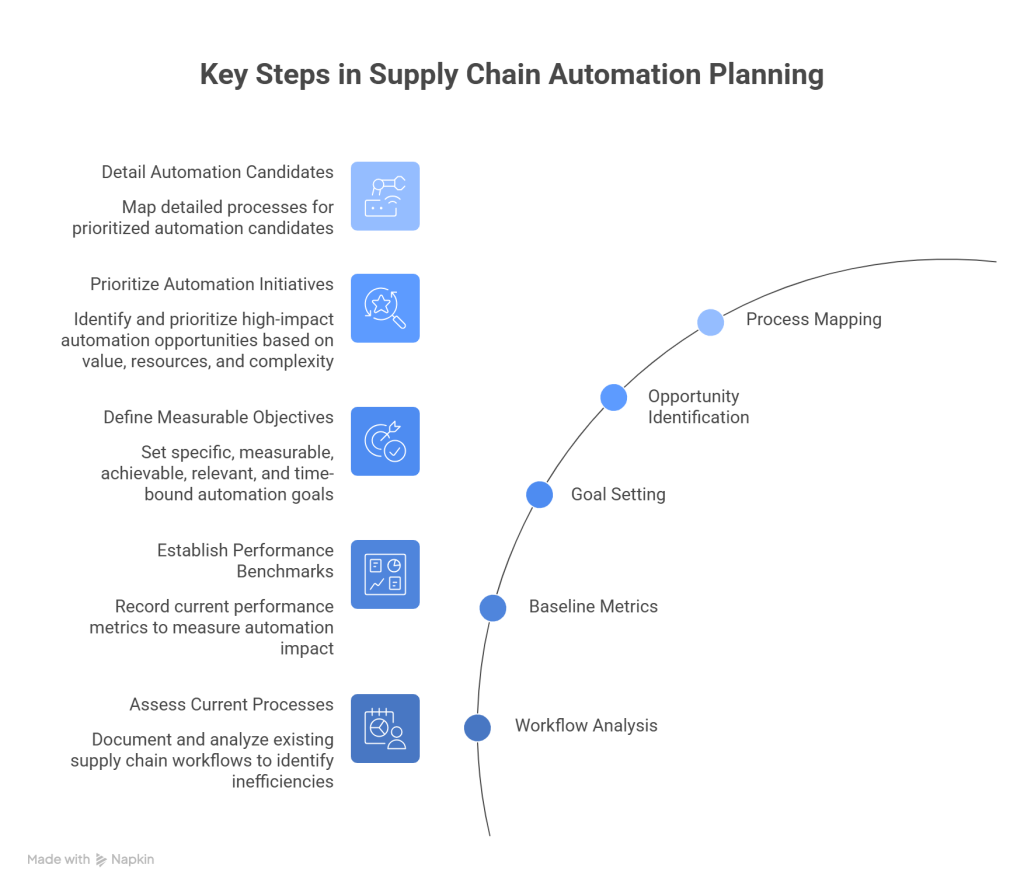
Before investing in automation, companies must thoroughly assess their existing supply chain processes to identify inefficiencies and bottlenecks. This assessment requires a comprehensive workflow analysis to pinpoint areas that are slow or prone to errors. Involving key team members from various departments provides valuable insights into their challenges and needs.
To establish a meaningful baseline, organizations should document current performance metrics. These metrics will later serve as benchmarks for measuring improvements after implementing automation. Experts recommend auditing the entire supply chain—from order processing to shipping—to understand where manual tasks are causing delays or errors.
2. Setting Measurable Automation Goals
Defining clear objectives keeps automation initiatives focused on high-impact outcomes. Successful organizations set specific goals such as reducing order processing time by a targeted percentage (e.g., 20%), which subsequently guides technology selection and implementation strategy. Other common objectives include minimizing manual work to free employees for higher-value activities and improving data accuracy.
Organizations should also consider how automation aligns with broader business objectives. As one industry expert notes, “For the most part, automating any process will improve efficiency, accuracy, and scalability. In turn, this will enhance productivity and profitability”. However, companies must ensure that automation goals directly support their specific business challenges.
3. Identifying High-Impact Automation Opportunities
After identifying areas for automation, businesses should prioritize initiatives based on:
- Immediate value potential: Focus first on processes like order fulfillment or inventory tracking that deliver quick wins
- Resource requirements: Allocate resources effectively to ensure high-priority initiatives receive proper support
- Implementation complexity: Start with processes having well-defined workflows and limited need for human judgment
The Everest Group recommends using a structured methodology like their Enterprise Value Chain Approach (EVCA) to assess the suitability of processes for automation. This methodology helps businesses spotlight high-value opportunities based on cost savings potential and overall automation potential.
Consequently, many organizations first target order management for automation due to its high transaction volume, well-defined workflow, and limited need for human intervention. First mapping detailed processes, then identifying which tasks can be immediately automated through basic RPA, creates a logical progression toward full automation.
Implementation Strategy: From Tools to Training
Successful supply chain automation hinges on precise implementation strategies that bridge planning with execution. The right combination of technology, vendor partnerships, and workforce readiness determines whether automation delivers on its promise or becomes a costly experiment.

1. Selecting ERP, WMS, and TMS Platforms
Effective automation requires selecting systems that work as an integrated ecosystem rather than isolated solutions. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) serves as the central nervous system, providing full-featured, scalable cloud-based functionality that automates front and back-office processes. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) optimize inventory accuracy and facility operations, although they must be paired with Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES) in production environments. Transportation Management Systems (TMS) complete this trio by connecting shipping and logistics functions to warehouse operations.
Integration becomes much more complex in organizations operating multiple ERPs, regional instances, or highly customized environments. In these scenarios, a central planning engine like Atlas becomes essential, consolidating data into one unified source of truth.
2. Vendor Evaluation and Integration Planning
Beyond assessing technical capabilities, evaluate vendors based on their integration expertise across multiple ERP platforms, including SAP, NetSuite, Oracle, and Microsoft Dynamics. Prioritize platforms that integrate easily with your existing tech stack and support automation across the full vendor lifecycle.
Integration architecture options include:
- iPaaS solutions like Commport Integrated EDI with pre-built connectors
- Commport GDSN Datapool for product data management & synchronization
- Commport value-added network gateways with built-in EDI translators for secure partner connectivity
- Commport business analytics solution to connect, measure and track your supply chain data and key KPIs all in one dashboard.
3. Employee Training and Change Management
Prepare technicians who install, operate, support, upgrade, and maintain automated material handling equipment through certified training programs. Each supply chain training course typically consists of 200 hours. Provide thorough, role-specific training to internal users, with hands-on workshops and support materials.
Monitoring KPIs Post-Deployment
After rollout, establish dashboards to track performance metrics like vendor onboarding time, compliance rates, and user adoption. Continuously analyze data and stakeholder feedback to optimize workflows and automation rules. Companies with automated data collection and a central dashboard help leaders stay aligned and prioritize resources.
Conclusion
Supply chain automation stands as a transformative force reshaping how businesses operate in today’s complex global marketplace. Throughout this guide, we’ve seen how manual processes simply cannot scale to meet modern demands, while automated solutions deliver remarkable accuracy rates approaching 99.99%. Therefore, businesses must recognize automation not as optional but as essential for survival and growth in an increasingly competitive landscape.
The convergence of AI, RPA, and IoT technologies has fundamentally altered what’s possible in supply chain management. These technologies work together to create predictive rather than reactive systems that detect disruptions before they cascade into major problems. Additionally, the financial benefits prove compelling – from 20-30% reductions in operational costs to 2-3x productivity improvements in warehouse environments.
Success stories from industry leaders like DHL, Walmart, and Procter & Gamble clearly demonstrate that theoretical benefits translate into real-world advantages. Still, achieving these results requires methodical planning and implementation. Businesses must first evaluate existing workflows, set measurable goals, and identify high-impact opportunities before selecting technology platforms that integrate seamlessly.
After implementation, continuous monitoring becomes crucial for optimization. Companies that establish comprehensive dashboards to track KPIs position themselves to make data-driven refinements that compound benefits over time. Undoubtedly, the human element remains vital – thorough training and change management determine whether teams embrace or resist new automated processes.
As supply chains continue evolving, those who fail to automate will fall behind competitors who leverage these technologies effectively. Though the journey may seem daunting, partnering with experts like Commport B2B Network Solutions can significantly simplify the process. Automate Your Entire Supply Chain Process Today and join forward-thinking organizations already experiencing transformative results across their operations.
Commport B2B Network Solutions
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
Supply chain automation offers several key benefits, including reduced operational costs through RPA, improved inventory accuracy with real-time tracking, faster order fulfillment using warehouse robotics, and enhanced customer satisfaction via automated updates. These improvements can lead to significant cost savings and increased efficiency across the supply chain.
Effective planning for supply chain automation involves evaluating current workflows, setting measurable automation goals, and identifying high-impact automation opportunities. It’s crucial to assess existing processes, establish clear objectives aligned with business goals, and prioritize initiatives based on their potential value and complexity.
Modern supply chain automation is primarily driven by Artificial Intelligence (AI), Robotic Process Automation (RPA), and Internet of Things (IoT) technologies. AI enables data-driven decision-making, RPA handles repetitive tasks, and IoT facilitates real-time tracking and monitoring across the supply chain.
Most organizations see returns on their supply chain automation investments within 3-6 months, especially when focusing on high-volume, repetitive tasks. However, the exact timeframe can vary depending on the scope and complexity of the automation project.
Employee training is crucial for successful supply chain automation implementation. Typically, each supply chain automation training course consists of about 200 hours. Proper training ensures that employees can effectively operate, maintain, and leverage automated systems, maximizing the benefits of the new technology and smoothing the transition process.