Introduction
Global data synchronization saves retail companies approximately $10.5 billion annually through standardized barcode systems. However, many businesses still struggle with supply chain errors, including inadequate inventory management and inaccurate demand forecasting, all stemming from poor data quality.
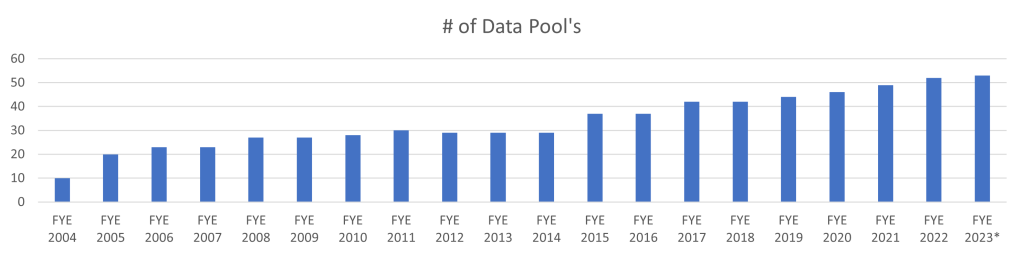
We’ve seen firsthand how the Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) transforms operations by connecting trading partners through a network of data pools. There are currently more than 50 GS1-certified GDSN data pools available, each offering different capabilities and user experiences. The GDSN data transmitted through these systems ensures synchronized and accurate information exchange across supply chains in real time. Additionally, a global data synchronization solution helps organizations identify procurement sources and calculate carbon emissions metrics, providing unprecedented operational transparency.
As we look at implementing effective GDSN solutions, it will be crucial for companies aiming to reduce costs, improve distribution speed, and deliver exceptional customer experiences.
Understanding the Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN)
The complex challenges of modern supply chains demand standardized, accurate data exchange between trading partners across the globe. This need led to the creation of systems that enable seamless sharing of product information, specifically, the Global Data Synchronization Network.
What is the GDSN and Why it Matters
The Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) is an internet-based, interconnected network of interoperable data pools governed by GS1 standards. Essentially, it functions as a bridge connecting brands and merchants, enabling companies worldwide to exchange standardized product master data with their trading partners.
GDSN serves as a tool to support high data quality through:
- Authoritative data sources
- Real-time data synchronization
- Standardized data formatting
Why does this matter? According to research, 81% of consumers are willing to switch to brands that provide more detailed product information. Furthermore, companies using GS1 standards on Order to Cash processes can save up to $48 per transaction. GDSN transforms how businesses share critical data, consequently improving supply chain visibility.
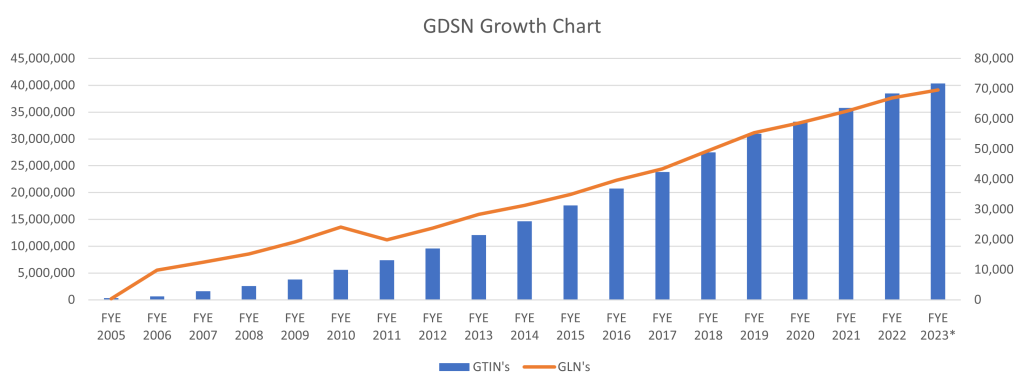
GDSN - Worlds largest product datapool with over 100 million active GTINs and over 50K active GLNs.
The Role of GS1 Standards in Global Data Exchange
GS1, the not-for-profit international organization behind GDSN, establishes global product identification and communication standards. These standards form the foundation for successful data synchronization, ensuring all participants speak the same “language.”
The GS1 Global Data Model standard defines a globally consistent set of foundational product attributes needed to list, order, store, move, and sell products. Meanwhile, the Attribute Definitions for Business (ADB) standard clarifies technical terminology, helping data senders get their content right.
Three key GS1 identification standards underpin GDSN:
- Global Trade Item Numbers (GTIN) – for product identification
- Global Location Numbers (GLN) – for unique location identification
- Global Product Classification (GPC) – for standardized product categorization
How GDSN Data Pools Enable Real-Time Synchronization
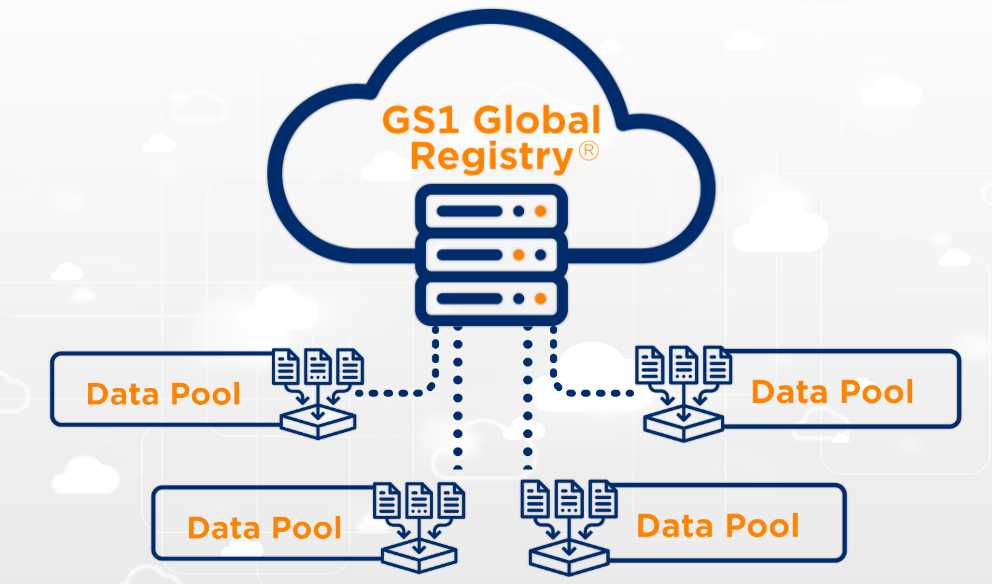
GDSN data pools act as electronic catalogs of standardized item data, serving as sources and/or recipients of master data. Currently, more than 50 GS1-certified data pools exist, each offering different capabilities, user experiences, and pricing.
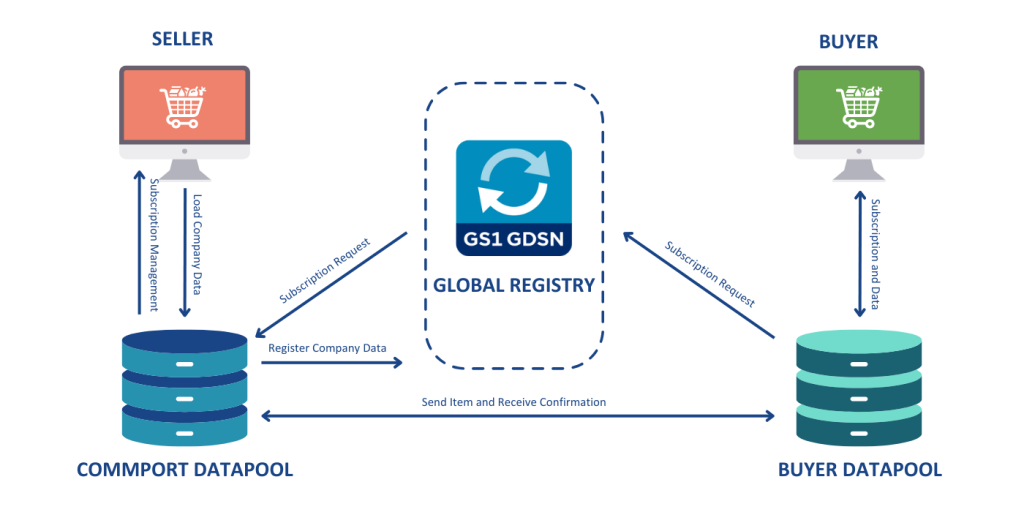
The synchronization process operates through a publish-subscribe pattern. First, sellers register product data in their data pool. Then, basic information is sent to the GS1 Global Registry. Next, buyers subscribe to receive specific product information. Subsequently, the seller’s data pool publishes the requested information to the buyer’s data pool. Finally, buyers confirm receipt, completing the synchronization.
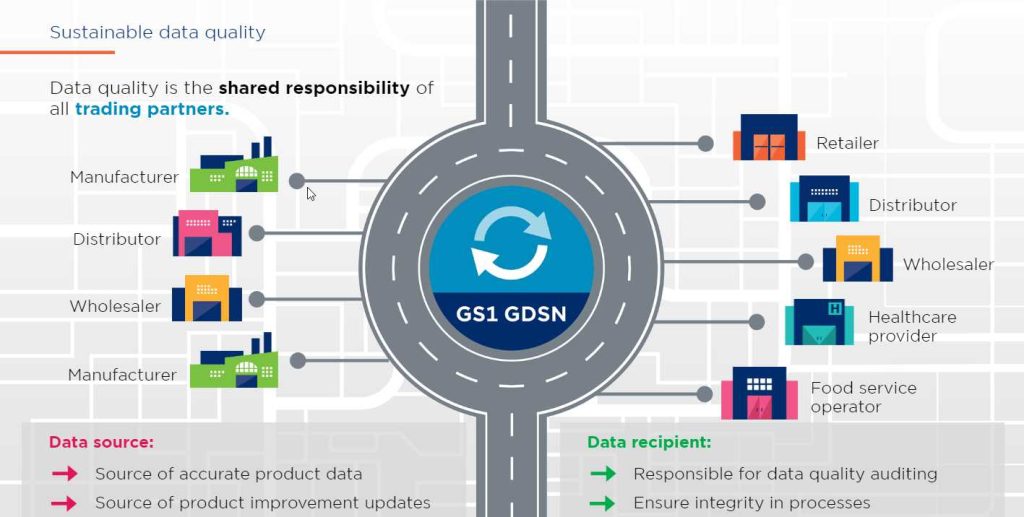
This automated, standards-based environment enables secure and continuous data synchronization, allowing all partners to have consistent item data in their systems simultaneously. Above all, GDSN ensures trading partners can securely, accurately, and efficiently share high-quality product data, creating a single point of truth across the entire supply chain.
How GDSN Works?
Putting the GDSN theory into action requires understanding the practical mechanics that power this massive data exchange network. I’ve seen how robust processes and standardized workflows create the foundation for successful global data synchronization implementation.
Data registration and validation process
Before any data enters the GDSN, it undergoes rigorous preparation and validation. The process starts when a data source (typically a manufacturer or supplier) loads product information into their chosen data pool. At this stage, the data must include mandatory elements like the 13-digit Global Location Number (GLN) to identify locations and the 14-digit Global Trade Item Number (GTIN) for product identification.
Once submitted, all data undergoes validation against the GS1 Data Quality Framework, which enforces current, complete, and correct data through:
- GS1 standard attribute definitions
- Standardized attribute values
- Automated validation rules
Notably, the GS1 Global Data Model defines foundational product attributes in four layers: Global Core, Global Category, Regional Category, and Country/Local. This structure ensures proper classification, with Global Product Classification (GPC) “bricks” serving as the foundation for categorizing similar products.
The flow of product data through GDSN
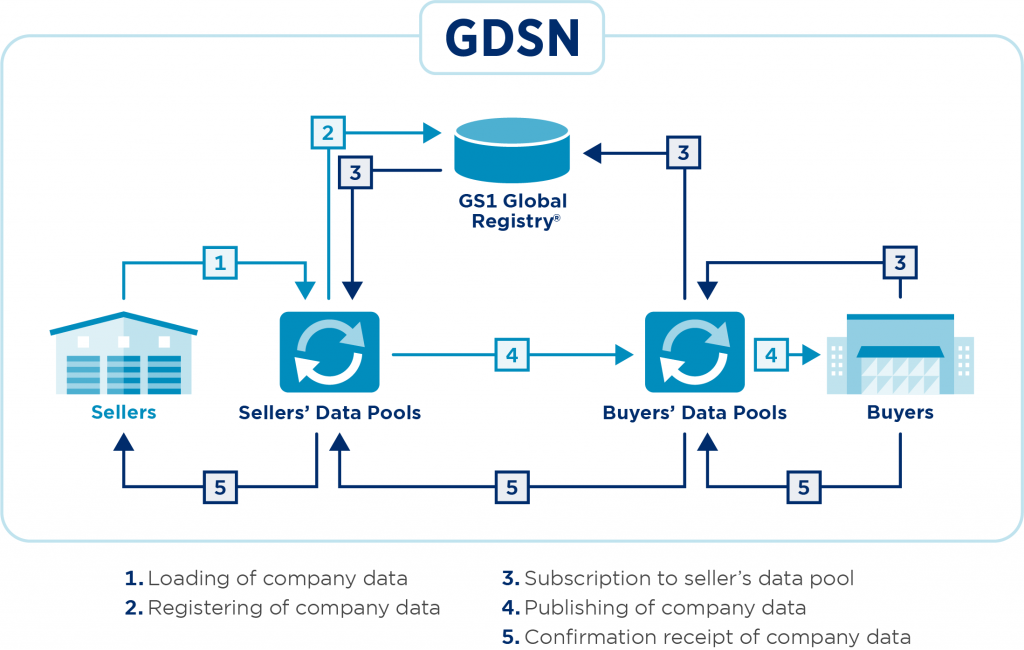
The journey of data through the GDSN follows five core steps:
- Load data: The seller registers product and company information in its data pool
- Register data: A subset of this information is sent to the GS1 Global Registry
- Request subscription: The buyer, through its own data pool, subscribes to receive specific seller information
- Publish data: Upon matching subscription with publication, the seller’s data pool sends the requested information to the buyer’s data pool
- Confirm & inform: The buyer sends confirmation back through the data pool network
Throughout this process, the Trading Partner Agreement (TPA) ensures protection of the data source’s information, acknowledging that the data source owns the data and providing legal protection.
Within the synchronized data flows, every product is assigned a unique identifier that houses all relevant information. This includes:
- Logistics data: Planning, management, and movement of products through the supply chain
- Shipping information: Product dimensions, weights, packaging details, and delivery specifications
- Compliance data: Regulatory information, certifications, and legal requirements
Additionally, the GDSN can deliver digital content through URL tags in GTIN records, providing access to images, PDFs, videos, and logos. Once properly implemented, this synchronized data empowers organizations to adapt quickly to changes, better balance supply and demand, and make informed decisions.
Business Benefits of Global Data Synchronization

Businesses implementing global data synchronization report tangible returns across multiple operational areas. The strategic importance of these benefits continues to grow as supply chains become increasingly complex and customer expectations evolve.
1. Improved supply chain visibility and transparency
Supply chain visibility allows companies to have an in-depth look at the entire life cycle of products, monitoring every process and touchpoint. With clear insight into your supply chain, you can forecast better, plan for potential delays, and prepare for increased demands. Moreover, according to research, 94% of consumers are more likely to be loyal to brands offering complete transparency. This loyalty translates directly to business growth, with 73% of consumers willing to pay more for products providing detailed information about sourcing and production processes.
2. Faster time-to-market and reduced errors
Organizations implementing the global data synchronization network experience significant improvements in operational metrics. A recent survey by GS1 USA found that businesses that implemented GDSN reported a 25% reduction in data errors and a 30% increase in operational efficiency. Particularly in retail, GDSN enables companies to get products on shelves faster, reduce logistics costs, and enhance customer relationships. These efficiencies give businesses a competitive edge as products reach the market more quickly with fewer discrepancies.
3. Enhanced customer experience through accurate data
According to Forrester Research, “The No. 1 feature online shoppers want from a website is product information”. Given these points, GDSN data enables consumers to make data-driven purchasing decisions based on trusted, globally distributed product content. The impact extends beyond retail—in healthcare, accurate product information ensures providers have access to critical data about medical products, reducing the risk of errors in patient care.
4. Cost savings from operational efficiency
The financial impact of global data synchronization software is substantial across industries:
- BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company) achieved a 30% reduction in outstanding days payable and a 73% reduction in ordering discrepancies
- McKinsey reports that companies with advanced supply chain transparency can reduce supply chain costs by up to 50%
- Implementing track and trace solutions can reduce inventory errors by up to 30%
As a result of these efficiencies, businesses optimize transportation costs, minimize excess inventory, and reduce operational expenses throughout the supply chain.
Choosing the Right Tools and Partners
Selecting the right technology partners for global data synchronization implementation can make or break your GDSN strategy. With more than 50 GS1-certified data pools available today, choosing the appropriate tools requires careful consideration of your specific business needs.
What to look for in a GDSN data pool provider
When evaluating GDSN data pool providers, remember that you don’t need to use the same provider as your trading partners. All GS1-certified data pools can exchange data with one another by definition. Nevertheless, you should examine these key factors:
- Service coverage and expertise: Ask about their experience in your specific industry and geographic markets
- Implementation support: Look for providers offering comprehensive project plans with dedicated support staff
- Pricing structure: Compare upfront costs, usage fees, and annual maintenance charges
- Technical capabilities: Assess whether they provide manual entry options, spreadsheet loading, or direct machine-to-machine methods
Requesting to speak with current clients can provide valuable insights about their experiences with setup, training, and ongoing support.
The role of global data synchronization software
Global data synchronization software serves as the communication bridge between your internal systems and the GDSN. Effective solutions should:
- Communicate with source data pools using XML documents via secure AS2 protocol
- Validate data against GS1 standards before transmission
- Support your specific integration needs and data governance requirements
Primarily, this software should adapt to your organization’s workflows rather than forcing you to change established processes. Unless the software provides comprehensive validation capabilities, you may face costly errors and compliance issues.
Integrating PIM systems with GDSN
Product Information Management (PIM) systems work alongside GDSN to create a centralized approach to data management. The integration process typically follows these steps:
- Implement a suitable PIM system as your central repository
- Collect and combine product data from various sources
- Cleanse and enrich this data within the PIM
- Map PIM fields to corresponding GDSN fields
- Publish to GDSN through your chosen data pool
The benefits of this integration include streamlined product data management, improved time-to-market, enhanced collaboration with trading partners, and better customer experiences. Forthwith, businesses should consider both systems as complementary tools that optimize different aspects of product information flow.
Conclusion
Throughout this exploration of global data synchronization, we’ve seen how GDSN creates substantial business value across multiple dimensions. Undoubtedly, organizations implementing standardized data exchange experience tangible benefits—from the 25% reduction in data errors to significant supply chain cost savings. These improvements stem from the structured framework provided by GS1 standards that ensure consistent, accurate information flows between trading partners.
The competitive landscape of 2025 will demand even greater supply chain efficiency and transparency. Companies that fail to adopt proper data synchronization practices risk falling behind competitors who leverage real-time data synchronization for faster market response. Because GDSN provides a single source of truth, businesses can make confident decisions based on reliable product information shared across their entire partner ecosystem.
Choosing the right implementation partner remains critical for GDSN success. The right data pool provider should align with your specific industry needs while offering comprehensive support throughout your implementation journey. Switch to Commport GDSN Datapool Solution today and reach global marketplaces with confidence and precision.
Last but certainly not least, remember that global data synchronization represents more than just a technical implementation—it forms the foundation of modern supply chain excellence. The strategic advantage comes from combining operational efficiency with enhanced customer experiences through trusted product data. Businesses that prioritize these synchronization initiatives now will find themselves well-positioned for whatever supply chain challenges emerge beyond 2025.
Commport GS1 Certified GDSN Datapool Solution
Download: GDSN Buyers Guide
Empower your business with global data synchronization; download our GDSN Buyer's Guide today and take the first step towards streamlined, accurate, and compliant product data management.
Frequently Asked Questions
Global data synchronization is the process of exchanging standardized product information between trading partners through a network called GDSN. It’s crucial for businesses as it improves supply chain visibility, reduces errors, speeds up time-to-market, and enhances customer experiences through accurate product data.
GDSN operates through a publish-subscribe model. Sellers register product data in their data pool, which is then sent to the GS1 Global Registry. Buyers subscribe to receive specific product information, and the seller’s data pool publishes the requested data to the buyer’s data pool. This process ensures all partners have consistent, up-to-date product information.
Key benefits include improved supply chain transparency, faster product launches, reduced data errors, enhanced customer satisfaction through accurate product information, and significant cost savings from increased operational efficiency. Companies have reported up to 30% reduction in data errors and 50% reduction in supply chain costs.
When selecting a GDSN data pool provider, consider factors such as industry expertise, implementation support, pricing structure, and technical capabilities. It’s also beneficial to speak with current clients to gain insights into their experiences with setup, training, and ongoing support.
Yes, global data synchronization can be integrated with Product Information Management (PIM) systems. This integration involves implementing a PIM system as a central repository, collecting and enriching product data, mapping PIM fields to GDSN fields, and publishing to GDSN through a chosen data pool. This combination optimizes product information flow and management.





