Introduction
EDI SLAs have become the backbone of modern supply chain operations, establishing critical performance standards that can determine success or failure in today’s hypercompetitive market.
The implementation of EDI in supply chain processes enables real-time data exchange, allowing key players such as suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers to receive prompt updates about inventory levels, shipping schedules, and payment status.
However, failing to meet these established SLAs can result in costly chargebacks, potentially amounting to thousands of dollars from business partners.
Almost 90% of retailers today require their vendors and suppliers to be EDI-compliant to do business with them, and EDI SLAs play key roles. From transaction processing times to system uptime requirements, SLAs outline the standards that ensure fast and accurate order fulfillment – a critical component for customer satisfaction.
By understanding these metrics, businesses can avoid the negative impacts that SLA violations can have on their organization across multiple dimensions.
Key Takeaways
- Monitor five critical metrics: transaction processing times, EDI 997 acknowledgment responses, system uptime (99.9%+), data accuracy rates, and error thresholds below 1%
- SLA violations trigger severe financial penalties: Major retailers like Walmart and Amazon impose chargebacks reaching hundreds of thousands of dollars for non-compliance
- Implement proactive monitoring tools: Use EDI dashboards, automated alerts, and ERP integration to identify at-risk transactions before they violate SLA terms
- Maintain regular partner communication: Schedule quarterly SLA reviews to optimize performance and address recurring issues before they damage trading relationships
- Prioritize system availability: Target 99.9% uptime minimum, with mission-critical operations requiring 99.99% availability to prevent supply chain disruptions
What is an EDI SLA and Why It Matters
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) serves as the backbone of modern supply chain operations. Understanding EDI SLAs and their significance can make the difference between successful business relationships and costly failures.
Let me break down these essential concepts.
Definition of EDI in Supply Chain Context
Electronic Data Interchange represents a standardized method for exchanging business documents electronically between trading partners. In supply chain environments, EDI replaces traditional paper-based methods with automated digital transmission of purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices, and other critical documents. This technology streamlines processes, reduces manual intervention, and improves data accuracy, making it indispensable for contemporary supply chains.
EDI in the supply chain standardizes supplier transactions, effectively lowering the risk of human error, miscommunication, improper shipments, and other operational mistakes. Through automation, businesses can ensure that data moves instantaneously between systems, eliminating inefficiencies that plague manual processing.
How SLAs Apply to EDI Transactions
Service Level Agreements for EDI define the terms and conditions under which data exchanges occur between trading partners. Essentially, an EDI SLA is a policy or agreement between two parties that stipulates and governs how EDI is utilized throughout the business relationship. These formal contracts establish clear expectations regarding response times, data accuracy rates, error handling procedures, and system availability.
SLAs pull together information on all contracted services and their expected reliability into a single document. Furthermore, they outline responsibilities and obligations for both parties, thereby ensuring accountability and providing legal protection.
Common SLA Terms: Response Time, Accuracy, Uptime
Effective EDI SLAs typically include these critical performance metrics:
- Transaction Processing Times: Defines how quickly EDI transactions like purchase orders should be processed and acknowledged
- Response Times: Specifies timeframes within which partners must respond to EDI messages
- System Availability: Ensures EDI systems maintain operational status within agreed-upon uptime percentages, often 99.5% during business hours or 99.999% for critical e-commerce operations
- Data Accuracy: Establishes standards for completeness and consistency across transactions
- Error Handling: Outlines procedures for detecting, reporting, and resolving discrepancies
Failing to meet these standards can result in costly chargebacks, damaged relationships, and ultimately, lost business opportunities.
Key Metrics That Define EDI SLA Success
Successful EDI implementations in supply chain operations depend on measurable performance metrics that define service quality. These key metrics establish clear expectations between trading partners and provide objective standards for evaluating EDI performance.

1. Transaction Processing Time: 850, 856, 810 Standards
The speed of EDI document processing represents a fundamental metric in any EDI SLA. This includes how quickly purchase orders (EDI 850), advance shipment notices (EDI 856), and invoices (EDI 810) move through the system. For instance, in retail environments, SLAs often specify maximum processing times for each transaction type to ensure timely order fulfillment.
2. Response Time for EDI 997 Acknowledgments
EDI 997 functional acknowledgments serve as digital receipts confirming successful document delivery and processing. Many trading agreements require sending these acknowledgments within specific timeframes—often within 24 hours of receiving a document. Monitoring acknowledgment timing helps identify potential system issues, as delayed 997s might signal problems with communication or processing.
3. System Uptime and Availability Benchmarks
Availability measures how consistently EDI systems remain operational and accessible. While uptime tracks raw system operation time, availability accounts for actual usability. High-availability EDI systems typically target 99.9% uptime (allowing approximately 129.6 minutes of downtime quarterly), though mission-critical supply chain operations often require 99.99% availability (permitting only 12.96 minutes of quarterly downtime).
4. Data Accuracy and Validation Rules
EDI validation verifies document integrity, accuracy, and compliance before transmission. This process includes:
- Syntax validation checking document structure and formatting
- Compliance validation ensuring adherence to industry guidelines
- Data integrity validation verifying completeness and correctness
5. Error Rate Thresholds and Resolution Timeframes
Most EDI SLAs establish acceptable error thresholds—commonly no more than 1% of transactions can contain errors. Equally important, SLAs define resolution timeframes, typically requiring error acknowledgment within 4 hours and predefined resolution windows of 24-48 hours to prevent supply chain disruptions.
Consequences of SLA Violations in EDI Supply Chains
The ripple effects of EDI SLA violations extend far beyond simple technical issues, often inflicting substantial damage to both finances and business relationships.
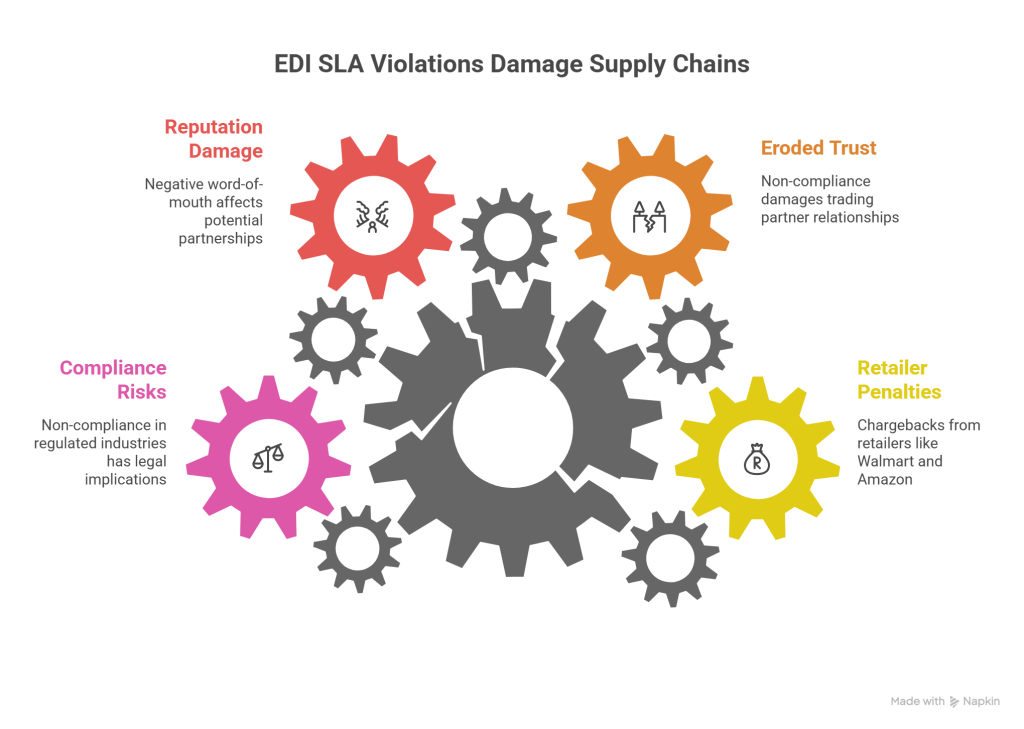
1. Chargebacks from Retailers like Walmart and Amazon
Failing to meet EDI requirements from major retailers results in immediate financial penalties. For instance, suppliers working with Walmart face strict On-Time In-Full (OTIF) penalties, considered among the strictest in the retail industry. Amazon, meanwhile, imposes various chargeback types through their Amazon Vendor Central portal, including Purchase Order On-Time Accuracy and Advance Shipment Notification (ASN) chargebacks. The financial impact is substantial—one retailer charges USD 3.00 per carton for ASN errors, whereas Amazon’s penalties for shipment-order mismatches can reach hundreds of thousands of dollars. Consequently, 66% of organizations reported losing up to USD 500,000 in 2020 due to EDI integration failures.
2. Impact on Trading Partner Relationships
Non-compliance with EDI SLAs fundamentally erodes trust between trading partners. When transactions are rejected, deliveries arrive late, or communication breaks down, the resulting business disruptions can severely damage established relationships. Furthermore, an organization’s score with trading partners can drop significantly, leading to reduced shelf space or even partnership termination.
3. Reputation Damage and Lost Business Opportunities
A company’s marketplace standing deteriorates quickly following repeated SLA violations. Nevertheless, the impact extends beyond current relationships—negative word-of-mouth spreads rapidly in today’s digital environment, affecting potential business partnerships. In fact, organizations struggling with EDI compliance often find themselves at a competitive disadvantage as potential partners choose more reliable alternatives.
4. Compliance Risks in Regulated Industries
Modern EDI requirements increasingly encompass additional compliance standards, including SOC2 compliance and personally identifiable information (PII) protection. Non-compliance, therefore, carries dual risks: financial penalties plus potential legal implications if regulated data is compromised.
Avoid these costly consequences with Commport EDI Solutions. The Leading EDI provider in North America With Over 6000+ Trusted Customers. Book a Free Consultation Today.
Tools and Practices to Monitor and Meet EDI SLAs
Maintaining EDI SLAs requires sophisticated monitoring tools and proactive practices that give supply chain managers control over their electronic transactions. As EDI complexity grows, manual monitoring becomes increasingly ineffective.
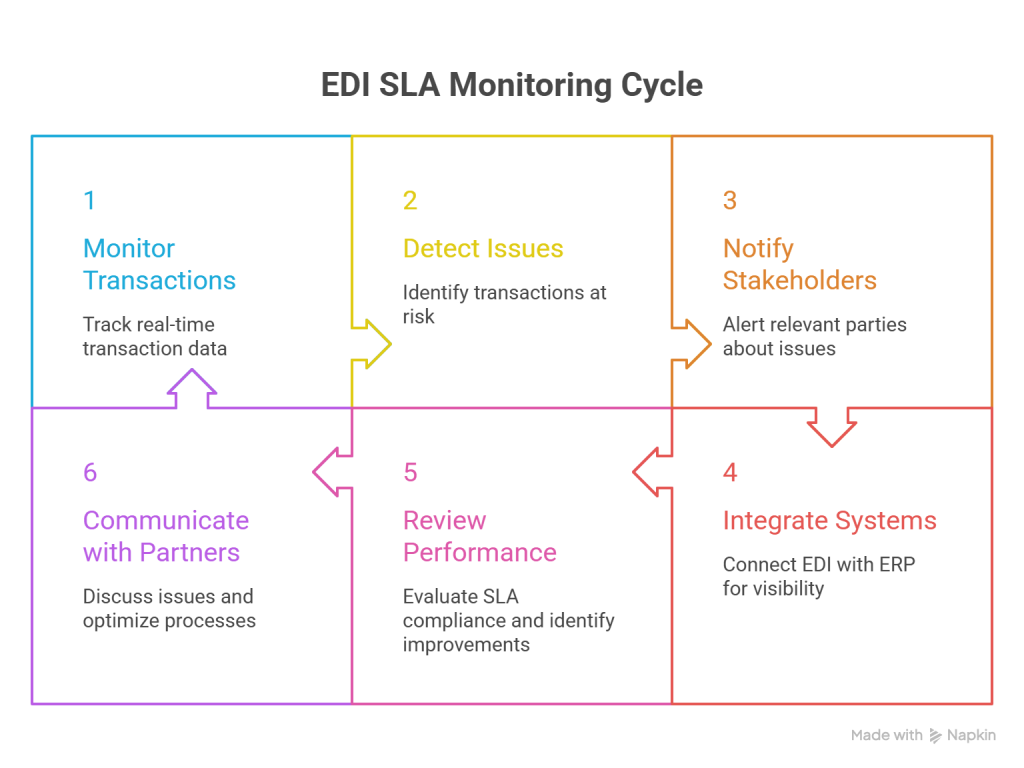
1. SLA Monitoring Dashboards in EDI Platforms
Modern EDI platforms include comprehensive dashboards that serve as command centers for your EDI operations. These visual interfaces transform raw transaction data into actionable insights, enabling teams to track the status of individual documents as they move between trading partners. Specifically, dashboards display real-time metrics on transaction throughput, processing times, and error rates – vital indicators of SLA compliance.
2. Automated Alerts for At-Risk Transactions
Proactive notification systems represent the front line of SLA defense. These alerts trigger when:
- Transactions fail or experience delays beyond defined thresholds
- Acknowledgments (997/999) are missing or delayed
- Processing times approach SLA limits
Notably, sophisticated alert systems escalate issues automatically if the primary contact doesn’t respond within a specified timeframe, ensuring critical problems don’t remain unaddressed.
3. Integration with ERP Systems for Real-Time Visibility
Integrating EDI with enterprise systems creates a unified view of your supply chain. This connection enables business users to instantly check transaction status without waiting in IT queues or digging through logs. Subsequently, teams can resolve problems before they impact customers or trigger SLA violations.
4. Periodic SLA Reviews and Partner Communication
Despite robust monitoring tools, regular communication remains essential. Schedule quarterly reviews of mapping accuracy and document flows to identify optimization opportunities. Track partner-specific performance against SLAs and address recurring issues before they damage relationships.
Ensure your EDI system meets all SLA requirements with Commport EDI Solutions. The Leading EDI provider in North America With Over 6000+ Trusted Customers. Book a Free Consultation Today.
Conclusion
EDI SLAs stand as critical components in today’s supply chain ecosystem. Throughout this article, we explored how these agreements establish the framework for successful business relationships between trading partners. Most notably, nearly 90% of retailers now mandate EDI compliance, making these standards non-negotiable for vendors seeking market access.
The key metrics we discussed—transaction processing times, acknowledgment response windows, system availability, data accuracy standards, and error thresholds—collectively determine whether your EDI operations succeed or fail. These benchmarks actually serve as the guardrails for effective supply chain communication, preventing costly disruptions before they occur.
Failure to meet established SLA requirements certainly carries significant consequences. Financial penalties from major retailers like Walmart and Amazon can reach hundreds of thousands of dollars. Additionally, repeated violations erode trading partner trust, damage marketplace reputation, and create compliance risks that extend beyond immediate financial impacts.
Proactive monitoring emerges as the best defense against these potential pitfalls. Dashboard solutions, automated alerts, ERP integration, and regular performance reviews together create a robust system for maintaining SLA compliance. These tools essentially function as early warning systems, allowing teams to address issues before they trigger violations.
Supply chain success in today’s digital marketplace depends largely on reliable information exchange. Therefore, mastering EDI SLA requirements provides a competitive advantage that extends beyond mere compliance. Companies that excel at meeting these standards ultimately build stronger partner relationships, reduce operational costs, and position themselves for sustainable growth in an increasingly connected marketplace.
Commport EDI Solutions - #1 Top Rated EDI Solutions in North America
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
Key metrics for EDI SLA performance include transaction processing times, response times for EDI 997 acknowledgments, system uptime and availability benchmarks, data accuracy rates, and error rate thresholds. These metrics help ensure efficient and reliable information exchange between trading partners.
An EDI SLA (Service Level Agreement) is a formal agreement between trading partners that defines the terms and conditions for electronic data interchange. It’s crucial in supply chain management as it establishes clear expectations for response times, data accuracy, and system availability, ensuring smooth and efficient operations between partners.
Violating EDI SLAs can result in significant financial penalties, such as chargebacks from major retailers. It can also damage trading partner relationships, harm a company’s reputation, lead to lost business opportunities, and create compliance risks in regulated industries.
Companies can use SLA monitoring dashboards in EDI platforms, implement automated alerts for at-risk transactions, integrate EDI with ERP systems for real-time visibility, and conduct periodic SLA reviews with trading partners. These tools and practices help identify and address potential issues before they lead to SLA violations.
EDI plays a crucial role in modern supply chain management by enabling automated, standardized electronic document exchange between trading partners. It streamlines processes, reduces manual errors, improves data accuracy, and facilitates real-time information sharing, which is essential for efficient supply chain operations in today’s fast-paced business environment.