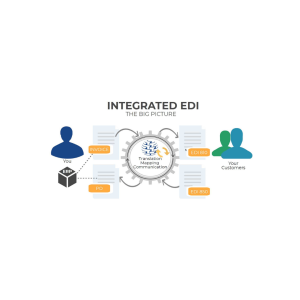
Introduction
EDI mapping is a cornerstone of modern business communication, enabling organizations to automate the transfer of data between disparate systems, streamline operations, and minimize human error.
This blog meticulously explores EDI mapping from foundational concepts to advanced practices, dissecting its technical intricacies, business value, solutions for common challenges, and emerging trends. Throughout, this guide highlights actionable insights, robust examples, and up-to-date statistics to empower enterprises aiming for operational excellence with EDI mapping
Ke Takeaways
- Universal Translator for Data: EDI mapping is the foundation of interoperability between disparate business systems, automating the secure, accurate flow of documents across organizations and industries.
- Boosts Efficiency and Reduces Errors: Automated mapping slashes processing times and minimizes manual errors, enabling companies to focus on strategic objectives rather than document handoffs.
- Supports Regulatory Compliance: Robust EDI mapping solutions ensure businesses meet industry standards for data exchange, privacy, and reporting—crucial for sectors like healthcare and retail.
- Scalable for Any Industry: Whether supporting global retailers, healthcare providers, or logistics firms, EDI mapping adapts to evolving needs, new partners, and advancing standards.
Define EDI Mapping
EDI mapping is a conversion process in which the translation of data structures from a proprietary file (in CSV format, txt, SAP IDoc, ERP-specific, etc.) to an EDI standard format (EDIFACT, ANSI X12, etc.) and vice versa.
Effective mapping ensures that data can flow seamlessly between trading partners, streamlining business operations, reducing manual data entry, and minimizing errors. Many organizations use specialized software and tools to facilitate the mapping process, making it more efficient and reliable.
Why EDI Mapping Matters
- Enables automated, accurate, and secure exchange of business documents.
- Reduces manual data entry and the associated cost of errors.
- Essential for compliance in industries like retail, healthcare, logistics, and manufacturing.
- Bolsters business agility, allowing organizations to onboard new partners or switch formats quickly.
How EDI Mapping Works
EDI mapping involves several well-defined steps, each of which is critical for ensuring smooth interoperability and reliable data exchange.
1. Data Analysis
The process starts by analyzing the source and destination data structures. Organizations must:
Catalog internal data sources (ERP, databases, flat files).
Identify each data element required for the business process (e.g., product codes, quantities, addresses).
Review the partner’s EDI implementation guide specifying their preferred EDI standard (ANSI X12, EDIFACT), transaction sets, codes, required segments, and elements.
2. Mapping Specification
Once data requirements are understood, the mapper defines explicit rules for translating every field in the internal format to its EDI equivalent, addressing:
Field-to-field correspondence (e.g., “OrderID” maps to “BEG03” in X12 850 Purchase Order).
Transformations (concatenation, splitting, formatting adjustments, and lookups).Default values, conditional logic, and cross-referencing product codes or units.
3. Data Transformation
With rules defined, mapping software or EDI middleware is used to implement the transformation. The engine takes source data and applies rules to output standardized EDI messages, which are then ready for transmission.
4. Testing and Validation
Rigorous testing is essential—sample transactions are run to catch errors and ensure correct translation and transmission, safeguarding operational reliability.
5. Implementation and Maintenance
The mapping is deployed in production, with ongoing monitoring to ensure accuracy as business requirements, trading partners, or EDI standards evolve.
EDI Mapping Example
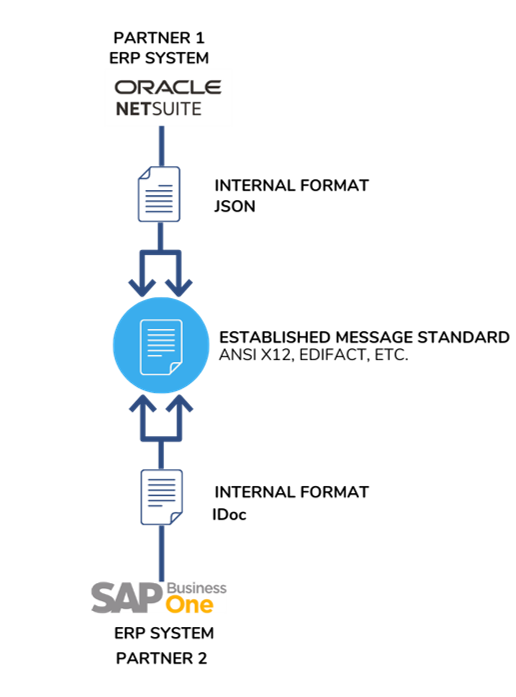
Mapping EDI data to ERP data structures are translated from an EDI standard format (EDIFACT, ANSI X12, etc.) to a proprietary file that can be easily ingested into a back-end system (CSV format, txt, SAP IDoc, Flat File, or any ERP specific format).
- As shown in the diagram, trading partner 1 uses Oracle ERP which uses a JSON internal format and trading partner 2 uses the SAP ERP system with IDoc internal format. To communicate a message to trading partner 2, that JSON file needs to be converted into an EDI transaction and sent to trading partner 2 using a standardized EDI Format like ANSI X12 or EDIFACT.
- Now since trading partner 2 ERP uses iDoc for its internal format, the EDI file is converted into an iDoc file before being ingested into SAP ERP.
- Mapping for EDI systems is bilateral so EDI providers like Commport, map the data flow in both directions.
EDI Standards and Mapping Complexity
Two dominant EDI standards shape mapping globally:
ANSI X12: Common in North America, covers documents like 850 (Purchase Order), 810 (Invoice), 856 (ASN).
EDIFACT: Used internationally, supporting global trade and logistics.
Each standard contains hundreds of transaction sets, segments, and elements—mapping accuracy is essential for regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Benefits of EDI Mapping
Mapping is a crucial component to meeting trading partner demands, eliminating manual entry, while streamlining the movement of data from front-end to back-end systems.
Automation –Automatically send external data to critical internal systems which creates a repeatable process not touched by human input.
Accuracy – Eliminate the manual processing which eliminates the risk for user error, and in turn ensures EDI data is accurately imported into back-end systems.
Connection – Allows for the creation of formats like XML or flat file which can easily be used to communicate EDI data to business trading partners.
Conclusion
EDI mapping facilitates the seamless translation of data between different formats. This process ensures compatibility between the internal systems of trading partners, enabling the efficient exchange of standardized business documents. It is a critical component in achieving interoperability and smooth communication in the global business landscape.
Ready to find out more about Commport EDI Solutions?
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
EDI mapping is the process of translating data between different formats to enable the smooth exchange of business documents in Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). It involves mapping data fields from one system to another, ensuring compatibility between trading partners.
It is necessary to bridge the gap between the internal data structures of different business systems. It ensures that data can be accurately and seamlessly exchanged between trading partners, promoting interoperability and efficient communication.
It involves creating a translation map that defines the relationship between data elements in the sender’s format and those in the receiver’s format. This map guides the transformation of data during the EDI exchange, ensuring proper interpretation on both ends.
Yes, businesses can perform EDI mapping in-house if they have the expertise and resources to create and manage mapping solutions. However, many organizations opt for EDI service providers or software solutions that offer pre-built maps for common transactions.
It is not a one-time process. It may require ongoing maintenance, especially when there are changes in data structures, formats, or when new trading partners are onboarded. Regular updates and monitoring help ensure the continued accuracy of data exchange.