Introduction
EDI SAP integration automates how businesses exchange critical documents and manage their supply chains, ensuring data flows seamlessly between systems and partners.
While many organizations rely on this technology daily, mastering its implementation requires specialized knowledge that shouldn’t depend on a single team member. In fact, Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) with SAP systems enables the automatic transmission of the right data at the right time, significantly reducing manual work, minimizing errors, and accelerating transaction processing.
What is SAP EDI exactly?
At its core, SAP EDI refers to the standardized electronic exchange of business documents between SAP systems and trading partners.
Common SAP EDI transactions include
- EDI 850 (purchase orders sent from buyers to suppliers)
- and EDI 810 (invoices sent from suppliers to buyers).
Additionally, these transactions follow specific standards—primarily X12 in North America and EDIFACT in Europe. Therefore, understanding these regional differences becomes crucial when implementing an effective EDI solution within your SAP environment.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore everything you need to know about successfully implementing and managing EDI SAP integration. From choosing the right integration method to overcoming common challenges, we’ve created this resource specifically for IT leaders looking to optimize their document exchange processes and supply chain operations.
Key Takeaways
- Choose integration method strategically: Direct integration works for simple setups, middleware handles multiple formats, while cloud-based solutions offer superior scalability for growing businesses.
- Focus on core EDI transactions: Master purchase orders (850), shipping notices (856), and invoices (810), as these form the foundation of most business communications.
- Plan implementation systematically: Identify required document types, configure IDocs and communication ports, map partner profiles, and conduct thorough testing before production deployment.
- Address common challenges proactively: Standardize multiple EDI formats, align business processes across partners, secure adequate technical resources, and implement robust security measures.
- Leverage modern tools effectively: Use SAP Cloud Platform Integration for scalability, SAP PI/PO for on-premise control, or specialized third-party solutions for complex requirements.
Understanding EDI in SAP Context
Electronic data interchange serves as the backbone of automated communication between SAP systems and trading partners. Unlike traditional methods that relied on paper-based processes, modern EDI SAP integration enables businesses to exchange standardized business documents digitally without human intervention. This section explores the fundamentals of EDI in the SAP environment, its key transactions, and integration aspects.
How to read an EDI File?
Each line of the file is referred to as a segment. Each EDI file starts with ISA (Interchange Control Header) segment and ends with IEA (Interchange Control Trailer) segment.
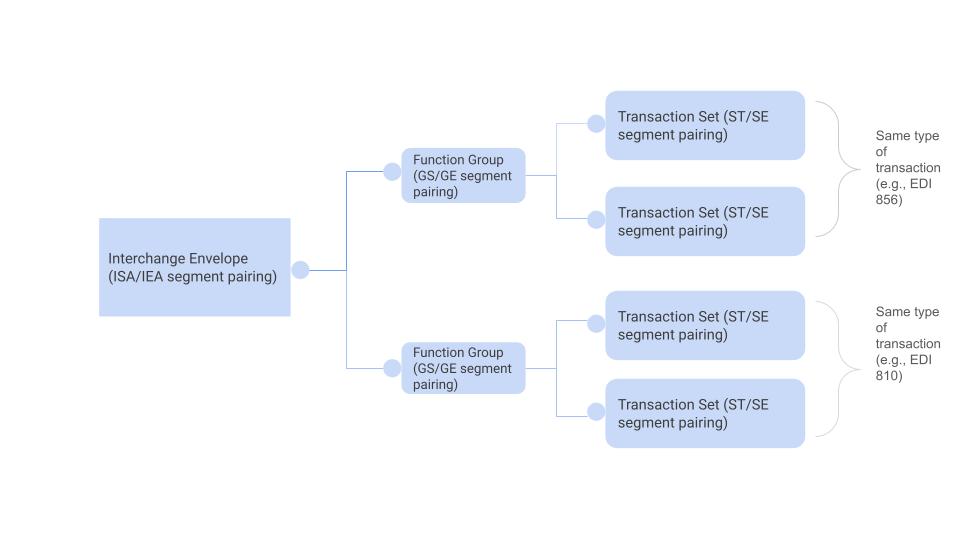
There can be ‘n’ number of GS/GE segment pair. Each GS segment can have ‘n’ number of transaction set (SE/ST segment pair) of same type.
ISA (Interchange Control Header) Segment
ISA is a fixed-length positional.
| Element Name | Usage | Sample Value |
| ISA01 | Authorization Info Qualifier. Fixed length – 2. Code ’00’ indicates that no authorization information present in ISA02 | 00 |
| ISA02 | Authorization Information. Fixed length – 10 | Ten spaces |
| ISA03 | Security Info Qualifier. Fixed length – 2. Code ’00 ‘indicates that no security information present in ISA04. | 00 |
| ISA04 | Security Information. Fixed length – 10 | Ten spaces |
ISA-01 through ISA-04 are hardly used anymore and that is why these are kept as 00 and blank now-a-days.
| Element Name | Usage | Sample Value |
| ISA05 | Interchange Sender ID Qualifier. Fixed length -2 . Used to define the ID sent in the ISA06. | ZZ |
| ISA06 | Interchange Sender ID. Fixed length – 15 | SRCA |
| ISA07 | Interchange Receiver ID Qualifier. Fixed length – 2. Used to define the ID sent in the ISA08. | ZZ |
| ISA08 | Interchange Receiver ID. Fixed length – 15 | DSTB |
The commonly used qualifiers for ISA05/ISA07 are –
- 01 (DUNS: Dun & Bradstreet’s master Data Universal Numbering System)
- 12 (Telephone number)
- ZZ (Mutually Defined)
| Element Name | Usage | Sample Value |
| ISA09 | Interchange Date. Fixed length – 6. Format – YYMMDD | 231116 |
| ISA10 | Interchange Time. Fixed length – 4. Format – HHMM | 1700 |
| ISA11 | Code to identify the agency responsible for the control standard used by the message. Fixed length – 1. ‘U’ stands for ‘U.S. EDI Community of ASC X12’ | U |
| ISA12 | EDI Version Number. Fixed length – 5 | 00401 |
| ISA13 | Control number for tracking purpose. It must match with IEA02. Fixed length – 9 | 000001000 |
| ISA14 | Acknowledgement Requested (TA1). Code ‘0’ indicates that no acknowledgment has been requested. | 0 |
| ISA15 | Usage Indicator. Code ‘P’ indicates that the interchange envelope contains production data. ‘T’ indicates non-prod data | T |
| ISA16 | Component/Sub Element Separator. The delimiter used to separate component data elements within a composite data structure; this value must be different than the data element separator and the segment terminator. | > |
In the above example, * is element separator.
CRLF is segment separator.
Sub element separator
PID represents product description.
PID01 = F, which means free-form
PID05 is using component separator. It has 2 parts. 1st part is CNT HSN10201, 2nd part is 700. This is just an example for showing how to use sub element separator. Always refer to partner’s EDI implementation guidelines for actual usage.
IEA (Interchange Control Trailer) Segment
| Element Name | Value |
| IEA01 | Count of the GS segments |
| IEA02 | Must match with ISA13 |
GS (Functional Group Header) Segment
| Element Name | Description | Sample Value |
| GS01 | Functional Identifier Code | PO |
| GS02 | Application Sender’s Code | SRCA |
| GS03 | Application Receiver’s Code | DSTB |
| GS04 | Date (CCYYMMDD) | 20231116 |
| GS05 | Time (HHMM) | 1700 |
| GS06 | Group Control Number | 1000 |
| GS07 | Responsible Agency Code | X |
| GS08 | Version / Release / Industry Identifier | 004010 |
GE (Functional Group Trailer) Segment
| Element Name | Description | Sample Value |
| GE01 | Number of Transaction Sets Included | 1 |
| GE02 | Group Control number. Must match GS06 | 1000 |
ST (Transaction Set Header) Segment
| Element Name | Description | Sample Value |
| ST01 | Transaction Set Identifier Code | 850 |
| ST02 | Transaction Set Control Number | 000000010 |
SE (Transaction Set Trailer) Segment
| Element Name | Description | Sample Value |
| SE01 | Total number of segments included in a transaction set including ST and SE segments | 20 |
| SE02 | Transaction Set Control Number. Must Match ST02. |
000000010 |
Example
Here,
- This is an original (BEG01 -> 00) and stand-alone (BEG02 -> SA) purchase order
- 08292233294 is the PO number (BEG03) and PO date is 16th Nov, 2023 (BEG05)
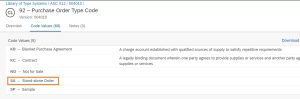
- Reference Department (REF01) is 038 (REF02)
- Requested delivery date (DTM01 -> 002) is 25th Nov, 2023 (DTM02)
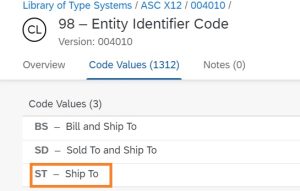
- Ship To (N101) XYZ RETAIL (N102), Ship to Address is 91875 SOLON RD (N301), SOLON (N401), Ohio (N402), ZIP code – 44139 (N403), US (N404)
- 6 PO line items (CTT01 – is the accumulation of the number of PO1 segments)
Qualifier List
In the above example, I have mentioned some of the qualifiers. All the list of values are present in Code list of Integration Advisor.
BEG01: 00
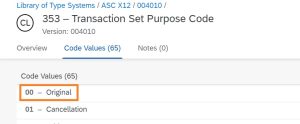
BEG02: SA
 https://community.sap.com/
https://community.sap.com/
REF01: DP
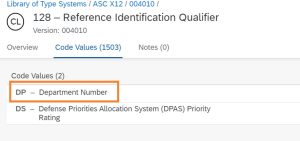
DTM01: 002
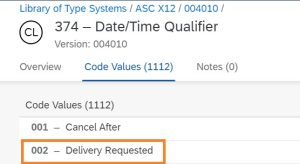
N101: ST
 https://community.sap.com/
https://community.sap.com/
What is SAP EDI and Why it Matters
SAP EDI represents the specialized implementation of electronic data interchange within SAP systems, enabling automated communication between an organization’s SAP ERP and external partners’ systems. Essentially, it acts as a digital bridge that facilitates the secure, automated exchange of vital business information through standardized formats.
At its core, SAP EDI relies on Intermediate Documents (IDocs) – SAP’s proprietary format that functions as a vessel carrying business transaction data between systems. These IDocs serve as the foundation for both internal and external communications, replacing less secure methods such as couriers, faxes, and emails.
The importance of EDI SAP integration becomes apparent when examining its business impact:
- Eliminates manual data entry and human errors
- Accelerates transaction processing and business cycles
- Ensures standardized communication across trading partners
- Improves data accuracy throughout supply chain operations
- Reduces operational costs by automating document exchange
Common SAP EDI Transactions:
The SAP EDI transactions framework supports numerous business documents, but three transaction types form the cornerstone of most implementations:
EDI 850 (Purchase Order): Initiates product or service orders from buyers to suppliers. This transaction contains critical information, including item descriptions, quantities, pricing, and delivery dates.
EDI 856 (Advanced Shipping Notice/ASN): Notifies buyers that shipments are en route. The ASN includes package contents, carrier details, tracking numbers, and estimated delivery dates, allowing for better inventory planning and receiving operations.
EDI 810 (Invoice): Enables suppliers to send digital billing documents requesting payment for delivered goods or services. This transaction includes comprehensive details about items, quantities, pricing, and payment terms.
Beyond these core transactions, SAP EDI supports numerous other document types, including order acknowledgments (855), inventory inquiries (846), and payment remittance advice (820). Each transaction type follows specific standards such as ANSI X12 (predominantly used in North America) or EDIFACT (common in Europe and international trade).
How EDI fits into SAP ECC and S/4HANA
SAP EDI integration with ERP systems occurs at multiple touchpoints across business processes.
For SAP customers using either ECC or S/4HANA, EDI messages can be seamlessly mapped into IDocs and directly posted into the system. This integration typically happens through:
- Procure-to-Pay (P2P): Automates the exchange of purchase orders, acknowledgments, shipping notifications, and vendor invoices between SAP and suppliers.
- Order-to-Cash (O2C): Supports customer-facing processes by sending order confirmations, delivery notes, and invoices to customers, streamlining sales and fulfillment workflows.
- Logistics Execution: Integrates with warehouse and shipping functions through IDocs for delivery processing, shipment notifications, and goods movement.
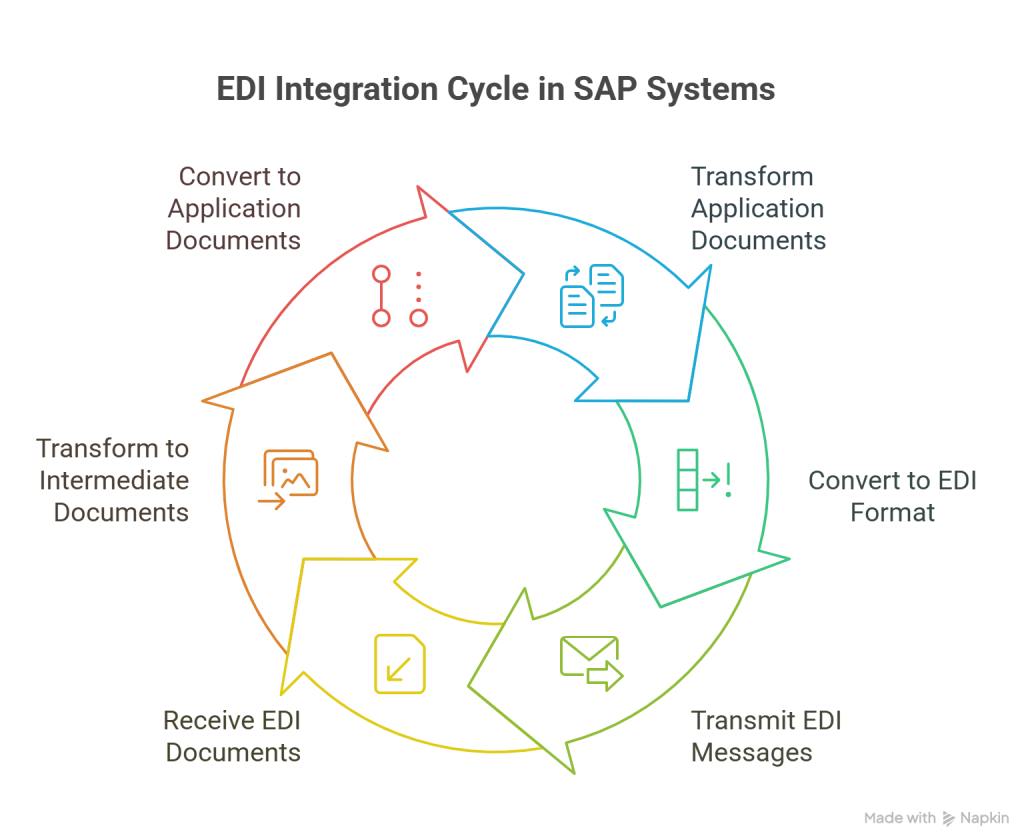
The integration mechanism primarily follows two distinct workflows:
- Outbound Process: Transmits data from SAP to external systems by transforming application documents into intermediate documents, converting them to EDI format, and sending them to recipients.
- Inbound Process: Receives EDI documents from external sources, transforms them into intermediate documents, and then converts them into application documents that SAP can process.
Furthermore, organizations can implement the SAP EDI solution through various approaches, including third-party EDI platforms, SAP’s own products like SAP Process Orchestration, or SAP Cloud Platform integration. Each approach offers different benefits depending on an organization’s specific requirements, existing infrastructure, and partner ecosystem.
Choosing the Right SAP EDI Integration Method
Selecting an appropriate EDI SAP integration approach requires careful consideration of your organization’s specific needs, technical capabilities, and business objectives. As organizations migrate toward cloud-based ERP systems like S/4HANA, the method you choose can significantly impact scalability, efficiency, and future growth potential. Let’s examine the three primary integration methods available for SAP EDI implementations.

1. Direct Integration: When Simplicity Works
Point-to-point or direct integration establishes a straightforward connection between your SAP system and trading partners without intermediary components. This approach works particularly well for organizations with straightforward requirements and a limited number of trading partners.
Direct integration offers several distinct advantages:
- Faster transmission speeds with reduced latency
- Greater control over EDI transactions
- Lower operational costs without third-party intermediary fees
- Simplified architecture without additional integration layers
Nevertheless, this method becomes problematic as your trading partner network expands. According to industry experts, direct EDI is “the least scalable of options” because connections running in too many directions create excessive complexity. Moreover, maintaining numerous direct connections requires substantial technical expertise and ongoing support resources.
Direct integration makes the most sense for organizations with stable, well-defined trading relationships that prioritize speed and control over scalability.
2. Middleware Integration: Handling Multiple Formats
Middleware integration introduces a specialized translation layer between your SAP system and external partners. This approach excels at converting different data formats in real-time, enabling seamless communication between disparate systems.
Key middleware options for SAP EDI solution implementations include:
- SAP Process Integration/Process Orchestration (PI/PO) for on-premise environments
- Value-Added Networks (VANs) that provide mailbox-style routing services
- Specialized EDI translation engines with SAP-specific connectors
The primary strength of middleware lies in its ability to normalize communications across multiple standards and formats. This capability proves particularly valuable when dealing with partners who utilize different EDI standards, protocols, or document formats.
Middleware integration typically requires more technical expertise to set up initially but delivers significant benefits for organizations managing complex supply chains with diverse partner requirements. SAP PI/PO, specifically, offers a centralized platform for managing EDI communication while providing direct integration with SAP business systems.
3. Cloud-Based Integration: Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud-based EDI SAP integration represents the newest approach and continues gaining popularity due to its compelling operational benefits. This model leverages internet-based platforms—often provided by third-party services—to manage the entire EDI lifecycle.
Notably, cloud integration offers:
- Reduced hardware and software maintenance requirements
- Simplified partner onboarding processes
- Pay-as-you-go pricing models that align costs with actual usage
- Enhanced scalability to accommodate growth
SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) exemplifies this approach, providing a centralized cloud platform for managing EDI communications. It supports multiple communication protocols, including AS2, SFTP, and FTPS, while offering pre-built adapters for various applications.
For enterprises running SAP S/4HANA, cloud-based EDI integration provides powerful capabilities for managing high transaction volumes and optimizing workflows across the entire supply chain. Cloud integration particularly benefits multi-threaded processing requirements, enabling businesses to handle multiple transactions simultaneously—a critical advantage for high-volume manufacturers and distributors.
Commport EDI simplifies integration with SAP. Trusted by over 6,000+ brands globally. Let our Commport team of experts help you with your next EDI SAP integration.
Consequently, organizations should evaluate each integration method against their specific business requirements, existing infrastructure, technical resources, and growth projections. The optimal SAP EDI approach balances immediate operational needs with long-term strategic objectives, ensuring your EDI foundation supports both current and future business processes.
Step-by-Step SAP EDI Implementation Guide
Implementing EDI SAP integration requires careful planning and execution across multiple technical areas. First, let’s explore the step-by-step process for setting up this critical business communication channel within your SAP environment.
1. Identifying Required EDI Document Types
Before configuration begins, you must determine which document types your business processes require. Common EDI documents include purchase orders (850), shipping notices (856), and invoices (810). Sales and Distribution (SD) Partners are mandatory components of any sales order and serve as key data elements for EDI interchange. Generally, both communication partners (senders and receivers) and business partners (suppliers, buyers, and delivery points) must be identified prior to implementation.
2. Setting up iDocs and Communication Ports
Intermediate Documents (IDocs) form the foundation of SAP EDI communication. To establish this framework, you’ll need to:
- Configure your SAP system to generate appropriate IDoc types for your business documents
- Set up communication ports that define how your SAP system connects with external partners
- Establish appropriate routing rules based on your business requirements
During this phase, Partner type LS (logical system) can be utilized for testing purposes, allowing you to validate configurations before connecting with actual trading partners.
3. Mapping Partner Profiles and Document Formats
Partner profiles define how your SAP system identifies and communicates with trading partners. To create these essential mappings:
- Set up partner profiles in EDI Basis using transaction code WE20
- Map external partner identifiers (such as GLNs) to internal SAP partner numbers using the EDPAR table (transaction code VOE4)
- Create a new partner at the Partner level with Partner type KU
This mapping process enables your SAP EDI solution to route documents and apply the appropriate processing rules correctly. Additionally, the system requires proper maintenance of conversion between external identifiers and SAP master data, including Sold-to Party, Ship-to Party, and Sales Organization data.
4. Testing and Validation of EDI Transactions
Once configurations are complete, thorough testing becomes essential. Initially, use test partner profiles with Partner type LS to validate basic connectivity. Subsequently, test each transaction type individually before attempting end-to-end process validation. Throughout testing, verify that:
- External partner identifications correctly map to internal SAP partner numbers
- Documents flow properly through communication channels
- Business validations execute correctly
- Error handling works as expected
Furthermore, examine both outbound and inbound processes, as each follows distinct workflows requiring separate validation. The complete EDI SAP integration process demands meticulous attention to detail, yet yields substantial business benefits when properly implemented.
Key Tools and Technologies for SAP EDI Integration
Selecting the right tools for your SAP EDI ecosystem impacts implementation success and ongoing operations. Currently, several technologies exist to facilitate effective EDI SAP integration, each offering distinct advantages depending on your infrastructure and business requirements.
1. Using SAP PI/PO for On-premise Integration
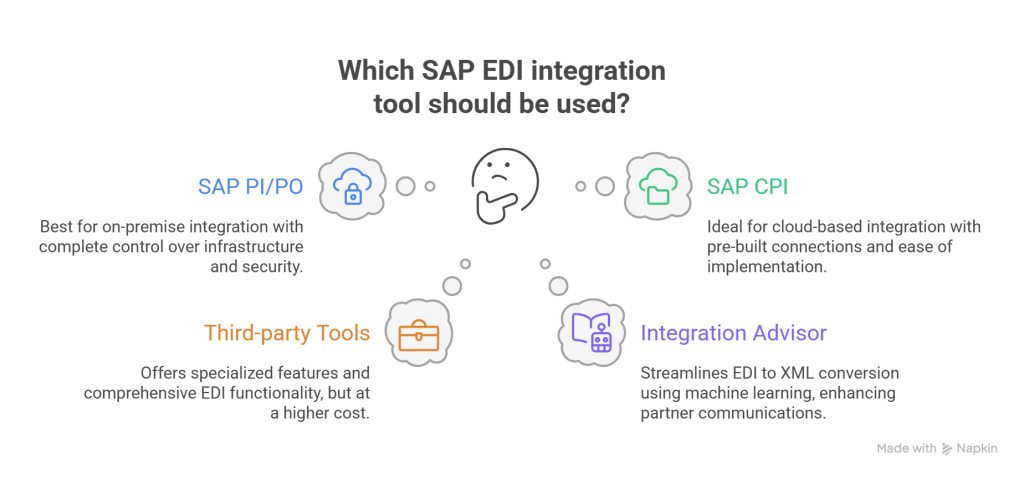
SAP Process Integration/Process Orchestration (PI/PO) serves as a comprehensive tool for managing electronic communications within on-premise environments. This platform centralizes all EDI communications while offering robust document format conversion capabilities and thorough monitoring of document flows. PI/PO excels at handling complex integration scenarios across both SAP and non-SAP applications. Since it operates locally instead of in the cloud, it provides organizations with complete control over their integration infrastructure and security protocols.
2. SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) Overview
For cloud-based integration needs, SAP Cloud Platform Integration (CPI) offers a modern alternative that runs entirely online. This Platform-as-a-Service solution includes pre-built connections for common business scenarios while eliminating the need to maintain dedicated servers. CPI typically proves easier to implement than traditional integration tools. Indeed, SAP S/4HANA Cloud users can leverage SOAP APIs maintained by SAP on the API Business Hub, providing more modern, extensible and structurally simplified integration options.
3. Third-party EDI Tools: Pros and Cons
Many organizations opt for third-party integration tools that often deliver specialized features unavailable in standard SAP tools. These solutions frequently offer industry-specific capabilities and enhanced support services. Altogether, third-party options may provide more comprehensive EDI functionality for companies with large supply chains. The primary drawback remains their typically higher cost compared to using SAP’s built-in tools.
4. EDI to XML Conversion Using Integration Advisor
SAP’s Integration Content Advisor (ICA) represents a breakthrough for edi integration sap. This crowd-based machine learning tool runs on SAP Cloud Platform Integration, creating and maintaining B2B integration content faster and more efficiently than previous methods. ICA streamlines the conversion between EDI formats and XML, simplifying partner communications regardless of their preferred document standards.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Despite technical advancements, implementing EDI SAP integration presents several obstacles that organizations must address. Let’s examine these challenges alongside practical solutions.

1. Handling Multiple EDI Standards and Formats
Organizations often struggle with managing various standards simultaneously—ANSI X12, EDIFACT, and proprietary formats—especially when dealing with international partners. This complexity frequently causes message translation errors and communication breakdowns. To overcome this challenge:
- Implement a centralized translation engine capable of handling multiple standards
- Create comprehensive mapping templates for recurring document types
- Establish clear validation rules for each format
2. Aligning Business Processes Across Partners
Even perfectly configured SAP EDI systems can falter when business processes don’t align across organizations. Critical issues arise from mismatched expectations about order handling, shipping procedures, or invoicing practices. Successful alignment requires:
- Documenting end-to-end processes with all partners
- Agreeing on transaction timelines and response expectations
- Creating exception handling procedures for non-standard situations
3. Managing Technical Resources and Support
Many companies face resource constraints when implementing EDI SAP integration. Although the technical skills required for effective maintenance extend beyond standard SAP expertise, few organizations maintain dedicated EDI specialists. Address this gap by:
- Establishing clear operational responsibilities
- Developing comprehensive documentation
- Creating ongoing training programs
- Considering managed services for specialized support
4. Ensuring Data Security and Compliance
As EDI SAP transactions often contain sensitive business information, security becomes paramount. Yet compliance requirements continuously evolve, creating ongoing challenges. Protect your integration by:
- Implementing strong encryption for all transmissions
- Establishing comprehensive audit trails
- Regularly reviewing security protocols
- Automating compliance checks within your SAP EDIsolution
Commport - Contax Partnership
Commport, a leader in data integration, is teaming up with CONTAX, an expert in SAP and Acumatica solutions. Together, they’re offering integrated EDI (Electronic Data Interchange) solutions that act as the digital bridge between your company and your trading partners. Think of it as a seamless data highway where information flows effortlessly, without the manual errors and delays that can slow you down.
What This Means for Your Business
This partnership is built on the idea of making your life easier. By combining Commport’s expertise in handling electronic data with CONTAX’s deep knowledge of powerful ERP systems, you can achieve:
- Seamless Connectivity: Get a robust connection that ensures your data exchanges with suppliers and customers are reliable and fast.
- Streamlined Operations: Automate manual tasks and eliminate the need for time-consuming data entry, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic work.
- Enhanced Data Accuracy: Reduce errors and inconsistencies, leading to better decision-making and fewer costly mistakes.
Conclusion
Mastering EDI SAP integration stands as a critical capability for modern businesses seeking to streamline their supply chain operations. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the fundamental aspects of implementing effective electronic data interchange within SAP environments. The standardized exchange of business documents like purchase orders (850), shipping notices (856), and invoices (810) essentially eliminates manual processes while significantly reducing errors.
Choosing the right integration method—whether direct, middleware, or cloud-based—depends largely on your organization’s specific requirements and growth projections. Each approach offers distinct advantages, with cloud-based solutions providing superior scalability for expanding businesses. Consequently, your selection should balance immediate operational needs against long-term strategic objectives.
The implementation process requires careful planning, from identifying required document types to configuring IDocs and communication ports. Therefore, thorough testing becomes essential before moving to production. Additionally, selecting appropriate tools such as SAP PI/PO, Cloud Platform Integration, or third-party solutions will impact both implementation success and ongoing operations.
Organizations must also address common challenges including multiple EDI standards, business process alignment, technical resource management, and data security. Certainly, these obstacles can be overcome with proper planning and expertise. Commport EDI simplifies integration with SAP. Trusted by over 6000+ brands globally. Let our Commport team of experts help you with your next EDI SAP integration.
Successfully implemented EDI SAP integration transforms how businesses exchange information with trading partners. This transformation leads to faster transaction processing, improved data accuracy, and reduced operational costs. Most importantly, it positions your organization to respond more effectively to changing market demands while maintaining seamless communication throughout your supply chain network.
Commport EDI SAP Integration Services
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
Implementing EDI in SAP involves mapping EDI to SAP IDoc, configuring communication ports, setting up partner profiles, and creating process orchestrations for inbound and outbound messages. Thorough testing of each transaction type is crucial before going live.
While both enable system integration, EDI is specifically designed for standardized B2B document exchange, whereas APIs allow software to access functions in other applications. EDI is more structured and widely used for supply chain communications, while APIs offer more flexibility for various integration scenarios.
The most frequently used EDI transactions in SAP are EDI 850 (purchase orders), EDI 856 (advanced shipping notices), and EDI 810 (invoices). These form the core of automated business document exchange between trading partners.
The choice depends on your specific needs. Direct integration works well for simple setups with few partners. Middleware is ideal for handling multiple formats. Cloud-based solutions offer the best scalability and flexibility, especially for growing businesses or those transitioning to S/4HANA.
To address common challenges, organizations should standardize multiple EDI formats, align business processes with partners, secure adequate technical resources, and implement robust security measures. Regular training, comprehensive documentation, and considering managed services for specialized support can also help overcome implementation hurdles.