Introduction
The GS1 Global Data Model (GDM) represents a revolutionary approach to standardizing product information exchange across global supply chains. This comprehensive framework harmonizes product attributes, creates unified data standards, and enables seamless communication between trading partners worldwide. By implementing harmonized product attributes through the GS1 Global Data Model, businesses can achieve unprecedented levels of operational efficiency, data accuracy, and supply chain transparency.
Core Objectives of GS1 GDM:
- Harmonization: Create one global language of product data.
- Efficiency: Reduce time spent reconciling inconsistent product attributes.
- Scalability: Enable global expansion without data fragmentation.
- Trust: Build consistency in how consumers and trading partners view product data.
With the rise of omnichannel commerce and digital shelf demands, the GS1 GDM provides the foundation for interoperability between systems like ERP, PIM, GDSN, and eCommerce platforms.
GS1 Global Data Model - One product. One experience. Every channel.
Key Takeaways
- The GS1 Global Data Model ensures harmonized product attributes, reducing inefficiencies and inconsistencies across industries.
- Businesses adopting GDM can accelerate product launches, cut costs, and build greater consumer trust.
- Supporting technologies like PIM and GDSN are essential for successful implementation and scalability.
- Challenges exist, but the future promises innovation through AI, 2D barcodes, and digital product passports.
- Ultimately, the GS1 GDM is not just about compliance—it’s about creating a globally trusted product data ecosystem.
Why GS1 is Developing a Global Data Model?
As global commerce grows increasingly fragmented, each marketplace and stakeholder presents unique data demands. This complexity often leads to escalating data management expenses and inconsistent data quality throughout the value chain.
1. Challenges for Brand Owners
Brand owners are frequently tasked with producing data formats tailored to individual retailers, complicating efforts to expand into new channels or regions. The necessity to support hundreds of unique formats heightens the risk of losing control over data integrity, potentially resulting in missed sales opportunities and diminished brand reputation.
- Over 1,000 new SKUs introduced annually
- 700 attributes managed per SKU
- 500 unique formats required for global retail partners
2. Retailer Struggles
Retailers invest significant resources in verifying basic product data and chasing down missing or incorrect details. Synchronizing product content across online and offline platforms becomes a daunting challenge when data formats vary widely, leading to operational delays and inefficiencies.
- 10 to 15 supplier interactions needed to launch each SKU
- Roughly 15,000 incidents of inaccurate product data per year
- 5–10 hours dedicated to onboarding and training for brand partners
3. Omni-Channel Consumer Expectations
While physical shoppers can interact with products and access reliable packaging information, digital consumers must rely on online product data that’s often scarce or inconsistent. This gap leads to confusion, frequent returns, and lost sales.
- 89% of shoppers use their phones to research while shopping
- 54% conduct research at home before purchasing
- Product return rates range from 10–30%, depending on the sector
A Unified Industry Response
To address these challenges, over 30 leading organizations are joining forces with GS1 to create the GS1 Global Data Model. This collaborative initiative includes pilot programs and strategic business case development to drive harmonization and efficiency in product data exchange.
Understanding the GS1 Global Data Model Foundation
The GS1 Global Data Model serves as the cornerstone of modern supply chain data management, establishing a standardized set of product attributes necessary for listing, ordering, moving, storing, and selling products globally. This data model addresses the increasing complexity of product information exchange by providing a unified framework that transcends geographical and industry boundaries.
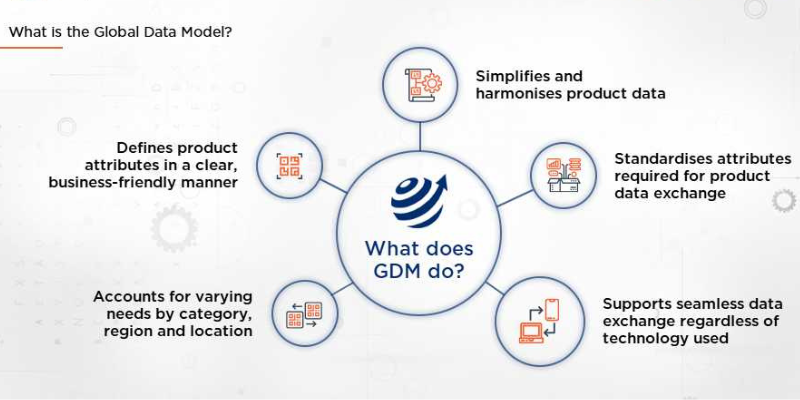
The complexity of today’s product data exchange poses significant challenges for brands and retailers. Divergent product standards have been categorized as major obstacles to international trade, with research indicating that standard harmonization can increase product-level trade flows by 67%. The GS1 Global Data Model directly addresses these challenges by simplifying and harmonizing global data exchange, enabling faster, less expensive, and more accurate data creation and distribution.
The Business Imperative for Standardization
Organizations increasingly recognize the critical importance of standardized product information management. The global supply chain analytics market, valued at $9.39 billion in 2024, is projected to reach $32.27 billion by 2033, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 16.69%. This substantial growth reflects the heightened demand for accurate, standardized data that reduces inefficiencies throughout the supply chain.
The GS1 Global Data Model enables organizations to achieve significant operational improvements. Companies implementing standardized product data management systems report up to 25% faster processing of product information compared to traditional methods. Furthermore, businesses that prioritize product data quality experience 25% fewer product returns on average, which directly impacts customer satisfaction and operational costs.
Architectural Framework: Layered Structure of the Global Data Model
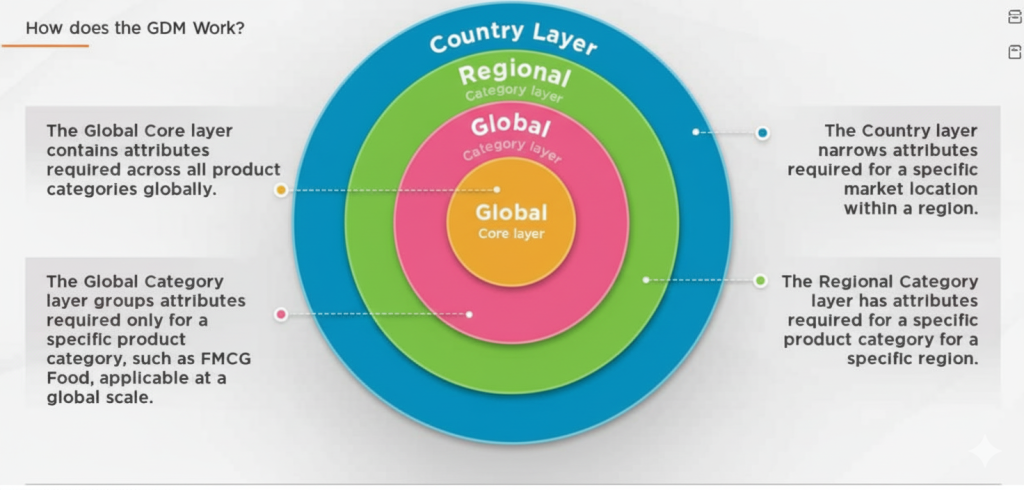
The GS1 Global Data Model employs a sophisticated layered architecture designed to accommodate varying regional requirements while maintaining global consistency. This hierarchical structure consists of four distinct layers: Global Core, Global Category, Regional Category, and Country layers.

1. Global Core Layer
The Global Core Layer comprises attributes required across all product categories, establishing fundamental data elements necessary for basic product identification and exchange. These universal attributes ensure consistent product information regardless of geographical location or industry sector. Key elements include basic identification data, fundamental product characteristics, and essential trading partner information.
2. Global Category Layer
The Global Category Layer contains attributes specific to particular product categories applicable at a global level. These category-specific requirements address the unique data needs of different product types while maintaining global applicability. For instance, storage temperature requirements are mandatory for meat products but not applicable to non-perishable goods.
3. Regional Category Layer
The Regional Category Layer incorporates attributes required for specific product categories within designated regions. These attributes address regional regulatory requirements, consumer preferences, and market-specific needs. For example, allergen statement requirements are mandatory in North America due to regulatory compliance but may not be required in other regions.
4. Country Layer
The Country Layer encompasses attributes required for specific product categories within individual countries. These localized requirements address nation-specific regulations, cultural preferences, and market dynamics. Examples include packaging material quantity requirements that vary by country or specific labeling mandates unique to particular markets.
Harmonized Product Attributes: Core Components and Implementation
Inconsistent product data leads to inefficiencies, regulatory challenges, and customer dissatisfaction. According to a survey by Gartner, 30% of organizations believe poor product data quality costs them over $15 million annually.
Key Problems Without Harmonization:
- Duplicate Efforts – Different retailers demand different formats, requiring suppliers to duplicate work.
- Inaccurate Product Information – Consumers lose trust when product details differ across platforms.
- Regulatory Risks – Failure to comply with labeling requirements across regions.
- Time-to-Market Delays – Launching products globally becomes slow and resource-intensive.
- Supply Chain Inefficiencies – Discrepancies in data can cause order errors, returns, and increased costs.
To eliminate these problems, GS1 introduced the Global Data Model with harmonized product attributes to ensure consistent product information across all trading partners and geographical locations. These standardized data elements encompass essential product characteristics, specifications, and metadata required for effective supply chain management.

Essential Attribute Categories
The harmonized product attributes encompass several critical categories designed to address comprehensive product information needs.
Basic identification attributes include
1. Core Product Attributes
- Global Trade Item Number (GTIN)
- Brand name
- Product description
- Net content and weight
- Packaging type
2. Category-Specific Attributes
- Food & Beverage: Nutritional facts, allergens, ingredients.
- Healthcare: Regulatory approvals, dosage, usage instructions.
- Apparel: Size, color, fabric composition.
3. Regulatory Attributes
- Compliance information (e.g., FDA, EU standards).
- Expiry dates, batch numbers.
4. Digital Shelf Attributes
- Product images, marketing copy, keywords, and videos.
5. Technical Attributes
- Barcodes, 2D codes, RFID tags, logistics identifiers.
By unifying these elements, the GDM ensures that whether a product is listed on Amazon in the U.S. or Carrefour in Europe, the data looks and feels the same.
Implementation Best Practices
Successful implementation of harmonized product attributes requires systematic planning and execution. Organizations must begin by conducting comprehensive attribute mapping exercises to identify current data structures and alignment opportunities with GS1 standards. The GS1 Global Data Model Attribute Analysis Tool provides valuable guidance for this mapping process, enabling organizations to identify gaps and opportunities.
Data quality management becomes paramount during implementation. Organizations should establish robust validation processes ensuring attribute completeness, accuracy, and consistency. The implementation of data governance frameworks helps maintain long-term data integrity while supporting ongoing attribute management requirements.
Benefits of Harmonized Product Attributes via GS1 GDM
- Streamlined cross-border commerce.
- Faster product launches across geographies.
- Greater data accuracy and consumer trust.
- Lower operational and compliance costs.
- Unified data flow between trading partners.
The GS1 GDM addresses these issues by providing a single version of product data across markets.
Implementation Strategy and Best Practices
Successful GS1 Global Data Model implementation requires structured planning, phased execution, and ongoing management commitment. Organizations must develop comprehensive strategies addressing technical, operational, and organizational aspects of the transformation.
1. Planning and Preparation Phase
The initial planning phase involves a comprehensive assessment of current data management practices, identification of improvement opportunities, and development of implementation roadmaps. Organizations should conduct thorough attribute mapping exercises comparing existing data structures with GS1 Global Data Model requirements.
Stakeholder engagement represents a critical success factor. Implementation teams should include representatives from IT, operations, marketing, regulatory, and trading partner management functions. Cross-functional collaboration ensures comprehensive requirements gathering and facilitates organizational change management.
2. Pilot Implementation Approach
Pilot implementations provide valuable learning opportunities while minimizing organizational risk. Organizations should select representative product categories and key trading partners for initial deployment. Pilot programs enable refinement of processes, validation of technical capabilities, and demonstration of business value.
The pilot phase should focus on data quality improvement, process automation, and trading partner integration. Comprehensive testing ensures system reliability while identifying potential challenges before broader deployment. Success metrics should be established to quantify benefits and support expansion decisions.
3. Full-Scale Deployment
Full-scale deployment involves systematic expansion of standardized attribute management across all product portfolios and trading relationships. Organizations must maintain focus on data quality, process efficiency, and ongoing system optimization throughout the expansion process.
Change management becomes critical during full deployment. Training programs should address new processes, system capabilities, and quality standards. Ongoing support structures ensure sustained adoption while monitoring systems track performance against established metrics.
Technology Integration: GDSN and Data Pool Architecture
The Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) represents the technological infrastructure enabling GS1 Global Data Model implementation. This internet-based network of interoperable data pools facilitates standardized product data exchange between trading partners across geographical boundaries.
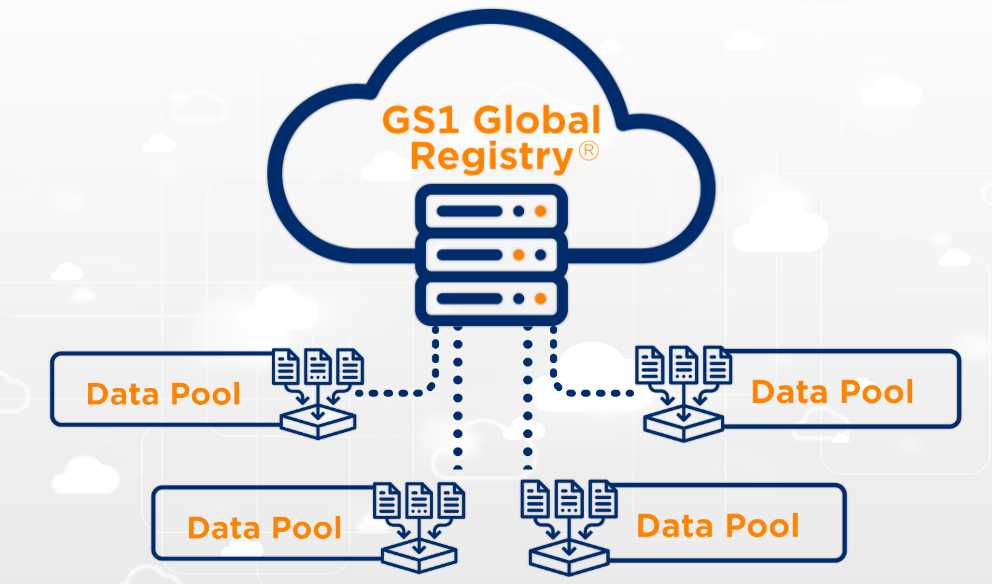
1. GDSN Network Architecture
The GDSN operates through a sophisticated publish-subscribe mechanism connecting trading partners via certified data pools. The GS1 Global Registry serves as the central directory, matching subscriptions with publications while maintaining network integrity. As of June 2025, the network encompasses 100 million items and 125,000 locations shared across 245 countries through 44 GDSN-certified data pools.
Data pools serve as intermediaries, providing validation, transformation, and transmission services for product information. Each certified data pool must demonstrate complete interoperability with other network participants while maintaining compliance with GS1 standards. This distributed architecture ensures scalability, resilience, and global accessibility.
2. Integration Benefits and Capabilities
Organizations leveraging GDSN integration experience substantial operational improvements. Real-time data synchronization eliminates manual processes, reduces errors, and accelerates product launches. Studies indicate that businesses implementing GDSN can achieve 2× speedier time-to-market for new products compared to non-adopters.
The network’s automated validation capabilities perform real-time quality checks against over 10,000 data quality rules, preventing errors and ensuring compliance before information reaches trading partners. This proactive approach significantly reduces data rejection rates and associated operational disruptions.
Benefits of Implementing the GS1 Global Data Model
The implementation of the GS1 Global Data Model and harmonized product attributes delivers measurable business value across multiple dimensions. Organizations report significant improvements in operational efficiency, cost reduction, and revenue enhancement following successful deployment.
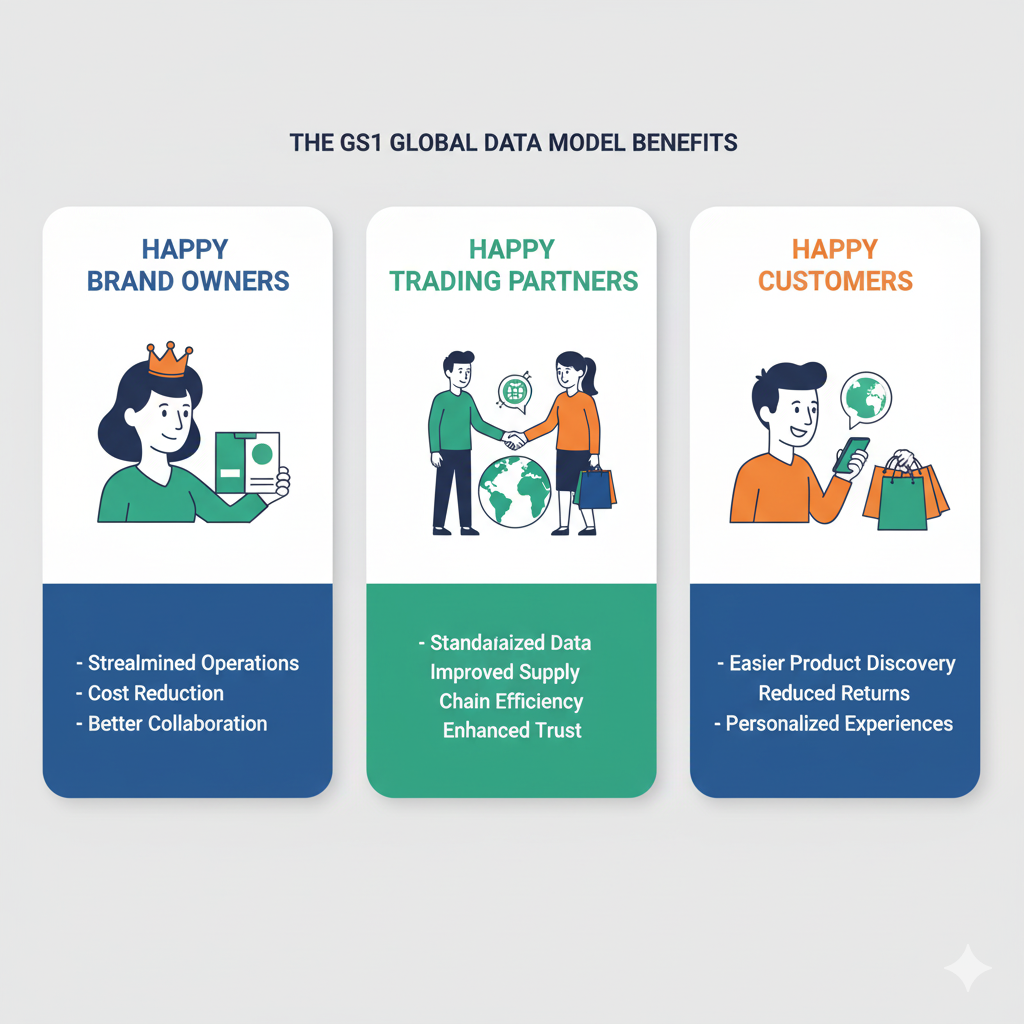
For Brands
- Streamlined Operations: The GDM simplifies the process of managing product data, allowing companies to focus on core business activities rather than data discrepancies.
- Cost Reduction: By minimizing errors and improving data accuracy, businesses can significantly lower costs associated with returns and customer service inquiries.
- Better Collaboration: The standardized approach fosters better communication and collaboration among trading partners, leading to more efficient supply chain operations.
For Trading Partners
- Standardized and Harmonized Product Data: Trading partners benefit from a single, unified set of product attributes across markets, reducing inconsistencies and eliminating the need for multiple data formats. This ensures everyone—from manufacturers to retailers—speaks the same “data language.”
- Improved Supply Chain Efficiency: By leveraging harmonized product attributes, trading partners can accelerate onboarding, reduce manual data entry, and minimize errors. This leads to faster time-to-market and smoother collaboration throughout the supply chain.
- Enhanced Consumer Experience and Trust: Consistent, accurate product information shared through the GS1 Global Data Model builds consumer confidence and loyalty. Retailers can provide shoppers with reliable details (e.g., ingredients, allergens, sustainability attributes), while manufacturers strengthen brand reputation.
For Consumers
- Easier Product Discovery: With standardized product information, consumers can quickly find the products they need, whether online or in-store.
- Reduced Returns: Accurate product descriptions and specifications lead to fewer returns, as customers are more likely to receive exactly what they expect.
- Personalized Experiences: Businesses can leverage consistent product data to create tailored marketing strategies, enhancing the overall shopping experience for consumers.
Industry-Specific Applications and Use Cases
The GS1 Global Data Model’s flexibility enables adaptation across diverse industry sectors while maintaining core standardization principles. Each industry benefits from tailored attribute sets addressing specific operational requirements and regulatory constraints.
1. Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG)
The FMCG sector represents the primary target for GS1 Global Data Model implementation, encompassing food, near-food products, alcoholic beverages, pet food, and tobacco categories. These industries require comprehensive attribute sets addressing nutritional information, allergen declarations, ingredient lists, and storage requirements.
Retailers in the FMCG sector leverage harmonized product attributes to enhance omnichannel experiences, supporting both physical and digital commerce initiatives. Standardized product information enables consistent shelf planning, automated replenishment, and enhanced consumer engagement through digital platforms.
2. Healthcare and Pharmaceuticals
Healthcare applications of the GS1 Global Data Model focus on patient safety, regulatory compliance, and supply chain integrity. Unique device identification (UDI) requirements drive standardized attribute management supporting medical device tracking throughout the healthcare delivery system.
Pharmaceutical implementations emphasize traceability requirements, enabling accurate lot tracking, expiration date management, and recall capabilities. The model’s standardized approach supports serialization initiatives while maintaining interoperability across healthcare systems and trading partners.
3. Retail and E-commerce
Retail applications emphasize enhanced consumer experiences through rich, standardized product content. Harmonized product attributes support advanced search capabilities, comparison shopping, and personalized recommendations across digital platforms.
E-commerce implementations benefit from consistent product information across multiple marketplaces and sales channels. Standardized attributes reduce listing errors, improve search visibility, and enhance customer confidence through accurate, comprehensive product descriptions.
Future Trends and Technological Evolution
The GS1 Global Data Model continues evolving to address emerging market needs and technological advances. Future developments focus on enhanced digital capabilities, expanded industry coverage, and improved integration with emerging technologies.
1. Digital Transformation Initiatives
The rise of digital commerce drives enhanced content requirements beyond traditional product attributes. Rich media assets, 360-degree imagery, and interactive content become increasingly important for consumer engagement. The GS1 Global Data Model evolves to accommodate these enhanced content requirements while maintaining standardization principles.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies enable automated attribute extraction, quality validation, and content enhancement. These capabilities reduce manual efforts while improving data accuracy and completeness. Organizations can leverage AI-powered tools to accelerate implementation and maintain ongoing data quality.
2. Industry Expansion
Current GS1 Global Data Model coverage focuses primarily on FMCG categories, with planned expansion into additional sectors including cosmetics, apparel, and general merchandise. The GS1 Advisory Council encourages development roadmaps aligned with marketplace requirements and industry priorities.
New industry applications require specialized attribute sets addressing sector-specific requirements. Fashion and apparel implementations emphasize style, color, size, and material attributes. Cosmetics applications focus on ingredient transparency, usage instructions, and regulatory compliance information.
3. Technology Integration Evolution
The transition toward 2D barcode technologies through initiatives like GS1 Sunrise 2027 enhances product identification capabilities while maintaining backward compatibility. Enhanced identification systems support richer product information while enabling direct consumer engagement through mobile technologies.
API-driven connectivity replaces traditional batch processing approaches, enabling real-time data synchronization and enhanced responsiveness. Modern integration approaches support cloud-based architectures while maintaining security and reliability standards required for enterprise implementations.
Challenges and Solutions
While GS1 Global Data Model implementation provides substantial benefits, organizations face various challenges requiring systematic solutions. Understanding common obstacles and proven mitigation strategies enables successful deployment outcomes.
1. Data Quality Management
Maintaining consistent data quality across multiple systems and trading partners represents a primary challenge. Organizations must establish comprehensive validation frameworks ensuring accuracy, completeness, and consistency of product attributes. Automated quality checking systems reduce manual efforts while improving reliability.
Master data management becomes critical for maintaining single sources of truth across organizational systems. Centralized data governance ensures consistency while distributed validation supports real-time quality assurance. Organizations should implement progressive quality improvement programs addressing systemic data issues.
2. Technical Integration Complexity
Integrating GS1 Global Data Model standards with existing enterprise systems requires careful planning and execution. Legacy system limitations may constrain attribute management capabilities, requiring system upgrades or replacement initiatives. Organizations should develop phased integration strategies minimizing operational disruption.
API-based integration approaches provide flexibility while maintaining system independence. Modern middleware solutions facilitate data transformation and routing between systems while preserving existing operational processes. Organizations can leverage cloud-based integration platforms to accelerate deployment while reducing infrastructure requirements.
3. Organizational Change Management
Cultural resistance to standardized processes represents a significant implementation challenge. Organizations must invest in comprehensive change management programs addressing training, communication, and performance management aspects. Success requires sustained leadership commitment and clear communication of business benefits.
Cross-functional collaboration becomes essential for successful implementation. Organizations should establish governance structures ensuring coordination between IT, operations, marketing, and trading partner management functions. Regular communication and progress monitoring maintain momentum throughout the implementation process.
Conclusion
The GS1 Global Data Model stands as a pivotal advancement in harmonizing product attributes and transforming supply chain data management for modern commerce. By unifying data standards across global, regional, and local layers, GS1 empowers companies to achieve operational excellence, optimize collaboration, and accelerate digital transformation. The adoption of harmonized product attributes through GS1 enhances data accuracy, increases speed-to-market, reduces manual errors, and establishes trusted transparency between trading partners.
This model’s scalable architecture ensures businesses of all sizes and sectors benefit from efficient product data exchange, regulatory compliance, and brand integrity. The integration with the Global Data Synchronization Network further facilitates seamless, real-time sharing of accurate product information, supporting consumer needs and future-proofing supply chains in an ever-evolving marketplace. As global commerce continues to expand, leveraging the GS1 Global Data Model future-proofs organizations, setting a solid foundation for innovation, efficiency, and sustained growth.
Ultimately, the GS1 Global Data Model’s harmonized approach not only bridges the gaps between diverse international standards but also drives business value, responsiveness, and collaborative success for all stakeholders involved
Commport GDSN Datapool - GS1 Certified Datapool Since 2005
Download: GDSN Buyers Guide
Empower your business with global data synchronization; download our GDSN Buyer's Guide today and take the first step towards streamlined, accurate, and compliant product data management.
Frequently Asked Questions
The GS1 Global Data Model is a standardized framework that defines harmonized product attributes to ensure consistent, accurate, and shareable product information across global supply chains.
It helps businesses streamline product data management, reduce duplication, speed up product launches, and improve collaboration with trading partners worldwide.
Trading partners gain from standardized product data, improved efficiency in supply chain operations, and enhanced customer trust through consistent product details across all channels.
By ensuring product attributes are harmonized, consumers receive reliable, transparent, and accurate product information across physical and digital channels, enhancing their shopping experience.
GDSN (Global Data Synchronization Network) and PIM (Product Information Management) solutions enable businesses to publish, synchronize, and distribute harmonized product attributes, ensuring compliance with the GS1 Global Data Model and seamless global data sharing.