Introduction
QuickBooks EDI integration has become essential for modern businesses looking to streamline their operations. QuickBooks serves as the accounting backbone for over 4.5 million businesses worldwide, while EDI facilitates more than 20 billion transactions annually across supply chains. Despite this widespread adoption, many suppliers using QuickBooks eventually face a significant challenge: retailers demand EDI compliance, but QuickBooks wasn’t built for it.
Without proper integration, staff must manually re-key EDI data into QuickBooks, a tedious process that consumes 15–30 minutes per transaction and creates 10–20% error rates. Essentially, integrating EDI with QuickBooks eliminates this manual document handling, ensuring important documents such as purchase orders, invoices, and shipping details are directly processed within QuickBooks. This EDI automation not only reduces errors but also saves valuable time for your team.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll walk you through everything you need to know about effectively connecting QuickBooks and EDI systems. From understanding the technical aspects of mapping EDI documents to QuickBooks transactions to choosing the right integration method for your business size, we’ll cover the entire implementation process. Additionally, we’ll highlight common pitfalls to avoid and provide a clear roadmap for successful integration, helping your business meet trading partner requirements while maximizing efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- Automate document workflows: EDI integration converts purchase orders (850) to QuickBooks sales orders, generates invoices (810), and processes payments (820) without manual intervention.
- Choose the integration method by QuickBooks version: Enterprise users need direct API integration via Web Connector, while Online users benefit from cloud-based EDI platforms.
- Prioritize field mapping and testing: Map over 100 QuickBooks fields precisely to EDI documents and test with 20+ sample transactions before going live to prevent costly rework.
- Achieve real-time financial synchronization: Integration updates inventory levels, COGS calculations, and accounts receivable automatically, accelerating month-end closing procedures by 50% or more.
- Standardize master data before integration: Clean up item codes and customer records in QuickBooks first to prevent mismatches that derail implementation and require constant manual corrections.
Understanding the Role of EDI in QuickBooks
The integration of business systems has become fundamental for organizations seeking to enhance operational efficiency. In this section, we’ll explore how EDI systems work with QuickBooks and why this connection matters for modern businesses.

What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
Electronic Data Interchange represents a computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in standardized electronic formats between trading partners. Unlike traditional methods involving paper, fax, or even email (which still requires human handling), EDI enables direct system-to-system communication without manual intervention.
In an EDI environment, documents flow automatically between computer applications. This standardized approach transforms business communications by:
- Eliminating manual data entry and associated errors
- Accelerating transaction processing speeds
- Enhancing document security through encryption and authentication
- Streamlining the exchange of critical business documents
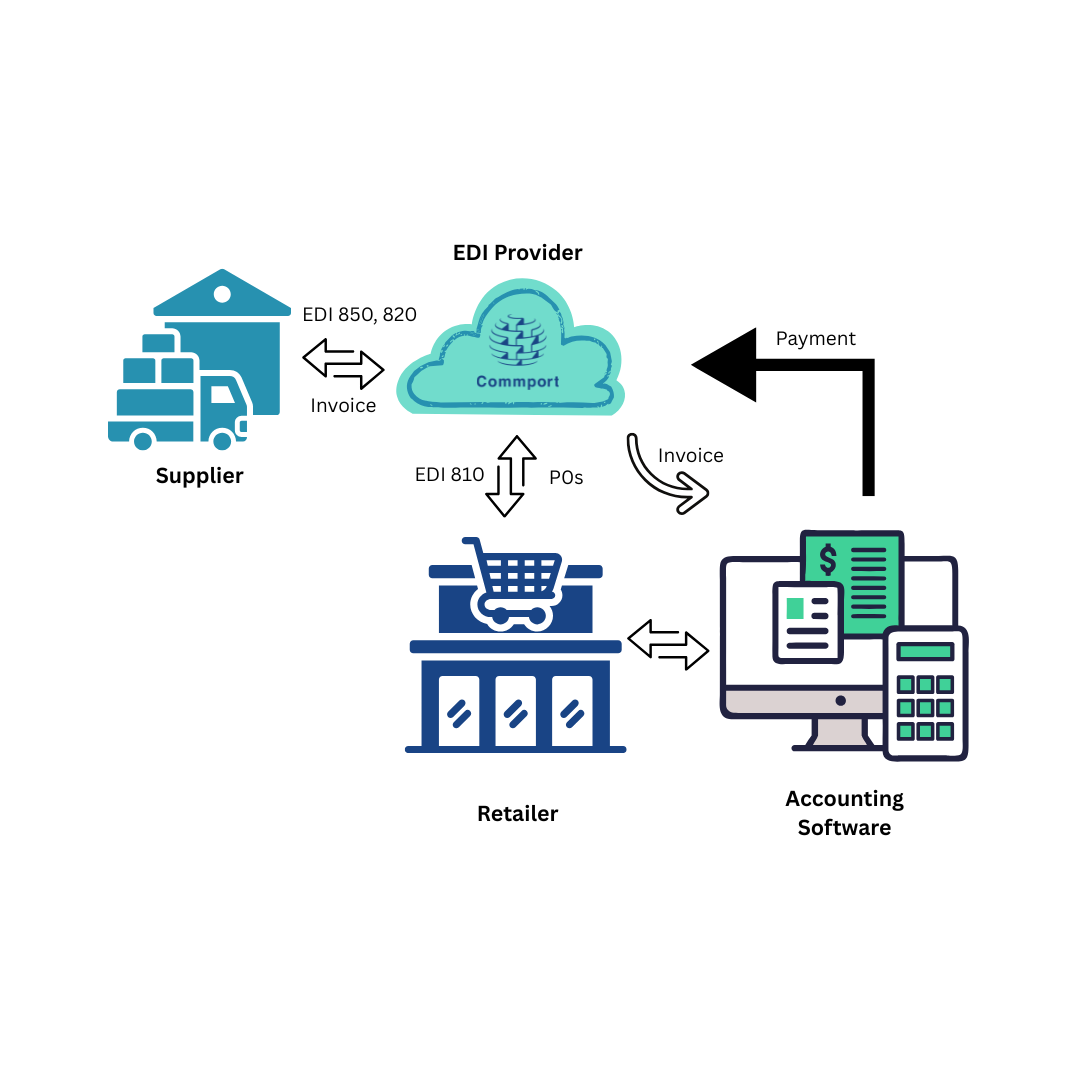
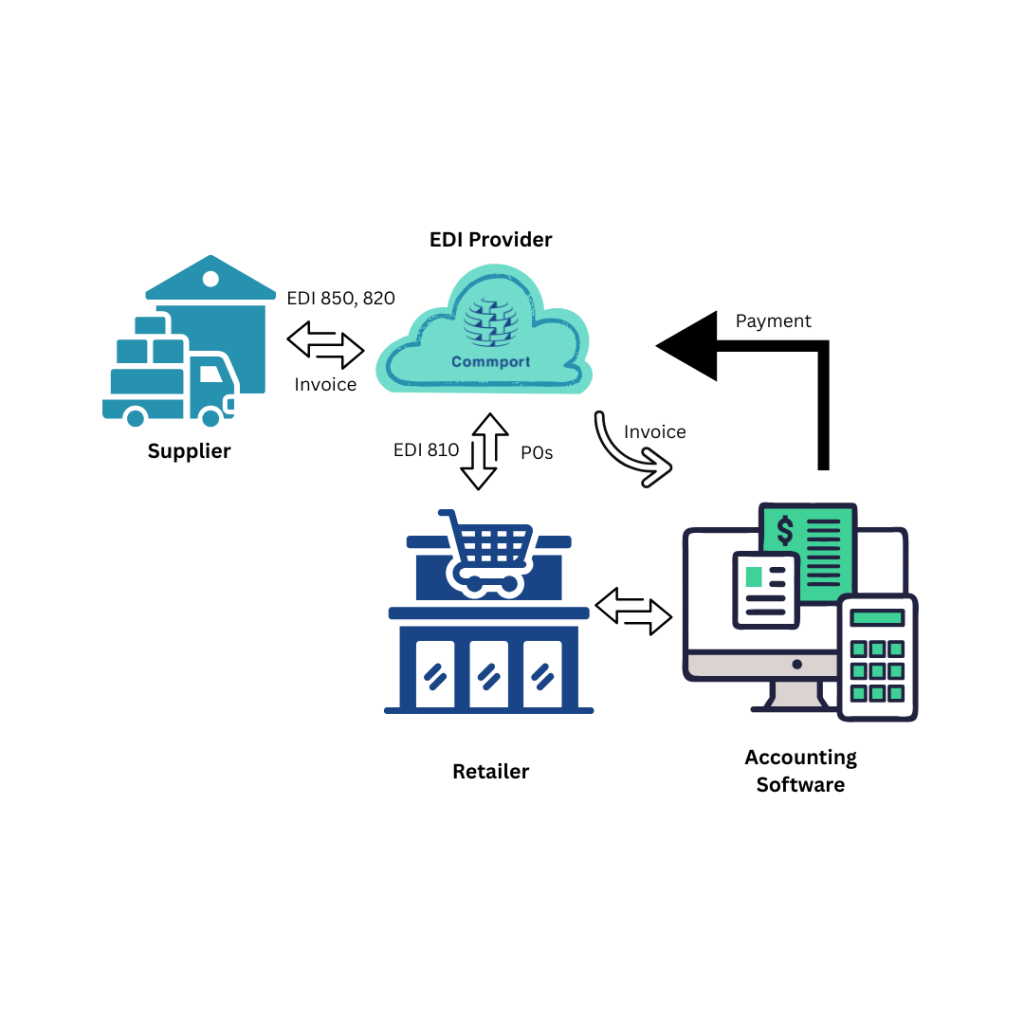
Common EDI documents include purchase orders (EDI 850), invoices (EDI 810), shipping notices (EDI 856), and payment instructions (EDI 820). These standardized formats ensure that receiving systems can correctly interpret and process incoming data without human interpretation.
How QuickBooks Handles Accounting Workflows
QuickBooks serves as a popular accounting system designed specifically for small to medium-sized businesses. At its core, QuickBooks manages essential financial functions including tracking sales, handling invoices, and streamlining payroll processes.
QuickBooks’ basic functionality revolves primarily around financial management—billing, payroll processing, and reporting. Through its interface, businesses can maintain accurate financial records and generate necessary documentation for transactions.
Furthermore, QuickBooks offers workflow automation capabilities that help organizations handle routine tasks. With workflow features, companies can automate common processes like reviewing invoices, collecting payments, and approving transactions. This automation within QuickBooks itself helps reduce manual effort for accounting teams.
However, QuickBooks alone has limitations when connecting with external trading partners and systems. This is where EDI integration becomes valuable.
Why QuickBooks and EDI Need to Work Together
The connection between QuickBooks and EDI systems addresses a critical business need: enabling seamless communication between your financial system and trading partners. When integrated properly, these systems create several valuable improvements:
First, QuickBooks EDI integration automates document exchange, eliminating the need for manual data entry. Consequently, when a trading partner sends a purchase order (EDI 850), the system automatically translates it into QuickBooks format and creates the corresponding sales order or invoice. This automatic process cuts processing time dramatically and minimizes costly errors from manual entry.
Second, the integration facilitates smooth invoicing workflows. Following an order shipment, invoices (EDI 810) generated in QuickBooks can be automatically sent through EDI to trading partners. This prevents manual invoicing tasks and ensures timely billing.
Third, payments received from trading partners can be automatically applied to the correct invoices in QuickBooks, thereby simplifying reconciliation without manual intervention.
Beyond these workflow improvements, the integration expands QuickBooks’ capabilities into enterprise resource planning (ERP) and warehouse or supply chain management. In addition, businesses can use inventory data from QuickBooks to quickly generate invoices for trading partners or automatically update stock counts between systems.
In essence, QuickBooks EDI integration transforms disconnected systems into a cohesive business platform that supports end-to-end transaction processing with minimal human involvement.
How QuickBooks EDI Integration Works Technically
The technical mechanics of QuickBooks EDI integration reveal a sophisticated data exchange system operating behind the scenes. Rather than forcing QuickBooks to perform functions it wasn’t designed for, most solutions employ specialized middleware to facilitate seamless communication between systems.

1. EDI 850 to QuickBooks Sales Order Mapping
Purchase order processing forms the foundation of QuickBooks EDI integration. When trading partners transmit purchase orders (EDI 850), the EDI system automatically receives them and translates this standardized data into a format compatible with QuickBooks. This process involves critical data mapping where structured EDI fields like “PO Number” and “Item Quantity” are matched precisely to corresponding QuickBooks fields.
During this translation process, field mapping ensures that incoming data lands exactly where it belongs in QuickBooks—no cleanup required. Subsequently, the integration automatically creates sales orders in QuickBooks, eliminating time-consuming manual entry. This technical handshake between systems ensures that order details flow directly into QuickBooks either as sales orders or invoices.
2. EDI 810 Invoice Generation from QuickBooks
Invoicing workflows benefit significantly from proper technical integration. Generally, your accounting team continues using QuickBooks to create invoices as they normally would. Those invoices are then automatically converted into EDI 810 format and transmitted to your trading partners through the EDI system.
The technical process works bidirectionally—invoices can originate in QuickBooks and be exported as EDI 810 documents, or conversely, you can generate EDI invoices in your EDI portal and automatically import them into QuickBooks accounts receivable. Therefore, businesses maintain flexibility in their invoicing workflow while ensuring trading partner compliance.
3. EDI 856 ASN Sync with Inventory Updates
Advance Ship Notices (ASN) represent another critical technical integration point. Once an order moves through fulfillment, the EDI system generates and transmits an EDI 856 ASN to the trading partner. Primarily, the integration pulls vital shipping information like tracking numbers directly from QuickBooks and automatically incorporates this data into the ASN.
Moreover, inventory management benefits from this technical connection. As orders are fulfilled, the integrated system updates inventory levels within QuickBooks. This real-time synchronization ensures inventory commitments are accurately tracked and Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) calculations remain precise. The impact is notable: reduced stockouts and overstocks through automated inventory control.
4. EDI 820 Payment Remittance to QuickBooks Deposits
Payment processing completes the technical integration cycle. EDI 820 documents (Payment Order/Remittance Advice) transfer payment data between buyers and sellers, typically sent jointly with electronic funds transfers. These documents include essential elements like payer identification, invoice numbers, payment amounts, and banking information.
Technically speaking, EDI systems can match these 820 payments to the appropriate invoices in QuickBooks, achieving automatic cash posting in less than an hour. Beyond basic payment data, the EDI 820 shows which specific invoices have been paid and any adjustments made (freight charges, returns, or deductions). Remittance integration tools can potentially post these payments automatically, streamlining reconciliation without manual intervention.
Through proper technical integration, the entire document workflow—from purchase orders to invoices to shipping notices to payments—flows automatically between systems, monitored through EDI dashboards that track exceptions and document status.
Real-Time Synchronization Across Accounting Functions
Synchronizing accounting functions in real-time represents the true value of QuickBooks EDI integration. When properly implemented, this synchronization eliminates the lag between EDI transactions and accounting records, creating a seamless financial ecosystem that enhances accuracy across departments.

Inventory Commitments and COGS Accuracy
Effective QuickBooks EDI integration transforms inventory management by maintaining precise stock level information. As EDI purchase orders arrive, they automatically create QuickBooks sales orders, immediately committing inventory in real-time. This instant commitment prevents overselling and provides accurate availability information.
Upon shipment, the system automatically reduces stock levels as Advanced Shipment Notices (ASNs) are generated. This synchronization directly impacts Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) calculations, ensuring they reflect actual inventory movement. COGS represents the direct expenses incurred in producing items or delivering services, including materials, labor, and production-related overhead.
Throughout this process, QuickBooks EDI integration offers:
- Instant access to real-time inventory data
- Better demand forecasting capabilities
- Reduced instances of stockouts and overstocks
- Accurate calculation of production costs per unit sold
For businesses managing inventory, QuickBooks can automatically adjust COGS whenever items are sold, debiting the COGS account while simultaneously crediting the Inventory Asset account.
Automated Accounts Receivable and Invoice Matching
Accounts Receivable operations gain remarkable efficiency through QuickBooks EDI integration. Invoices generated in QuickBooks can automatically convert to EDI 810 documents and transmit to trading partners. Afterward, incoming EDI 820 payment documents automatically match to the correct invoices, enabling cash posting in less than one hour.
This automation addresses a common pain point for QuickBooks users—manually matching payments to invoices. Many businesses still spend valuable time chasing late payments and manually reconciling transactions. Automated payment matching virtually eliminates these tasks, particularly since QuickBooks can perform automatic matching for QuickBooks Payments transactions.
For growing businesses, this integration cuts AR administrative work significantly—some report reductions of 50% or more. Beyond efficiency gains, automated AR processes minimize human error in payment applications, ensuring transactions are logged to the correct accounts every time.
General Ledger Updates from EDI Transactions
The impact of QuickBooks EDI integration extends to General Ledger precision. Each EDI-driven transaction automatically codes to the appropriate accounting accounts, ensuring accurate financial representation. Tax calculations based on synchronized item and customer data maintain compliance without manual verification.
Perhaps most notably, this synchronization accelerates month-end closing procedures. By eliminating manual reconciliation between systems, accounting teams avoid the tedious process of ensuring EDI transactions properly reflect in QuickBooks financial statements.
A comprehensive QuickBooks EDI solution automatically updates both inventory levels and financials within QuickBooks, eliminating duplicate data entry and the need to check multiple systems. As businesses grow, this integration capability becomes increasingly valuable, supporting cross-referencing of item and customer records through real-time syncing with QuickBooks.
Choosing the Right Integration Method for QuickBooks
Selecting an appropriate integration method determines the success of your QuickBooks EDI implementation. The right approach depends primarily on your specific business requirements, technical resources, and QuickBooks version.

1. Direct API Integration for QuickBooks Enterprise EDI
QuickBooks Enterprise users face unique integration challenges due to its on-premise nature. For these installations, the QuickBooks Web Connector (QBWC) serves as the backbone for EDI integration. This Windows application enables web services to exchange data with QuickBooks Desktop products through a secure connection.
One major advantage of direct API integration is security—because all communication is initiated by the Web Connector running on the same system as QuickBooks, there’s no need to open firewall ports. Furthermore, this approach offers extensive integration possibilities, including web-based application data exchange and integration with third-party systems.
2. Cloud-Based EDI Platforms for QuickBooks Online
QuickBooks Online users benefit from cloud-based EDI solutions that offer seamless connectivity. These platforms provide scalability, reduced IT overhead, and anywhere accessibility. Cloud EDI networks like Commport Communications excel at multi-retailer compliance, offering pre-built connections with major retailers that simplify setup.
At this point, it’s worth noting that most cloud platforms can connect QuickBooks Online to leading retailers in just a few clicks without lengthy setup cycles. First thing to remember when selecting cloud options is whether they offer real-time data exchange for sales orders, invoices, inventory updates, and shipping logs.
3. Third-Party Middleware vs Native QuickBooks Apps
When comparing middleware solutions to native apps, consider your technical expertise. If you maintain a strong IT team with EDI knowledge, middleware options like MuleSoft or Dell Boomi might work well. Nonetheless, native QuickBooks apps from the QuickBooks App Store often provide more specialized functions specific to accounting workflows.
These third-party apps deliver specialized features that QuickBooks doesn’t natively include—Intuit even supports these developers because they extend QuickBooks’ capabilities beyond its core accounting functions. Importantly, native apps typically offer direct integration with QuickBooks, eliminating the need for complex mapping or custom configurations.
4. Hybrid Integration for Multi-Channel Workflows
Hybrid approaches combine direct and indirect methods, giving you flexibility to handle various EDI tasks. Above all, this integration style enables you to manage simpler EDI tasks in-house while relying on third parties for complex integrations. This approach suits businesses with fluctuating transaction volumes or those expanding into new sales channels.
After all, your selection should align with both current needs and future growth. Commport EDI Solutions easily integrates with all major ERPs like SAP, NetSuite, QuickBooks and more. Easy to scale and affordable EDI pricing plans. Trusted by 6000+ brands, Get started today.
Implementation Roadmap and Common Pitfalls
Implementing a successful QuickBooks EDI integration requires careful planning and awareness of common challenges. Businesses that skip critical steps often face costly rework and trading partner relationship damage.
Step-by-Step Integration Setup Process
Successful QuickBooks EDI implementation typically follows three distinct phases. Initially, the assessment phase involves auditing your required EDI document types (850/810/856), mapping over 100 QuickBooks fields, and confirming specific trading partner requirements. Next, during solution selection, evaluate whether cloud EDI networks, API-based middleware, or native QuickBooks apps best suit your business needs. Finally, the deployment phase includes configuring communication protocols (AS2, SFTP), building document maps between X12 and QuickBooks, and testing with at least 20 sample transactions before going live.
Field Mapping and Document Testing
Field mapping represents the foundation of effective QuickBooks EDI integration. Each EDI document contains structured fields that must precisely match corresponding QuickBooks fields. Unfortunately, poor implementation often leads to constant manual corrections after integration. To prevent this, implement pre-validation rules that verify data (like checking if SKUs exist in QuickBooks) before posting. Prior to full deployment, test your connection by running sample orders with trading partners to validate document accuracy, field alignment, and status updates.
Handling Item and Customer Code Mismatches
Item and customer code mismatches commonly derail QuickBooks EDI implementations. Often, trading partners assign their own unmatched SKUs to your products, creating reconciliation challenges. The solution? Standardize your QuickBooks master data before integration or implement AI-powered tools for automatic field matching. For incorrect income accounts linked to products, fix historical transactions by editing the item, changing to the correct account, and checking the “Update for Historical Transactions” box before saving.
Dealing with Legacy QuickBooks Versions
For businesses using older QuickBooks versions, integration presents unique challenges. Some EDI platforms still prioritize QuickBooks Desktop, leaving Online users with partial functionality. API wrappers can solve this for QuickBooks Desktop 2015+, while QuickBooks Online requires special attention to API limitations, rate limits, and webhook handling. Commport EDI Solutions easily integrates with all major ERPs like SAP, NetSuite, QuickBooks, and more, offering scalable and affordable EDI pricing plans trusted by 6,000+ brands.
Conclusion
QuickBooks EDI integration stands as a critical business solution for modern companies seeking to streamline operations and meet trading partner requirements. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored how this powerful combination eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and saves valuable time across accounting functions.
Effective integration transforms disconnected systems into a cohesive platform that handles everything from purchase orders to payments with minimal human intervention. Consequently, businesses experience dramatic improvements in inventory management, accounts receivable operations, and general ledger accuracy. Real-time synchronization ensures your financial data remains consistent across all systems, therefore accelerating month-end closing procedures and enhancing overall accounting precision.
Commport EDI QuickBooks Integration
Need Help? Download: Commport's EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
QuickBooks EDI integration eliminates manual data entry, reduces errors, and saves time across accounting functions. It automates document workflows, improves inventory management, streamlines accounts receivable operations, and enhances overall financial accuracy.
When a trading partner sends a purchase order (EDI 850), the integration system automatically translates it into QuickBooks format and creates a corresponding sales order or invoice. This process eliminates manual entry and significantly reduces processing time.
Yes, QuickBooks EDI integration works with both versions, but the integration method differs. QuickBooks Enterprise users typically use direct API integration through the QuickBooks Web Connector, while QuickBooks Online users benefit more from cloud-based EDI platforms.
Before implementation, businesses should assess their required EDI document types, map QuickBooks fields to EDI fields, confirm trading partner requirements, and standardize their QuickBooks master data. It’s also crucial to select the right integration solution based on business needs and QuickBooks version.
The integration provides real-time synchronization of inventory levels. As EDI purchase orders arrive, they automatically create QuickBooks sales orders, immediately committing inventory. This process prevents overselling, provides accurate availability information, and ensures precise Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) calculations.