Introduction
Digital Transformation might sound like just another business buzzword, but the undeniable success of companies embracing it over the past decade proves it’s a powerful strategy. However, when digital experiences fall short, insufficient data management practices are often what’s holding organizations back. In today’s complex business environment, managing product information across multiple channels while maintaining consistency presents significant challenges.
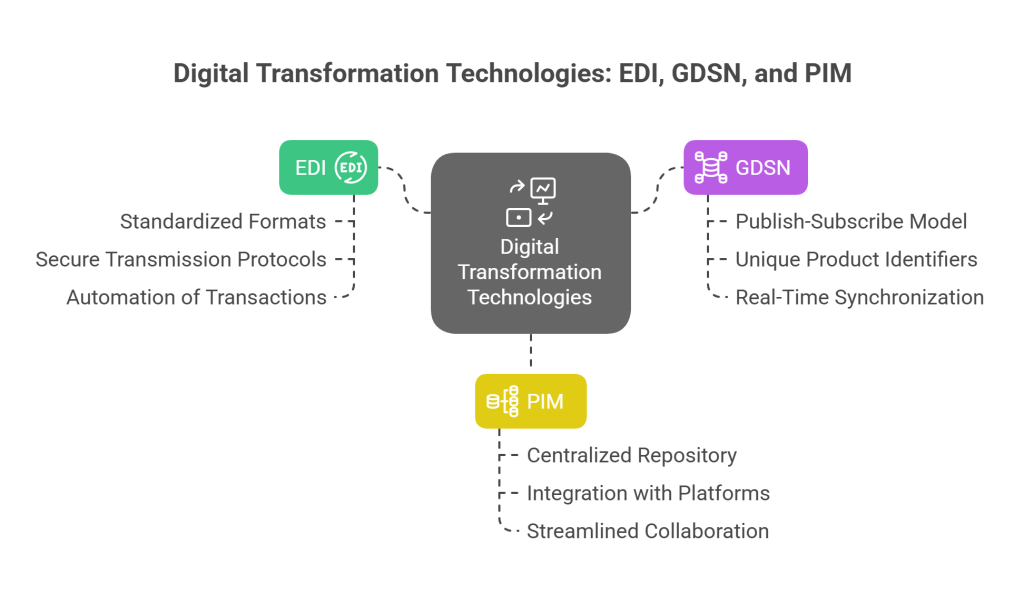
At its core, digital transformation is about leveraging cutting-edge technologies to make your business more efficient, understand customer needs better, and expand your business models. This is where three critical technologies come together: EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), GDSN (Global Data Synchronization Network), and PIM (Product Information Management). PIM serves as the cornerstone of your digital experience stack, acting as a single source of truth for all types of product data, while GDSN ensures accurate, up-to-date product information across supply chain partners globally.
By implementing these interconnected systems as part of your digital transformation strategy, you can achieve greater supply chain visibility, optimize operations, and unlock new growth opportunities. PIM solutions offer centralized data management that ensures consistency across all channels, while proper integration with EDI platforms and GDSN creates a powerful ecosystem for supply chain optimization.
Understanding the Core: What Are EDI, GDSN, and PIM?
To succeed in today’s complex business environment, companies need robust digital foundations that support seamless data exchange. Let’s explore the three cornerstone technologies that make this possible.
What is EDI and How Does it Support Digital Transformation?
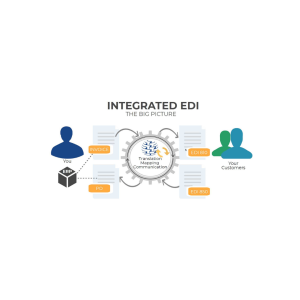
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in standardized electronic formats between organizations. Essentially, EDI provides a technical foundation for commercial “conversations” between two entities, whether internal or external. Unlike traditional paper-based methods, EDI enables direct communication between computer applications, eliminating manual intervention and paper usage.
EDI works through standardized formats that define the location and order of information in document exchanges. These standards ensure consistency and are governed by organizations like GS1, Peppol, and Accredited Standards Committee ANSI X12. The technology uses secure transmission protocols such as SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol) or AS2 (Applicability Statement 2) to safeguard data during transfer.
For companies pursuing digital transformation strategies, EDI serves as a critical enabler by automating business transactions like purchase orders, invoices, and shipping notices. This automation significantly reduces manual errors, speeds up transaction processing, and enhances overall supply chain optimization. According to research, EDI implementation can reduce order processing times dramatically, with many businesses reporting that EDI has reduced data entry errors by approximately 80%.
What is GDSN and Why is it Important for Supply Chain Visibility?
The Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) is an internet-based, interconnected network of interoperable data pools governed by GS1 standards. It functions as a bridge connecting brands and merchants, enabling companies worldwide to exchange standardized product master data with their trading partners.
GDSN operates through a publish-subscribe model. When suppliers update product information in their data pool, changes are automatically reflected across the entire network, ensuring all partners have access to current and complete information. Every product within the GDSN receives a unique identifier (GTIN – Global Trade Item Number) that houses all relevant product data, including color, category, size, weight, and shipping logistics.
For supply chain visibility, GDSN is transformative. It provides real-time synchronization of product data across global supply chains, eliminating discrepancies and enabling full end-to-end visibility. According to reports, 81% of consumers are willing to switch to brands providing more detailed product information, highlighting GDSN’s importance in today’s market. Furthermore, the network enables managers to see movement within the supply chain as it happens, allowing for better service and enhanced customer experiences.
What is PIM and How Does It Improve Product Data Management?
Product Information Management (PIM) is the process of managing and enriching product information and related digital assets across different teams to provide engaging product experiences. A PIM solution serves as a centralized repository for product data with cleansing rules, data deduplication, matching and merging, and translation capabilities.
PIM systems integrate with most e-commerce platforms, CRM systems, and ERP software, making them particularly valuable for businesses with constantly changing product catalogs. The centralized approach helps teams quickly access needed information, increasing productivity by preventing data silos.
For effective digital transformation business process management, PIM streamlines collaboration among multiple teams and third parties using structured workflows to enrich product content, ensure data accuracy, and simplify product launches. Additionally, PIM solutions automate product data syndication across multiple touchpoints—responding to omnichannel demands.
The main benefits include faster time to market, increased brand loyalty, improved operational efficiencies, better product data quality, and a more engaging omnichannel product experience. By centralizing product information, PIM systems eliminate redundant data entry, reducing errors and inconsistencies while enabling marketing teams to create more engaging content.
How These Systems Work Together in a Connected Supply Chain
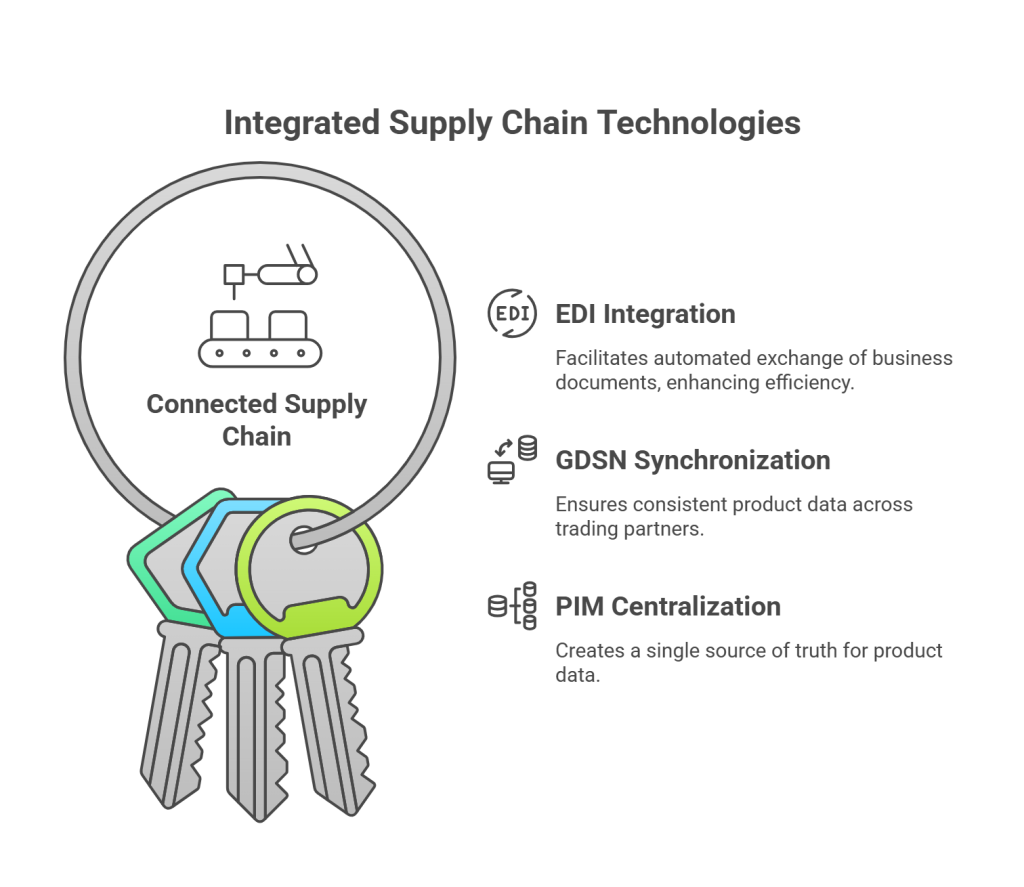
Beyond individual capabilities, the true power of EDI, GDSN, and PIM emerges when they operate as an integrated ecosystem. These technologies serve as the connective tissue that enables true end-to-end visibility and communication across the entire connected supply chain.
The Role of Integration in Digital Transformation Strategy
Integration of EDI, GDSN, and PIM forms the digital foundation for any successful digital transformation strategy. Rather than functioning as isolated systems, these technologies create a cohesive framework that enhances supply chain visibility and operational efficiency. Consequently, companies can build responsive networks that adapt to market changes and customer demands in real-time.
The integration process transforms fragmented operations into a cohesive, intelligent ecosystem that supports digital transformation and business process management. Through this integration, businesses gain access to comprehensive supply chain analytics that identify patterns, optimize inventory levels, and forecast demand with greater accuracy.
For organizations undertaking EDI migration from legacy systems, the integration with PIM and GDSN should be considered simultaneously to maximize benefits. Selecting the right EDI vendor and platform becomes critical, as these decisions impact how effectively the three systems communicate.
Data flow between EDI, GDSN, and PIM platforms
The data flow between these systems follows a structured process that ensures accuracy and consistency throughout the connected supply chain:
- Data Extraction & Centralization: PIM systems collect product data from various sources within the organization, creating a single source of truth
- Data Cleansing & Enrichment: Information is validated, standardized, and enhanced within the PIM system
- Registration & Publication: Standardized data is published to GDSN data pools and registered in the GS1 Global Registry
- Subscription & Synchronization: Trading partners subscribe to relevant product information through GDSN, enabling automatic updates
- Transaction Automation: EDI facilitates the automated exchange of business documents based on the synchronized product information
This integrated flow eliminates data silos that typically plague supply chains. With proper EDI tools and services, the entire process becomes seamless, reducing manual intervention and associated errors.
Real-Time Synchronization and Automation Benefits
Real-time synchronization creates substantial operational advantages. When product data is updated in the PIM system, it’s automatically propagated to GDSN and made available through EDI platforms to all trading partners. This synchronization ensures every stakeholder works with identical, accurate information.
Indeed, the automation benefits extend throughout the entire supply chain optimization process. Companies that integrate these systems report significant improvements in order accuracy and enhanced supply chain management. Moreover, this integration facilitates faster time-to-market for new products and updates, as centralized product data allows businesses to efficiently manage information and introduce new offerings more quickly.
The interconnected nature of these systems also improves collaboration with trading partners. By synchronizing product data through GDSN and communicating via standardized EDI formats, businesses reduce manual data exchange and streamline communications. Subsequently, this leads to better decision-making across the entire supply chain network, from manufacturers to retailers.
Key Business Benefits of Combining EDI, GDSN, and PIM
When businesses unite EDI, GDSN, and PIM systems, they unlock remarkable value that drives measurable business growth. The strategic integration of these technologies creates a foundation for successful digital transformation that delivers tangible benefits across the organization.
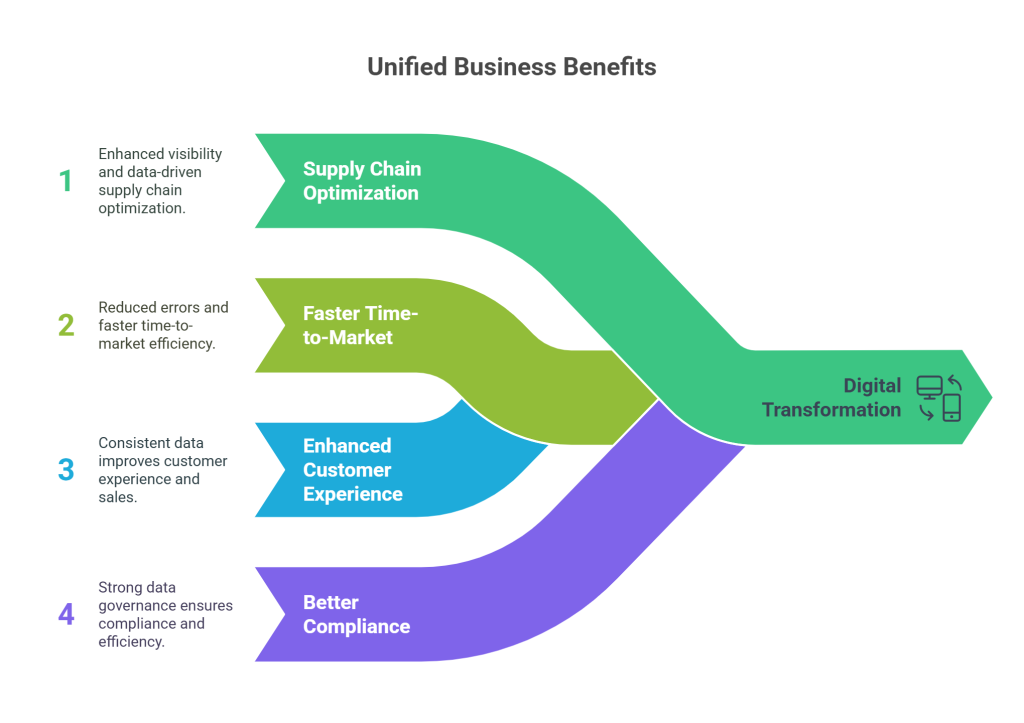
1. Improved Supply Chain Optimization and Analytics
The integration of EDI, GDSN, and PIM creates powerful supply chain optimization opportunities through enhanced visibility and data-driven decision making. Businesses implementing global data synchronization report tangible returns across multiple operational areas as supply chains become increasingly complex. Companies with advanced supply chain visibility can reduce supply chain costs by up to 50%. Specifically, organizations like BD (Becton, Dickinson and Company) achieved a 30% reduction in outstanding days payable and a 73% reduction in ordering discrepancies after implementing these technologies.
Notably, these integrated systems facilitate real-time inventory tracking across all channels, which helps minimize stockouts and prevent overstocking. This direct impact on the bottom line reduces storage costs while ensuring product availability when customers want them
2. Faster Time-to-Market and Reduced Manual Errors
Organizations implementing the global data synchronization network experience significant improvements in operational metrics. A recent survey found businesses that implemented GDSN reported a 25% reduction in data errors and a 30% increase in operational efficiency. Interestingly, companies using real-time inventory tracking report up to 25% reduction in stock discrepancies.
The centralization of product data management eliminates duplicate entries, streamlines collaboration with trading partners, and significantly improves operational efficiency. As a result, businesses can focus on more value-added activities like strategic decision-making and customer service rather than manual data entry.
3. Enhanced customer experience through consistent data
Above all, integrated systems ensure accurate, consistent product information reaches customers. According to research, 81% of consumers are willing to switch to brands providing more detailed product information. In essence, GDSN data enables consumers to make data-driven purchasing decisions based on trusted, globally distributed product content.
Ultimately, accurate, consistent, and secure data results in increased sales conversions and better relationships with distributors. Plus, by maintaining product information consistency across all channels, distributors and retailers have access to the same data pool, further enhancing the customer experience.
4. Better Compliance and Data Governance
Strong data governance is the cornerstone of long-term inventory management success. GDSN ensures compliance with global data standards and regulations, while all data input is checked and validated in the global data registry to ensure system compliance with rigid standards.
This standardization ensures everything in the supply chain operates efficiently, making it possible for data senders and receivers to synchronize and share pertinent data from any global location. Companies implementing strong data governance report significant improvements in decision-making regarding data optimization and compliance requirements.
Implementation Strategy: Building a Unified Data Ecosystem
Building a robust data ecosystem requires strategic planning and careful implementation. Let’s explore how organizations can create an integrated framework for digital transformation success.
1. Steps to Align Your Digital Transformation Business Process Management
Successful digital transformation begins with thorough business process management. Initially, assess your current operational state to establish a baseline for improvements. This critical first step helps identify pain points while evaluating existing strengths. Next, conduct strategic evaluation focusing on process standardization across your organization to ensure consistency. Thereafter, prioritize process improvements based on business impact to allocate resources effectively. Finally, integrate key performance indicators to measure success and ensure alignment with business objectives.
2. Choosing the right EDI vendor and PIM solution
Selecting appropriate technology partners significantly impacts your supply chain optimization efforts. When evaluating an EDI vendor, consider their industry experience, track record, and expertise in your specific sector. Review their service offerings to ensure they match your business needs. Additionally, assess their integration capabilities with existing systems like ERP or accounting software. For PIM solutions, prioritize features such as data centralization, customization capabilities, and robust security measures. Remember that compatibility with GDSN requirements is essential for successful implementation.
3. Migrating legacy systems to modern EDI platforms
EDI migration requires a structured approach. Before transitioning, thoroughly evaluate your existing infrastructure, examining system performance, reliability, compliance standards, and integration capabilities. Then, select from primary migration strategies: rehosting (lift-and-shift), replatforming (lift-tinker-shift), or rebuilding/refactoring. Implement effective data mapping using modern tools that provide visual interfaces for complex transformations. Primarily, adopt a phased approach with carefully planned waves to balance risk mitigation with business continuity.
4. Ensuring scalability and future-proofing your tech stack
Future-proofing your technology stack means investing in systems that can flex, scale, and adapt over time. A future-ready tech stack should be composable (built from modular components), interoperable (able to connect with APIs), scalable (supporting growth without overhauls), and resilient (designed with redundancy). Prioritize cloud-based inventory solutions, which offer unparalleled flexibility with up to 30% cost savings compared to traditional systems.
Transform your supply chain today by switching to Commport B2B network solutions trusted by over 6000+ customers and over 40+ years of experience. Commport is the market leader in providing solutions that can help you digitalize all your B2B communications with your trading partners worldwide!
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
Even with a solid implementation strategy, companies face several hurdles when integrating EDI, GDSN, and PIM systems. Identifying these challenges early can help organizations prepare effective solutions for their digital transformation journey.
1. Data Silos and Integration Complexity
Data silos occur when information is stored in separate systems with limited or no sharing between them. These isolation points stem from incompatible software, departmental boundaries, or lack of communication within organizations. For retailers, these silos result in fragmented customer views, inventory management inefficiencies, and delayed decision-making.
Integration complexity presents another significant barrier. Many EDI formats were not designed for human readability, making error detection challenging and time-consuming. Additionally, GDSN does not easily scale, as adding new trading partners often requires manual mapping. Furthermore, only about 33% of data pools work together, forcing suppliers to navigate compatibility issues.
To overcome these challenges, organizations should:
- Implement unified data platforms that consolidate information from various sources
- Adopt cloud-based solutions offering real-time synchronization
- Invest in data integration tools with robust API connections to existing systems
2. Resistance to Change and Training Gaps
Organizations often resist EDI adoption due to perceived high costs, technical complexity, and concerns about return on investment. Healthcare organizations similarly face resistance when implementing GDSN. Inadequate staff knowledge remains a major barrier, with employees requiring specific skill sets to manage these systems effectively.
Ineffective training is among the top reasons software implementations fail. To address these issues, companies should provide comprehensive training covering basic functionality followed by periodic refresher sessions. Cross-functional collaboration is essential, as effective data management requires teamwork across departments including marketing, sales, IT, and customer service.
3. Maintaining Data Quality Across Systems
Poor inventory management costs businesses nearly $2 trillion globally. Data quality challenges include incorrect prices, out-of-stock items, and duplicate orders. Without standardized data formats and attributes, product information becomes inconsistent across channels.
Establishing clear data governance is crucial for maintaining high-quality data. This involves defining data ownership, implementing quality standards, and ensuring compliance with regulations. Regular audits help identify and rectify quality issues while uncovering patterns in data errors. For GDSN specifically, all input data undergoes validation in the global registry to ensure compliance with standards, creating a secure environment for ongoing synchronization of reliable data.
Conclusion
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored how EDI, GDSN, and PIM systems work together to create a powerful foundation for digital transformation. These interconnected technologies certainly form the backbone of modern supply chain optimization, enabling businesses to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Companies that successfully integrate these systems gain remarkable supply chain visibility, allowing them to track products from manufacturing through delivery with pinpoint accuracy. Additionally, the rich supply chain analytics generated by this technological trio provide actionable insights that drive smarter business decisions. Businesses report significant reductions in operational costs while simultaneously improving data quality and customer experiences.
The journey toward a fully connected supply chain does present challenges. Data silos, integration complexity, and resistance to change can impede progress. Nevertheless, these obstacles become manageable through strategic planning, comprehensive training, and strong data governance policies.
Successful EDI migration requires careful vendor selection and implementation planning. Therefore, choosing the right EDI vendor with industry expertise and robust integration capabilities becomes a critical success factor. The right EDI platform paired with appropriate EDI tools creates the technical foundation for seamless business communications.
Transform your supply chain today by switching to Commport B2B network solutions trusted by over 6000+ customers and over 40+ years of experience, Commport is the market leader in providing solutions that can help you digitalize all your B2B communications with your trading partners worldwide!
The digital transformation landscape will undoubtedly continue evolving. However, organizations that establish these integrated data ecosystems now position themselves for lasting competitive advantage. After all, the businesses that thrive tomorrow will be those that build robust, adaptable, and interconnected supply chain technologies today.
Commport B2B Network Solutions
Frequently Asked Questions
EDI (Electronic Data Interchange), GDSN (Global Data Synchronization Network), and PIM (Product Information Management) are interconnected technologies that form the foundation of modern supply chain management. EDI facilitates automated business transactions, GDSN ensures global product data synchronization, and PIM centralizes product information management. Together, they create a unified ecosystem that enhances supply chain visibility, streamlines operations, and improves data accuracy.
Integrating these systems leads to improved supply chain optimization, faster time-to-market, reduced manual errors, and enhanced customer experiences. Businesses can expect benefits such as real-time inventory tracking, significant reductions in data errors, increased operational efficiency, and better compliance with global data standards.
Common challenges include dealing with data silos, integration complexity, resistance to change, and maintaining data quality across systems. Organizations may also encounter training gaps and difficulties in migrating from legacy systems to modern platforms.
To overcome challenges, companies should adopt unified data platforms, invest in comprehensive training programs, establish clear data governance policies, and implement a phased approach to system migration. Choosing the right vendors and solutions that align with specific business needs is also crucial.
When selecting an EDI vendor, consider their industry experience, integration capabilities, and service offerings. For PIM solutions, prioritize features such as data centralization, customization capabilities, and robust security measures. Ensure that both EDI and PIM solutions are compatible with GDSN requirements and can scale to meet future business needs.