Throughout this guide, we’ll walk you through practical steps to develop a comprehensive omnichannel retail strategy. We’ll explore how technologies like Product Information Management (PIM), Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN), and Product Experience Management (PXM) can transform your approach to customer engagement across all touchpoints.

In this complete guide to Omnichannel retailing strategy. You’ll learn:
So if you’re ready to go “all in” with Omnichannel Retailing, this guide is for you.
The retail landscape has evolved dramatically, with shoppers now expecting consistent brand experiences regardless of how they interact with your store. Understanding the fundamentals of omnichannel retailing is the first step toward meeting these evolving expectations.
Omnichannel retailing creates a unified, seamless shopping experience across all customer touchpoints. The prefix “omni” means “all,” referring to the integration of every possible way customers interact with your brand—physical stores, websites, mobile apps, social media, email, and more.
Unlike traditional retail approaches, omnichannel doesn’t treat these channels as separate entities but as interconnected parts of a whole ecosystem. This integration enables customers to start shopping on a mobile device, check inventory at a local store, and complete their purchase in person—all while experiencing consistent pricing, promotions, and service quality.

At its core, omnichannel retail transforms brick-and-mortar locations into hybrid spaces that complement digital channels through features like in-store pickup, mobile checkout, and seamless access to digital product information. This approach requires robust systems like Product Information Management (PIM) to maintain consistent product data across all channels.
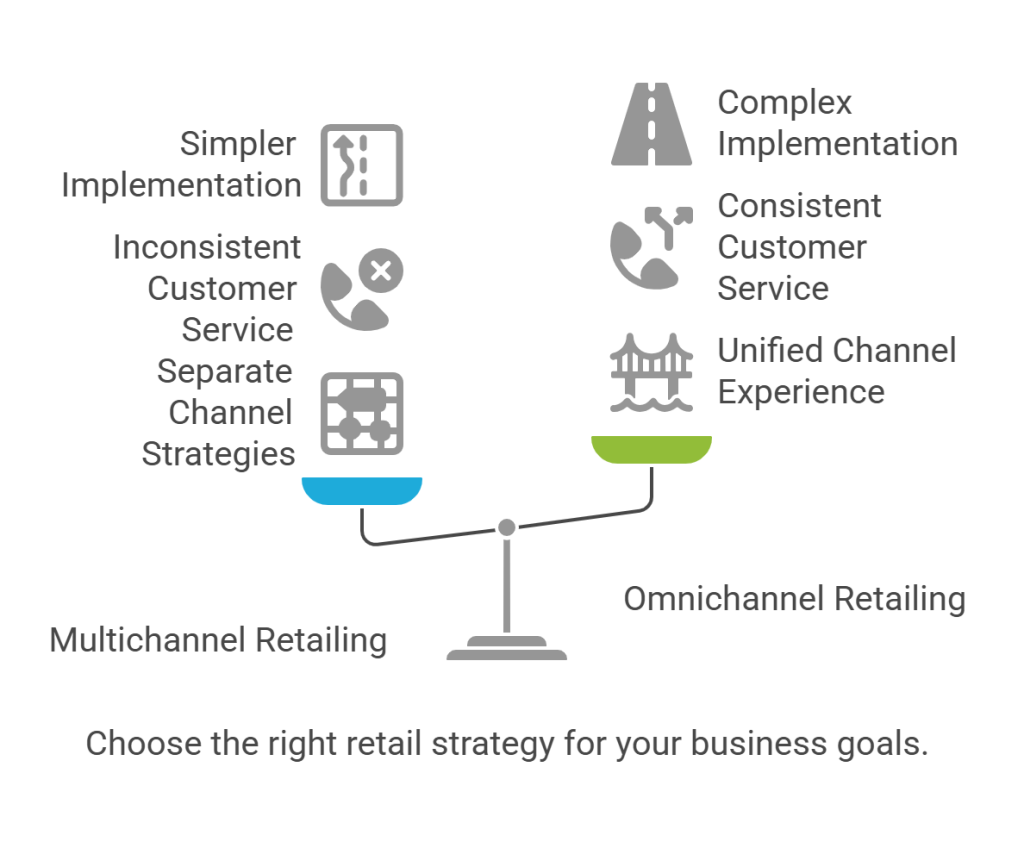
Though often confused, these approaches differ fundamentally in their focus and execution:
Consider this practical distinction: multichannel retail operates like separate bands playing in different venues, whereas omnichannel functions like a symphony in which all instruments harmonize to create one cohesive experience.
The business value of implementing an omnichannel retailing strategy is compelling:
First, omnichannel customers spend 15-30% more than single-channel shoppers and have a 30% higher lifetime value. Furthermore, brands with consistent omnichannel strategies enjoy a 13% annual improvement in customer retention rates.
Notably, these businesses see a 14.6% year-over-year increase in annual revenue. Beyond digital sales, 75% of consumers are more likely to visit a physical store after finding helpful local retail information online.
Omnichannel integration also generates valuable customer data, enabling you to track shopping patterns, optimize inventory, and personalize experiences. Technologies like Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) ensure this data remains consistent across channels, while Product Experience Management (PXM) helps create personalized experiences based on collected insights.
Despite these benefits, implementing an omnichannel strategy presents challenges, including significant technology investments and complex data management requirements. Nevertheless, as customer expectations continue to evolve, omnichannel integration has become essential for retail success rather than optional.
Understanding your customers' path to purchase across multiple channels is crucial for any successful omnichannel retailing strategy. According to research, 73% of customers use multiple channels when shopping for a product. Mapping this journey reveals valuable insights that can transform your retail operations.
Omnishoppers interact with your brand through numerous touchpoints before making a purchase decision. A comprehensive omnichannel customer journey includes both digital and physical interactions:
Modern customers might research product characteristics using a mobile app, compare prices on websites from their laptop, and finally purchase the product at a physical store. Consequently, 81% of shoppers begin their retail journey online before committing to a purchase.
Product Information Management (PIM) systems play a vital role at each touchpoint by ensuring product data remains consistent and accurate across all channels. When customers encounter inconsistent information, they lose trust in your brand and may abandon their purchase journey.
The emergence of omnishoppers has fundamentally transformed retail customer journeys. These consumers expect seamless experiences across channels and will use them interchangeably during the search and purchase process.
Digital natives, primarily Generation Z and Millennials, now demand a mobile-first approach since they rely heavily on smartphones for shopping. They’re highly influenced by social media recommendations and expect personalized interactions—86% of consumers would pay more for a better customer experience.
Notably, omnishoppers spend 13% more than non-omnichannel customers and purchase 250% more frequently when engaging with three or more channels. Understanding these behaviors requires unified data collection across all touchpoints.
This is where Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) becomes essential, ensuring that product information remains consistent and accurate across your entire retail ecosystem. GDSN standardizes data exchange between trading partners, eliminating inconsistencies that could disrupt the customer journey.
Effective journey mapping provides powerful insights that can transform your omnichannel retail strategy. By collecting and analyzing customer data across touchpoints, you can identify friction points in the purchase journey and increase conversion rates.
Product Experience Management (PXM) systems leverage these insights to deliver personalized experiences based on customer preferences and behavior patterns. PXM enables you to create tailored product content for different segments and channels, addressing specific customer needs at each journey stage.
Customer data platforms that eliminate silos between departments are particularly valuable for journey optimization. When marketing, sales, and customer service teams share the same customer view, they can collaborate more effectively to resolve pain points.
For instance, analyzing omnichannel data might reveal that customers frequently abandon purchases during mobile checkout. Armed with this insight, you can optimize your mobile payment process specifically for smartphone users, potentially increasing conversions significantly.
Omnichannel analytics also helps you measure the effectiveness of your retailing strategy across touchpoints, enabling continuous refinement based on real customer behavior rather than assumptions.
Empower your business with global data synchronization; download our GDSN Buyer's Guide today and take the first step towards streamlined, accurate, and compliant product data management.
Most customers regularly use at least three channels to engage with a single company, expecting consistent experiences across all of them. After mapping the customer journey, the next crucial step is building a unified retail strategy that effectively coordinates all your channels.
An omnichannel strategy is a customer engagement approach that uses interconnected, cross-channel communication to provide customers with a seamless, familiar experience across all touchpoints. Unlike traditional retail approaches, it places the customer at the center of operations instead of focusing primarily on products or channels.
At its core, an effective omnichannel retail strategy relies on a unified customer data model built on first-party data. This first-party data—information customers have opted to share with you—becomes the foundation for everything that follows in modern retail.
Generally, omnichannel strategies fall into three primary categories:
Product Information Management (PIM) systems play a vital role in any omnichannel strategy by centralizing and standardizing product data across all channels, ensuring consistency in the information customers receive.
For true omnichannel success, your online and offline operations must function as extensions of each other. This integration enables customers to interact with your business interchangeably across channels—ordering online and returning in-store, checking inventory before visiting, or adding items to their cart while en route to your location.
Accordingly, internal teams must work together more closely around business-level objectives rather than department-level goals. With budgets coming from multiple areas and customer touchpoints spanning more formats, this alignment becomes essential for success.
One powerful tool for connecting shoppers’ experiences is leveraging first-party data across all touchpoints. Loyalty programs can be particularly valuable, as they often collect zero-party data (information voluntarily provided by customers) and serve as a foundational component for scaling omnichannel strategies.
Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) further supports this alignment by ensuring data consistency between trading partners, eliminating disconnects between your online product information and what’s available in physical stores.
To effectively measure your omnichannel retail strategy, you need specific key performance indicators (KPIs) that track cross-channel performance. Without linked and systematic KPIs, there’s no way to measure effectiveness across integrated touchpoints.
Effective omnichannel KPIs should track customers’ buying process through four key stages:
Above all, remember that omnichannel KPIs differ from traditional metrics in several ways: they’re customer-centric, include qualitative measurements, consider the interdependence of multiple channels, and vary across industries.
Product Experience Management (PXM) systems support these measurement efforts by enabling you to create tailored product content for different segments and channels based on performance data, addressing specific customer needs at each journey stage.
Empower your business with global data synchronization; download our GDSN Buyer's Guide today and take the first step towards streamlined, accurate, and compliant product data management.
The backbone of any successful omnichannel retailing strategy lies in the technology that powers it. With 87% of consumers now purchasing items online that they previously bought in-store, implementing the right tech solutions has become non-negotiable for modern retailers.
Product Information Management (PIM) serves as a centralized hub for all product data, acting as the nervous system for your retail operations. This solution transforms raw product information into compelling, accurate content that flows consistently across all channels. Moreover, PIM eliminates data silos that traditionally plague retailers, reducing errors and ensuring customers receive the same information whether shopping online or in-store.
As a centralized repository, PIM simplifies the management of complex product catalogs, enabling retailers to rapidly update information across all touchpoints simultaneously. This centralization is particularly crucial when managing large inventories where manual updates would be virtually impossible.
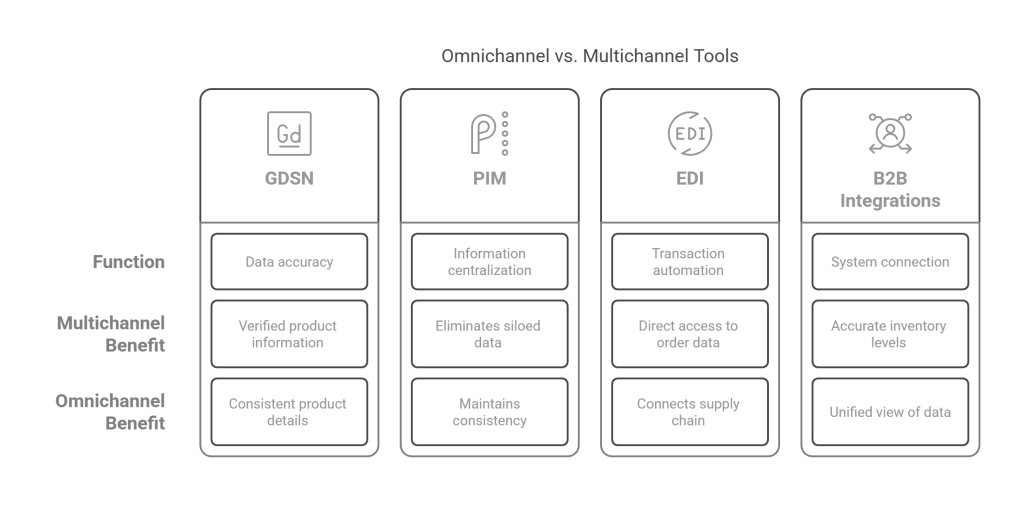
The Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) takes data consistency to the next level by enabling trading partners to exchange standardized product information efficiently and without error. This internet-based initiative ensures that product data remains accurate across your entire supply chain and customer-facing channels.
Through GDSN, high-quality product content is uploaded, maintained, and automatically shared with trading partners worldwide. Switch to Commport Datapool Solutions. Commport offers a wide range of Datapool solutions, such as GDSN, PIM, and PXM solutions, to effectively manage, optimize, distribute, and syndicate product data in real time.
Product Experience Management (PXM) builds upon PIM by focusing on how customers engage with your products. While PIM ensures data accuracy, PXM adapts and personalizes that data for each platform, delivering engaging, contextualized experiences tailored to individual preferences.
For instance, a global electronics brand might use PXM to show product pages in English with USD pricing to American customers, while German customers see the same products with localized content, EU regulations, and Euro pricing. This personalization boosts customer loyalty and creates stronger connections to your brand.
Your technology stack must prioritize seamless integration between systems. Modern omnichannel retail requires:
The ideal tech stack connects all aspects of your business—from order capture to fulfillment and returns management—creating a unified framework for omnichannel success. By leveraging these technologies together, you can create the seamless experience your customers increasingly demand.
After establishing your technology infrastructure, the next crucial step in your omnichannel retailing strategy involves optimizing both operations and marketing to deliver truly seamless experiences.
Creating consistent communication across all touchpoints has become increasingly vital for modern retailers. Recent data shows that businesses using more than two communication channels have grown from 15% in 2023 to over 25% in 2024. This shift reflects changing consumer preferences, with 92% of Gen Z more likely to purchase when messages feel personal and relevant.
The most effective communication strategy connects all customer touchpoints into one smooth, consistent experience. This includes email, voice, SMS, digital channels, social media, messaging apps, and live chat. For instance, allowing customers to start conversations on Instagram and continue via WhatsApp without repeating information significantly enhances their experience.
PIM systems support this unified communication by ensuring product information remains consistent across all interaction points, while GDSN maintains data synchronization between trading partners.
Omnichannel fulfillment requires a unified approach to managing inventory and orders across all sales channels. Best practices include:
A unified inventory system is critical for maintaining a single view across all sales channels. PXM solutions enhance this process by tailoring inventory information to each channel while maintaining consistency.
Effective retail marketing now demands personalization at scale. Due to the wealth of customer data available across channels, retailers can now tailor messages, offers, and experiences to individual preferences.
Loyalty programs serve as cornerstone elements in successful omnichannel marketing strategies. In fact, 84% of consumers say they’re more likely to return to a brand because of a strong loyalty program. The most successful programs have low barriers to entry, a balance of experiences and perks, and consistent communication.
First-party data collection is essential for building personalized journeys that create stronger customer relationships. PIM and PXM systems work together to enable this personalization by ensuring product data can be customized for different segments while maintaining accuracy.
To sustain omnichannel excellence, retailers must leverage automation and analytics. Supporting your strategy with automation tools like chatbots to answer FAQs or guide shoppers through purchase steps can significantly enhance efficiency.
Data analytics plays a pivotal role by unifying information across channels. This integration helps remove silos between teams and enables more effective customer engagement strategies. In essence, omnichannel analytics allows you to leverage artificial intelligence for deeper understanding of customer journeys.
Businesses using AI-powered analytics can track campaign results by channel—measuring clicks, conversions, and satisfaction—then use A/B testing to refine messaging. This data-driven approach is transforming retail operations by enabling personalized experiences at scale.
Empower your business with global data synchronization; download our GDSN Buyer's Guide today and take the first step towards streamlined, accurate, and compliant product data management.
Today’s shoppers fluidly connect online and offline channels, expecting a unified experience across devices. 90% of consumers switch between multiple devices every day – on average using three devices to complete a task.
Today’s shoppers fluidly connect online and offline channels, expecting a unified experience across devices. 90% of consumers switch between multiple devices every day – on average using three devices to complete a task. This device-switching translates directly into omnichannel shopping about 80% of customers now use more than one channel (web, mobile, in-store, etc.) during their buying journey.
Omnichannel customers spend significantly more (roughly 30% higher order value) than single-channel buyers. Meanwhile, physical retail remains critical: the vast majority of purchases still happen in-store (≈80% of U.S. retail sales, and over half of consumers say they enjoy the tactile experience of shopping in person.
In practice, this means shoppers frequently research online before buying in-store – about 58% of shoppers combine online research with in-store purchase decisions – and 71% expect real-time visibility of stock across both channels. Convenience features have exploded, for example, 50% of consumers now prefer buy-online-pickup-in-store (BOPIS), and roughly 67% of those shoppers make additional purchases when picking up orders. (In 2020, the adoption of BOPIS surged by 208%. In short, modern consumers demand seamless, convenient omnichannel journeys – blending mobile, web, and in-store touchpoints without friction.
Key behavioral trends include:
Sustainability is no longer optional – it is a key differentiator. Recent surveys find that a large majority of shoppers consider environmental impact when they buy. For example, 78% of consumers say sustainability factors (like eco-friendly materials or ethical practices) are important in their purchase decisions, especially among Gen Z and Millennials. Many are willing to change their behavior or pay more for green options. A Radial study found that 77% of consumers would accept longer delivery times if shipping were more sustainable – e.g. by consolidating orders, using slower ground transport, or offsetting carbon. (In that survey, 29% would wait an extra day and 38% would wait 3–5 days for a greener shipment.) Likewise, consumers are vocal about packaging: 60% say eco-friendly packaging (recycled or minimal materials) encourages them to shop with a brand. Around 19% even cite the ethical sourcing of products as a factor in their buying choices.
These expectations are influencing retailer practices. Many omnichannel companies now highlight “green” options at checkout or in logistics. For instance, some offer customers the choice of carbon-neutral shipping or slower economic delivery for a discount or for free. Others invest in recyclable or reusable packaging: one study notes that almost a third of consumers specifically want packaging made from recycled content, and roughly the same fraction want packaging they can return or reuse. Brands are answering by replacing plastic with kraft paper mailers, compostable void-fill, or even reusable shipping kits (some firms let customers send back insulated mailers for reuse.
Behind the scenes, retailers are radically retooling their networks to keep up with customer expectations. Three major innovations stand out:
These trends collectively point to a positive, dynamic future: consumers will enjoy ever-faster, more flexible shopping experiences, and retailers will harness technology and data to exceed sustainability and service expectations. By blending channels, committing to green practices, and innovating fulfillment, omnichannel retailers can both delight customers and drive growth in the years ahead.
Throughout this guide, we’ve explored how omnichannel retailing transforms traditional retail models into integrated ecosystems centered around customer experiences. Most importantly, retailers who embrace this approach retain 90% more customers while achieving 13% higher annual revenue growth compared to single-channel competitors.
Success in this integrated retail landscape depends heavily on three critical technological pillars. Product Information Management (PIM) serves as the foundation, centralizing and standardizing your product data across all channels. This centralization eliminates inconsistencies that frustrate customers and damage brand trust. Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) extends this consistency beyond your organization, ensuring seamless data exchange with trading partners and maintaining accuracy throughout your supply chain. Product Experience Management (PXM) completes the technological trinity by personalizing that standardized data for different channels and customer segments, creating tailored experiences that drive loyalty.
The future belongs to retailers who view physical and digital channels not as separate entities but as complementary touchpoints in a unified customer journey. Your customers already expect this seamless integration—75% demand consistent experiences regardless of how they interact with your brand.
Remember, implementing an effective omnichannel strategy requires commitment across your entire organization. Teams must align around customer-centric goals rather than departmental metrics. Accordingly, your KPIs should track the complete buying process from awareness through loyalty, measuring cross-channel performance rather than siloed metrics.
The path to omnichannel excellence may seem challenging, yet the rewards justify the investment. Customers who engage with three or more channels purchase 250% more frequently and spend significantly more per transaction. Additionally, the comprehensive data collection enabled by this approach provides unprecedented insights into customer behavior, allowing for continuous optimization.
Start your omnichannel journey today. Assess your current technological capabilities, map your customer journeys, and identify opportunities for greater integration. The retail landscape continues to evolve rapidly—retailers who master omnichannel strategies now will undoubtedly thrive in the years ahead.
Omnichannel retailing focuses on creating a seamless, integrated customer experience across all channels, while multichannel operates channels independently. Omnichannel is customer-centric, creating new experiences, whereas multichannel is product-centric and limited to individual channel capabilities.
An effective omnichannel strategy helps retailers retain 90% more customers, increase customer spending by 15-30%, and improve annual revenue by 14.6%. It also provides valuable customer data for personalization and inventory optimization.
Technology is crucial for omnichannel success. Product Information Management (PIM) centralizes product data, Global Data Synchronization Network (GDSN) ensures data consistency across channels, and Product Experience Management (PXM) enables personalized customer experiences.
Retailers can optimize omnichannel operations by synchronizing online and in-store inventories, implementing flexible fulfillment options like BOPIS and BORIS, leveraging loyalty programs, and using data analytics for personalized marketing and continuous improvement.
Effective omnichannel KPIs should track the customer’s buying process through four key stages: awareness (e.g., traffic across channels), engagement (e.g., product recommendations per visit), conversion (e.g., cross-channel conversion rates), and loyalty (e.g., customer retention rates).