Introduction
The retail landscape is experiencing its most significant transformation since the introduction of the Universal Product Code (UPC) in 1974. GS1 Digital Link represents a revolutionary standard that bridges the physical and digital worlds by transforming traditional barcodes into intelligent, web-enabled data carriers through 2D barcodes.
Unlike a conventional barcode that simply provides a numerical identifier (like a GTIN or UPC), the GS1 Digital Link acts as a bridge between the physical and digital worlds. It enables retailers, manufacturers, and consumers to access rich product data, such as traceability details, authenticity verification, nutritional information, recall notices, or even personalized marketing content, with a simple scan.
This technological leap represents more than a mere upgrade. It signifies a paradigm shift in how we conceive product identification and information sharing. Through sophisticated encoding mechanisms and web-enabled capabilities, this standard transforms every product into a gateway to unlimited digital content, creating unprecedented opportunities for engagement, transparency, and operational efficiency.
The journey toward this digital transformation has been carefully orchestrated by GS1, the global organization responsible for maintaining supply chain standards across industries. Their vision extends beyond simple identification to encompass a comprehensive ecosystem where products become intelligent nodes in an interconnected digital network. This evolution addresses critical challenges facing modern commerce. The demand for greater transparency, the need for enhanced consumer engagement, and the imperative for more efficient supply chain operations.
Key Takeaways
- GS1 Digital Link bridges the gap between physical products and digital ecosystems by transforming identifiers into web-enabled links.
- 2D barcodes are central to this transition, replacing traditional UPC/EAN codes with smarter, data-rich alternatives.
- Businesses across industries—from retail to healthcare—are already leveraging GS1 Digital Link for traceability, transparency, and consumer engagement.
- The benefits are universal, providing efficiency for businesses, trust for consumers, and innovation for retailers.
- The future of supply chains is digital-first, and GS1 Digital Link is a key driver of this transformation.
The Evolution from 1D to 2D Barcodes: A Historical Perspective
The Legacy of Linear Barcodes
The journey from linear barcodes to 2D barcodes represents decades of technological evolution driven by changing market demands and technological capabilities. The original UPC (Universal Product Code) barcode, introduced in 1974, revolutionized retail by enabling automated checkout and inventory management. This simple pattern of vertical lines became the foundation of modern commerce, processing billions of transactions annually.
However, the limitations of linear barcodes became increasingly apparent as supply chains grew more complex, and consumers demanded greater transparency. Traditional barcodes could only encode a product’s GTIN, providing no room for additional information such as expiration dates, batch numbers, or serial numbers. This constraint forced businesses to rely on separate systems for tracking different product attributes, creating inefficiencies and information silos throughout the supply chain.
The retail industry’s response to these limitations initially involved workarounds: multiple barcodes on packages, proprietary coding systems, and supplementary databases. These solutions, while functional, added complexity and cost to operations. The need for a more elegant and comprehensive solution became undeniable as e-commerce exploded and consumers began expecting instant access to detailed product information through their smartphones.
The Rise of 2D Barcodes and Matrix Codes
Two-dimensional barcodes emerged as the natural evolution of product identification technology. Unlike their linear predecessors, 2D barcodes encode information both horizontally and vertically, dramatically increasing data capacity while maintaining compact physical dimensions. QR codes, Data Matrix codes, and other 2D symbols began appearing in various industries, each offering unique advantages for specific applications.
The adoption of 2D barcodes initially faced resistance due to infrastructure requirements. Retailers needed new scanning equipment, software systems required updates, and staff needed training. However, the proliferation of smartphones equipped with cameras capable of reading 2D barcodes created a tipping point. Suddenly, every consumer carried a powerful barcode scanner in their pocket, transforming 2D barcodes from a supply chain tool into a platform for consumer engagement.
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated this transformation dramatically. Contactless interactions became paramount, and QR codes emerged as the preferred method for accessing menus, making payments, and sharing information. This widespread consumer familiarity with 2D barcodes created the perfect environment for GS1 Digital Link adoption, as businesses could leverage existing consumer behaviors while gaining powerful new capabilities.
Understanding GS1 Digital Link: The Foundation of Modern Product Intelligence
What is a GS1 Digital Link?
GS1 Digital Link represents the standardized methodology for encoding product identifiers—such as Global Trade Item Numbers (GTINs), Global Location Numbers (GLNs), and Serial Shipping Container Codes (SSCCs)—alongside dynamic attributes including batch numbers, serial numbers, and expiration dates, all within a single, web-enabled data carrier. This revolutionary approach accomplishes dual objectives: maintaining backward compatibility with existing systems while simultaneously unlocking entirely new capabilities through internet connectivity.
The architecture of GS1 Digital Link is elegantly simple yet profoundly powerful. At its core, the standard transforms traditional product identifiers into web-addressable URLs. This means that scanning a GS1 Digital Link-enabled 2D barcode doesn’t just retrieve a product number; it connects directly to web resources, opening doors to limitless digital experiences. The standard supports multiple data carriers, including QR codes, Data Matrix codes, and even emerging technologies like digital watermarks and Near Field Communication (NFC) tags.
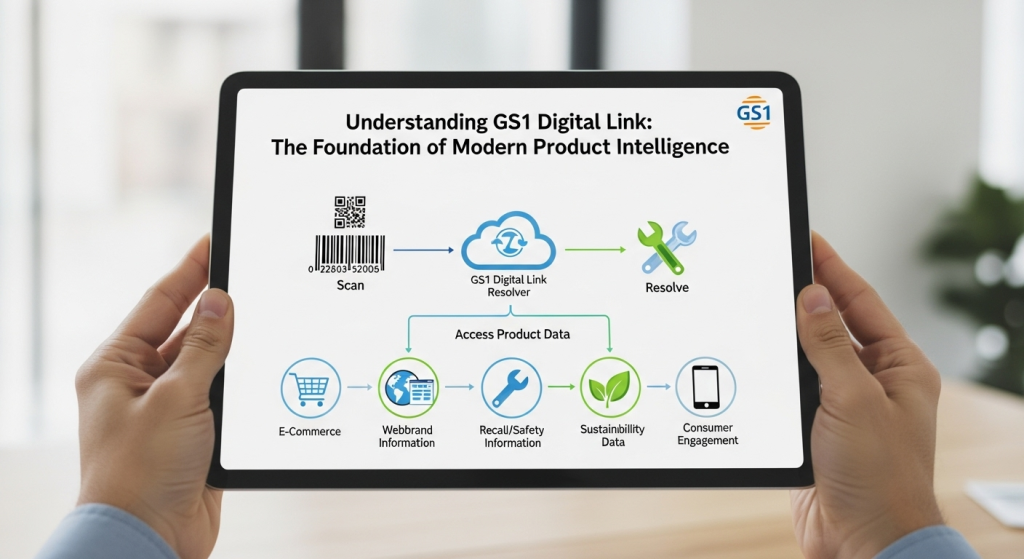
For example:
- A GTIN encoded in a Digital Link might look like:
- https://id.gs1.org/01/09506000134352
- When scanned, this link can direct a consumer to product details like:
- Ingredients or allergen information
- Sustainability practices
- Recall status
- User manuals or how-to guides
For businesses, it can link to:
- Inventory systems
- Regulatory compliance documentation
- Serialized tracking for anti-counterfeiting
This approach unifies product identification and information sharing across every stage of the supply chain.
The technical sophistication of GS1 Digital Link extends to its ability to encode multiple data elements within a single carrier. Unlike traditional linear barcodes that could only contain basic product identification, 2D barcodes powered by GS1 Digital Link can handle up to 7,098 numeric characters or 4,269 alphanumeric ones—far from the 85-character limit of 1D barcodes. This exponential increase in data capacity enables products to carry their entire digital identity on-pack, from basic identification to complex supply chain attributes and consumer-facing information.
The Technical Architecture Behind GS1 Digital Link
The engineering brilliance of GS1 Digital Link lies in its URI (Uniform Resource Identifier) structure, which follows standard web protocols while embedding GS1 identifiers. The syntax typically follows this pattern: https://domain.com/gtin/[GTIN-value], where additional attributes can be appended as path segments or query parameters. This structure ensures that every GS1 Digital Link is simultaneously a valid web address and a machine-readable identifier.
The standard employs a sophisticated resolver service architecture that acts as an intelligent routing system. When a GS1 Digital Link is scanned or accessed, the resolver determines the appropriate response based on various factors, including the requesting application, user context, and available resources. This context-aware routing enables a single code to serve multiple purposes, providing product information to consumers, authentication data to retailers, and supply chain information to logistics partners.
Furthermore, GS1 Digital Link incorporates robust data validation mechanisms to ensure accuracy and consistency. The standard specifies formatting rules for different identifier types and incorporates check digits to prevent errors. This rigorous approach to data integrity is crucial for maintaining trust in global supply chains where a single misidentified product could have cascading consequences.
How 2D Barcodes Enable Digital Link
2D barcodes serve as the physical carriers for GS1 Digital Link data, utilizing patterns of squares, hexagons, dots, and other geometric shapes to encode information in both horizontal and vertical dimensions. This two-dimensional approach dramatically increases data storage capacity compared to traditional linear barcodes while maintaining a smaller physical footprint on packaging.
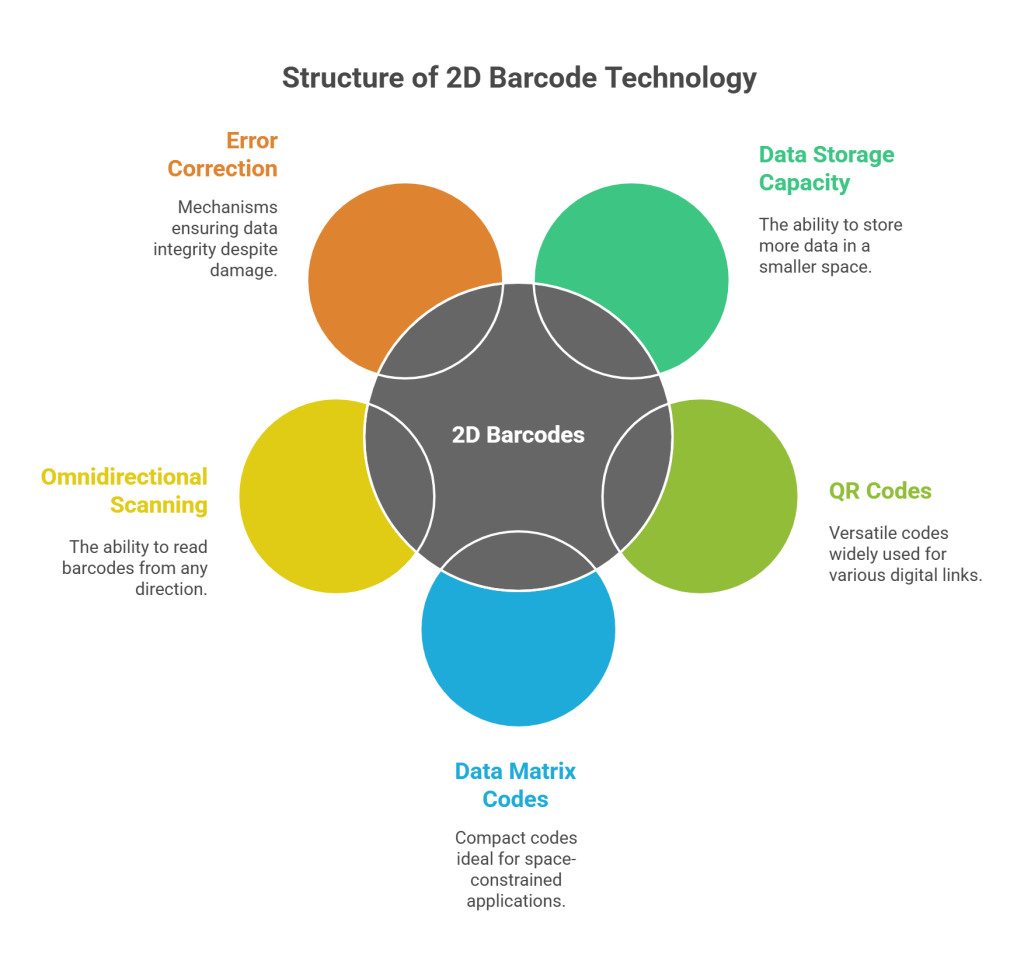
The most used 2D barcode formats for GS1 Digital Link include:
- QR Codes: Highly versatile and widely recognized by smartphones, capable of storing website URLs, product details, and promotional content
- Data Matrix Codes: Compact and efficient, particularly suitable for healthcare and aerospace applications where space is limited
Omnidirectional Scanning Capabilities
One of the significant advantages of 2D barcodes is their omnidirectional scanning capability, meaning they can be read from any direction, significantly reducing checkout times and improving operational efficiency. Additionally, built-in error correction mechanisms ensure data integrity even when barcodes are partially damaged or torn, reducing transaction delays and improving system reliability.
The Global Market Impact
The transition to 2D barcodes and GS1 Digital Link is driving substantial market growth across multiple sectors. The global 2D barcode reader market was valued at USD 8.5 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach USD 20.4 billion by 2034, growing at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 9.2%.
This growth is primarily driven by:
- Rapid adoption in the retail and e-commerce sectors
- Expanding usage in the food and beverage industries
- Increasing demand for supply chain traceability
- Growing consumer expectations for product transparency
The global e-commerce market, which heavily relies on 2D barcode technology, generated USD 4.3 trillion in revenue in 2025 and is projected to reach USD 5.9 trillion by 2029 with a CAGR of 8.0%. Major e-commerce giants including Amazon, Alibaba, and Shopify have integrated 2D barcode scanners in their warehouses to reduce stock errors, automate replenishment, and improve supply chain efficiency.
Sunrise 2027: The Global Initiative Transforming Retail
The Sunrise 2027 initiative represents one of the most significant coordinated transformations in retail history. By the end of 2027, retailers would need to ensure their POS systems are equipped with scanners capable of reading both traditional barcodes and 2D barcodes. The shift has already begun with the new technology being tested in 48 countries across the world, representing 88% of the world’s GDP. This ambitious timeline reflects both the urgency of modernization and the complexity of implementing change across global supply chains.

The initiative doesn’t mandate the immediate replacement of linear barcodes but rather establishes a transition period during which both technologies will coexist. This dual-capability approach acknowledges the massive installed base of linear barcode infrastructure while encouraging rapid adoption of 2D barcode capabilities. Retailers who embrace this transition early will find themselves at a significant competitive advantage, able to leverage advanced features while their competitors struggle with legacy limitations.
The preparation for Sunrise 2027 involves multiple stakeholders across the supply chain ecosystem. Manufacturers must update their packaging designs and printing processes, retailers need to upgrade scanning hardware and software systems, and solution providers must ensure their platforms can handle the increased data complexity. This coordinated effort requires careful planning, substantial investment, and ongoing collaboration between trading partners.
The Business Case for Early Adoption
Forward-thinking organizations are discovering that early adoption of GS1 Digital Link and 2D barcodes delivers immediate benefits that far outweigh implementation costs. Research revealed that 11% of GS1 UK’s 60,000 members had already implemented GS1-powered QR codes, with a significant 33% planning adoption within the subsequent 12 months. These early adopters are positioning themselves as innovation leaders, capturing market advantages through enhanced capabilities and improved operational efficiency.
The financial implications of the transition extend beyond simple cost-benefit analyses. Organizations implementing GS1 Digital Link report improvements in inventory accuracy, reduction in product recalls, and decreased shrinkage. The ability to track products at the individual item level enables precise inventory management, reducing both overstock and stockout situations. These operational improvements translate directly to bottom-line results, often recovering implementation costs within the first year of deployment.
Moreover, the consumer engagement opportunities created by 2D barcodes open new revenue streams and marketing channels. Brands can deliver personalized experiences, loyalty programs, and targeted promotions directly through product packaging. This direct-to-consumer connection bypasses traditional intermediaries, creating more intimate brand relationships while gathering valuable consumer insights. The data generated through these interactions provides unprecedented visibility into consumer behavior, enabling more effective product development and marketing strategies.
Implementation Strategies for Organizations
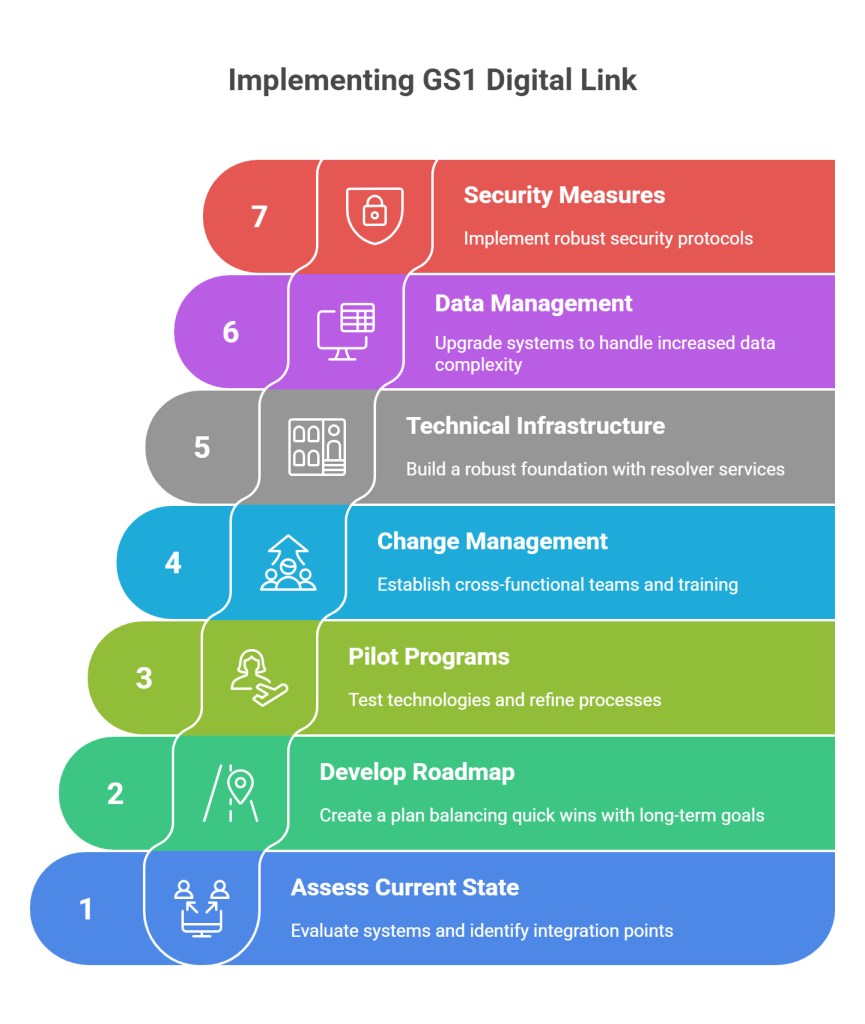
Planning Your GS1 Digital Link Journey
Successful GS1 Digital Link implementation requires a strategic approach that aligns technical capabilities with business objectives.
Organizations must begin by assessing their current state:
- Evaluating existing systems,
- Identifying integration points, and
- Understanding data management capabilities.
This assessment forms the foundation for developing a roadmap that balances quick wins with long-term transformation goals.
The implementation journey typically begins with pilot programs focusing on specific product lines or market segments. These controlled deployments allow organizations to test technologies, refine processes, and demonstrate value before scaling across the enterprise. Selecting appropriate pilot products is crucial—ideal candidates have strong consumer engagement potential, clear traceability requirements, or significant operational challenges that GS1 Digital Link can address.
Change management emerges as a critical success factor in GS1 Digital Link deployment. The transition affects multiple departments, from IT and operations to marketing and customer service. Establishing cross-functional teams ensures that all stakeholders understand the implications and opportunities of the new technology. Training programs must address not just technical skills but also the strategic possibilities that GS1 Digital Link enables, fostering innovation and creative problem-solving.
Technical Infrastructure Requirements
Building the technical foundation for GS1 Digital Link involves several key components that must work seamlessly together. The resolver service sits at the heart of the architecture, requiring careful selection between building custom solutions, leveraging cloud services, or partnering with specialized providers. Each approach offers different levels of control, scalability, and investment requirements that must align with organizational capabilities and objectives.
Data management systems must evolve to handle the increased complexity and volume of information that GS1 Digital Link enables. Traditional product information management (PIM) systems may require upgrades or replacement to support dynamic attributes, multilingual content, and real-time updates. The integration between these systems and the resolver service must be robust and performant, as any delays or errors directly impact user experience.
Security considerations take on heightened importance when products become web-connected. Organize data and implement robust authentication mechanisms, encrypt sensitive data, and protect against various cyber threats. The GS1 Digital Link standard includes provisions for verification and authentication, but organizations must still implement comprehensive security strategies that address their specific risk profiles and regulatory requirements.
Benefits Across the Supply Chain Ecosystem

1. Manufacturer and Brand Owner Advantages
Manufacturers and brand owners stand to gain tremendously from GS1 Digital Link adoption, with benefits extending far beyond simple product identification. The ability to connect directly with consumers through product packaging creates unprecedented marketing opportunities. Every product becomes a digital touchpoint, enabling brands to deliver rich content, personalized experiences, and interactive features that strengthen consumer relationships and drive loyalty.
The operational benefits for manufacturers are equally compelling. GS1 Digital Link enables precise tracking throughout the production process, from raw materials to finished goods. This granular visibility improves quality control, reduces waste, and enables rapid response to issues. When problems do arise, the ability to trace affected products down to the individual item level minimizes recall scope and associated costs, protecting both consumers and brand reputation.
Supply chain collaboration reaches new levels of efficiency with GS1 Digital Link. Manufacturers can share real-time information with partners, synchronizing data across the entire value chain. This transparency reduces disputes, accelerates problem resolution, and enables collaborative planning. The standard’s support for verifiable credentials and blockchain integration further enhances trust and accountability in complex supply networks.
Manufacturing Sector Roadmap
Manufacturers must approach GS1 Digital Link as a strategic initiative that touches multiple aspects of their operations. Production lines require the capability to print and verify 2D barcodes at high speeds. Quality control processes need updating to validate not just barcode readability but also data accuracy and web connectivity. These operational changes require careful planning to minimize disruption while ensuring compliance with customer requirements.
Supply chain integration becomes critical as manufacturers must share GS1 Digital Link data with multiple downstream partners. Electronic data interchange (EDI) systems need enhancement to transmit GS1 Digital Link URLs and associated data. Partner portals must provide access to resolver configurations and content management tools. These integrations ensure that the value created through GS1 Digital Link flows throughout the supply chain.
Brand management opportunities through GS1 Digital Link require collaboration between manufacturing and marketing teams. Product packaging designs must incorporate 2D barcodes while maintaining brand aesthetics. Content strategies must address various consumer segments and use cases. Marketing campaigns can leverage the interactive capabilities of GS1 Digital Link to create engaging consumer experiences. These opportunities position manufacturing companies as innovation leaders while strengthening brand relationships.
2. Retailer and Distributor Opportunities
Retailers embracing GS1 Digital Link discover transformative capabilities that extend throughout their operations. At the point of sale, 2D barcodes enable dynamic pricing, automatic application of promotions, and instant access to product information. This transition is driven by the need for enhanced product transparency, traceability, and authentication. Staff equipped with mobile devices can access comprehensive product data, improve customer service and reducing training requirements.
Inventory management undergoes a revolution with GS1 Digital Link’s granular tracking capabilities. Retailers can monitor products at the individual item level, enabling sophisticated analytics and optimization strategies. Expiration date management becomes automatic, reducing waste and ensuring product freshness. The ability to track products through their entire lifecycle, from receipt to sale, provides insights that drive operational improvements and cost reductions.
The omnichannel capabilities enabled by GS1 Digital Link help retailers create seamless experiences across physical and digital channels. Products scanned in-store can trigger online experiences, while online purchases can include detailed tracking through fulfillment and delivery. This convergence of channels creates competitive advantages in an increasingly digital retail landscape where consumer expectations continue to rise.
Retail Sector Roadmap
Retailers approaching GS1 Digital Link implementation should begin with careful assessment of their current infrastructure and capabilities. Point-of-sale systems require evaluation for 2D barcode scanning capability, with upgrades planned where necessary. Staff training programs must address both technical scanning procedures and the enhanced capabilities that GS1 Digital Link enables. These preparations ensure smooth transitions when products with 2D barcodes begin arriving from suppliers.
Inventory management systems need enhancement to handle the additional data that GS1 Digital Link provides. Batch numbers, expiration dates, and serial numbers become accessible at scan time, requiring systems capable of capturing and utilizing this information. Integration with existing warehouse management and enterprise resource planning systems ensures that enhanced data flows throughout the organization, maximizing operational benefits.
Consumer-facing applications represent significant opportunities for retailer differentiation. Mobile apps that leverage GS1 Digital Link can provide product information, reviews, and recommendations. In-store displays triggered by product scanning create interactive shopping experiences. Loyalty programs become more sophisticated when products can identify themselves and their attributes. These applications transform shopping from transaction to experience, building customer loyalty and driving sales.
3. Healthcare and Pharmaceutical Applications
The healthcare sector has emerged as an early adopter of GS1 Digital Link, recognizing its potential to improve patient safety and operational efficiency. Pharmaceutical products equipped with 2D barcodes enable instant verification of authenticity, helping combat the global counterfeit drug problem. Healthcare providers can access complete medication information, including doing instructions, contraindications, and recall notices, directly at the point of care.
Patient safety improvements extend beyond medication management. Medical devices tracked with GS1 Digital Link provide complete maintenance histories, calibration records, and operating instructions. This information accessibility reduces errors and ensures proper device utilization. In surgical settings, the ability to track instruments and implants at the individual item level improves inventory management and enables precise patient records for future reference.
The integration of GS1 Digital Link with electronic health records creates new possibilities for healthcare delivery. Scanning a medication automatically updates patient records, reducing documentation burden and improving accuracy. Adverse event reporting becomes streamlined, with direct links from products to reporting systems. These efficiencies allow healthcare providers to focus more time on patient care while maintaining comprehensive documentation.
4. Food and Beverage Industry Transformation
The food and beverage industry leverages GS1 Digital Link to address critical challenges around safety, traceability, and consumer engagement. Products can carry complete ingredient lists, allergen information, and nutritional data accessible through simple scanning. This transparency is particularly valuable for consumers with dietary restrictions or health conditions who need detailed product information for safe consumption.
Freshness management represents a game-changing application in perishable food handling. GS1 Digital Link enables dynamic shelf-life tracking, with products automatically updating their status as they approach expiration. Retailers can implement sophisticated markdown strategies, automatically adjusting prices based on remaining shelf life. This precision reduces food waste while ensuring consumers receive fresh products, creating value throughout the supply chain.
The farm-to-fork traceability enabled by GS1 Digital Link builds consumer trust while improving food safety. In the event of contamination or quality issues, affected products can be identified and removed from the supply chain within hours rather than days. Consumers can verify the origin of their food, understanding the journey from production through processing to retail. This transparency becomes increasingly valuable as consumers seek to support local producers and sustainable farming practices.
5. Fashion and Apparel Innovation
The fashion industry embraces GS1 Digital Link to combat counterfeiting while creating engaging consumer experiences. Luxury brands implement authentication systems where scanning a product’s 2D barcode confirms its authenticity through blockchain-verified records. This capability protects brand value while giving consumers confidence in their purchases, particularly important in secondary markets where counterfeit goods proliferate.
Sustainability storytelling becomes powerful when fashion items can share their complete lifecycle information. Consumers can access details about materials, manufacturing processes, and worker conditions. Brands committed to ethical production can differentiate themselves through transparency, building loyalty among conscious consumers. End-of-life instructions, including recycling and disposal guidance, support circular economy initiatives.
The personalization possibilities in fashion retail are particularly exciting. Scanning a garment can reveal styling suggestions, care instructions, and complementary items. Virtual try-on experiences launched through 2D barcode scanning bridge physical and digital retail. Brands can offer exclusive content, limited releases, or personalized offers to customers who engage with products through scanning, creating unique value propositions that drive sales and loyalty.
6. Consumer Experience Enhancement
Consumers represent the ultimate beneficiaries of GS1 Digital Link deployment, gaining access to unprecedented levels of product information and engagement. A 2024 GS1 US survey found 77% of consumers believe product information is a purchasing essential. Scanning a product’s 2D barcode instantly reveals ingredients, allergens, nutritional information, and usage instructions in the consumer’s preferred language. This transparency empowers informed purchasing decisions and builds trust between brands and consumers.
The sustainability implications of GS1 Digital Link resonate strongly with environmentally conscious consumers. Access to detailed supply chain information enables verification of ethical sourcing claims, carbon footprint data, and recycling instructions. Brands can share their sustainability stories directly through product packaging, creating emotional connections that transcend traditional marketing messages. This transparency becomes a competitive differentiator as consumers increasingly prioritize environmental and social responsibility.
Personalization reaches new heights when products can identify themselves digitally. Consumers can access customized recipes, styling suggestions, or usage tips based on their preferences and purchase history. Loyalty programs become more sophisticated, rewarding specific behaviors and creating gamified experiences that drive engagement. The bidirectional nature of GS1 Digital Link also enables consumers to provide feedback, report issues, or access support directly through product scanning.
Conclusion
The transformation enabled by GS1 Digital Link extends far beyond simple technical upgrades to existing systems. This revolutionary standard fundamentally reimagines how products interact with the digital world, creating unprecedented opportunities for value creation across entire supply chains. From manufacturers seeking deeper consumer connections to retailers optimizing operations and consumers demanding transparency, GS1 Digital Link addresses critical needs while enabling capabilities we’re only beginning to explore.
The journey toward Sunrise 2027 represents more than a deadline; it marks the beginning of a new era in commerce where physical and digital converge seamlessly. Organizations that embrace this transformation early will find themselves with significant competitive advantages: deeper consumer relationships, more efficient operations, and platforms for innovation that their competitors lack. The investments required pale in comparison to the value created through enhanced capabilities and market positioning.
Success with GS1 Digital Link requires more than technical implementation; it demands strategic vision, organizational commitment, and cultural change. Organizations must think beyond scanning barcodes to imagine new business models, consumer experiences, and operational paradigms. The standard provides the foundation, but imagination and execution determine the heights achievable. Those who approach GS1 Digital Link as merely a compliance requirement will miss the transformative opportunities it presents.
Looking forward, the convergence of GS1 Digital Link with emerging technologies promises even greater possibilities. As artificial intelligence, blockchain, and augmented reality mature, GS1 Digital Link will serve as the crucial connection point enabling these technologies to interact with physical products. The organizations building strong GS1 Digital Link foundations today position themselves to leverage these future innovations as they emerge.
The invitation is clear: embrace GS1 Digital Link not as an obligation but as an opportunity. Transform products from static objects into dynamic platforms for engagement and intelligence. Build supply chains that are transparent, efficient, and resilient. Create consumer experiences that delight, inform, and inspire. The tools are available, the standards are established, and the moment is now. The only question remaining is not whether to implement GS1 Digital Link, but how quickly and comprehensively organizations can seize the opportunities it presents.
Commport Datapool Solutions - Trusted by 3000+ Brands
Download: GDSN Buyers Guide
Empower your business with global data synchronization; download our GDSN Buyer's Guide today and take the first step towards streamlined, accurate, and compliant product data management.
Frequently Asked Questions
GS1 Digital Link is a standard that connects physical products to the digital world by encoding web links within 2D barcodes. This enables consumers, retailers, and regulators to access detailed product information using a simple scan from a smartphone or scanner.
Unlike traditional 1D barcodes that only carry product identifiers (like GTINs), GS1 Digital Link uses 2D barcodes (such as QR codes or Data Matrix codes) to store far more data, including batch numbers, expiry dates, and direct links to online product information.
GS1 Digital Link helps businesses improve supply chain visibility, enable smarter recalls, enhance product authentication, and engage directly with consumers. It also supports regulatory compliance by providing transparent, scannable access to accurate product details.
Yes. Consumers can scan 2D barcodes on product packaging with their smartphones to instantly view details like nutritional facts, allergens, sustainability information, and even promotions—making it a powerful tool for building brand trust.
GS1 has announced that by 2027, all retailers and supply chains worldwide should be ready to adopt 2D barcodes powered by GS1 Digital Link. This transition marks the future of connected packaging and digitized supply chain management.