Introduction
There are many types of EDI methods organizations will use to enable EDI across their trading community.
Electronic data interchange (EDI) is one of the most common forms of structured electronic exchange of business documents between organizations.
More than 85% of all electronic business transactions take place using EDI. EDI is used in industries including retail, banking, high-tech, manufacturing, and services.
8 Types of EDI Solutions
- Direct EDI/Point-to-Point
- EDI via AS2
- EDI via SFTP
- EDI via FTPS
- EDI via Value Added Network or EDI Service Provider
- Cloud EDI
- EDI Outsourcing
- Integrated EDI
1. Direct EDI/Point-to-Point
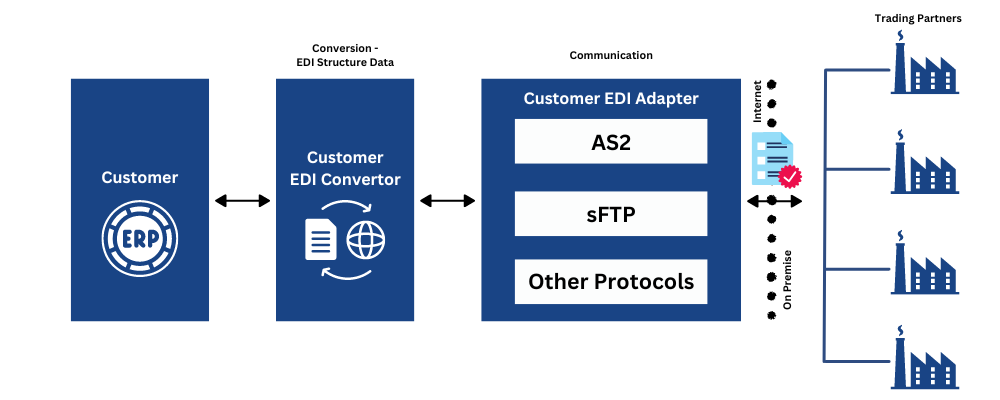
Direct EDI, sometimes referred to as point-to-point EDI, establishes a single connection between two business partners. In this approach, a business would connect with each of its business partners individually. Typically large corporations that have business partners with whom they exchange a high volume of EDI documents will choose this method.
While Direct EDI provides more control for each business, it can become very complex quickly. Different EDI trading partners often use separate EDI communication protocols which means you need to support each available option.
With the direct connection model, you will need to purchase a software package that enables you to use all the agreed-upon protocols, such as
2. EDI via AS2 (Applicability Statement 2)
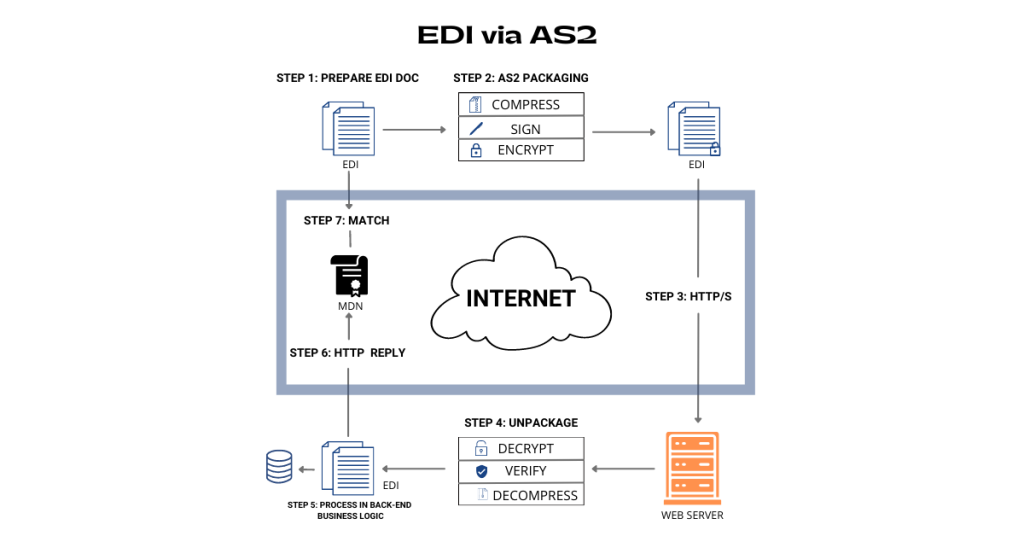
AS2 stands for Applicability Statement 2. Easily described as a business-to-business connection in a point-to-point manner via the web. AS2 is one of the most popular methods for transporting EDI data securely and reliably used by millions of businesses, including most major retailers, such as Amazon and Walmart.
3. EDI via SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol)
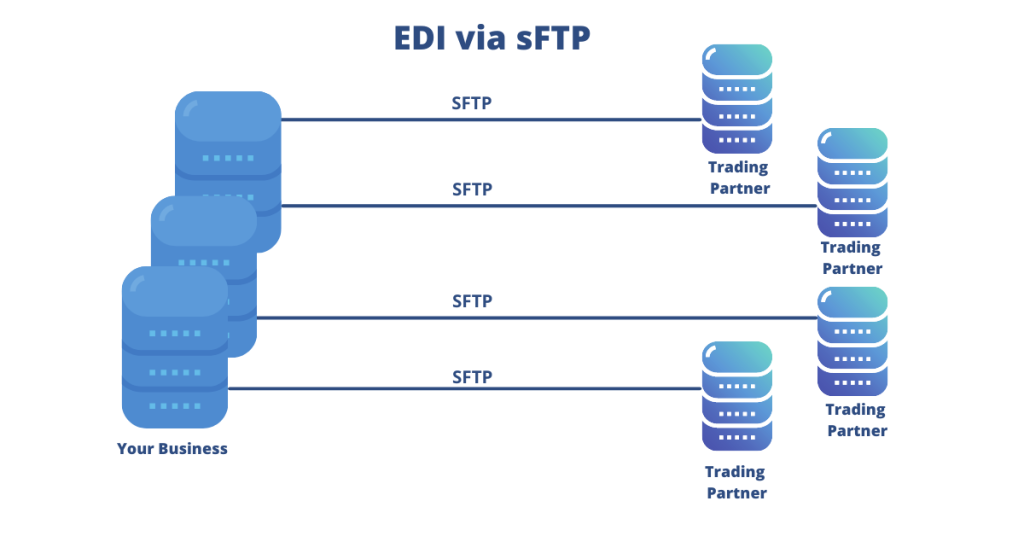
SFTP stands for Secure File Transfer Protocol, also called SSH File Transfer Protocol, and is a network protocol for accessing, transferring, and managing files on remote systems. SFTP provides organizations with a higher level of file transfer protection which allows businesses to securely transfer billing data, funds, and data recovery files.
4. EDI via FTPS (File Transfer Protocol)
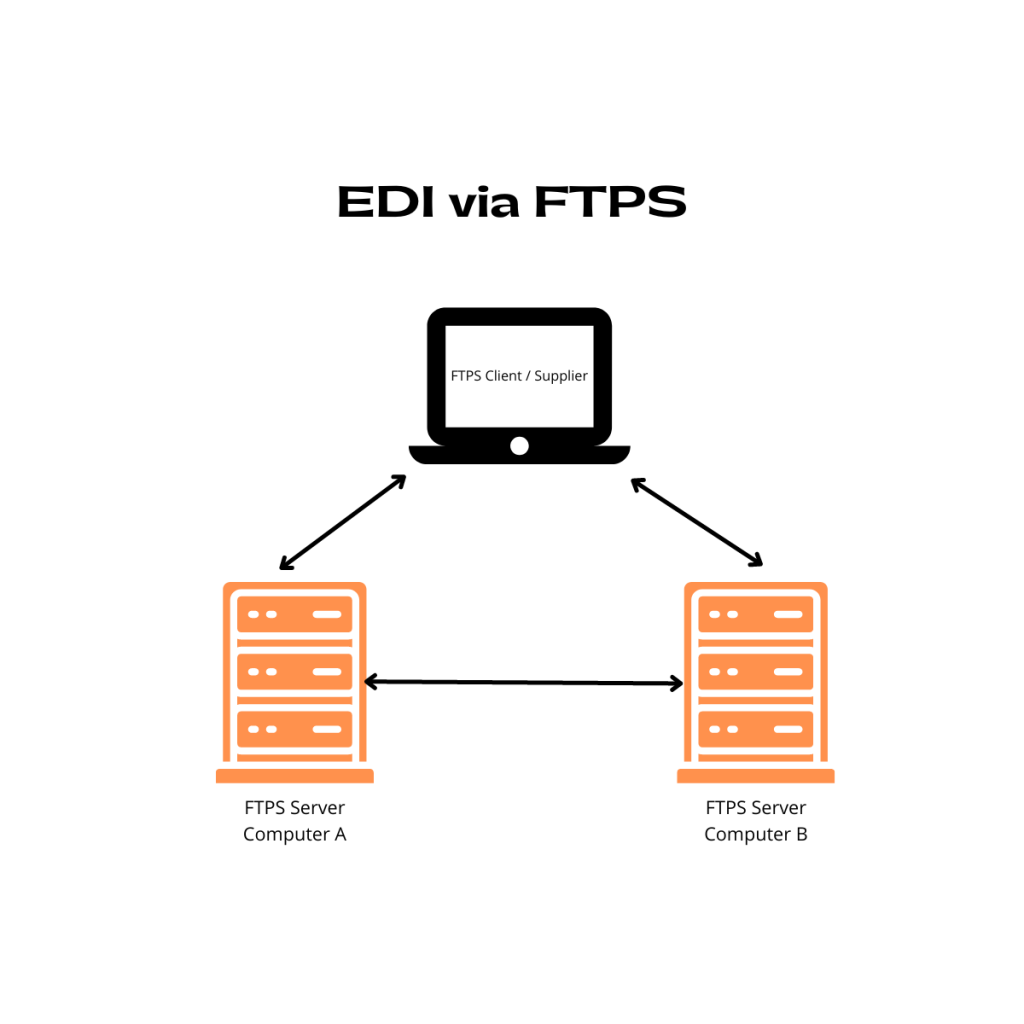
FTPS stands for File Transfer Protocol Secure which is an extension to the commonly used File Transfer Protocol. In FTPS, FTP data travels through the network using either Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols.
5. EDI via Value Added Network or EDI Services Provider
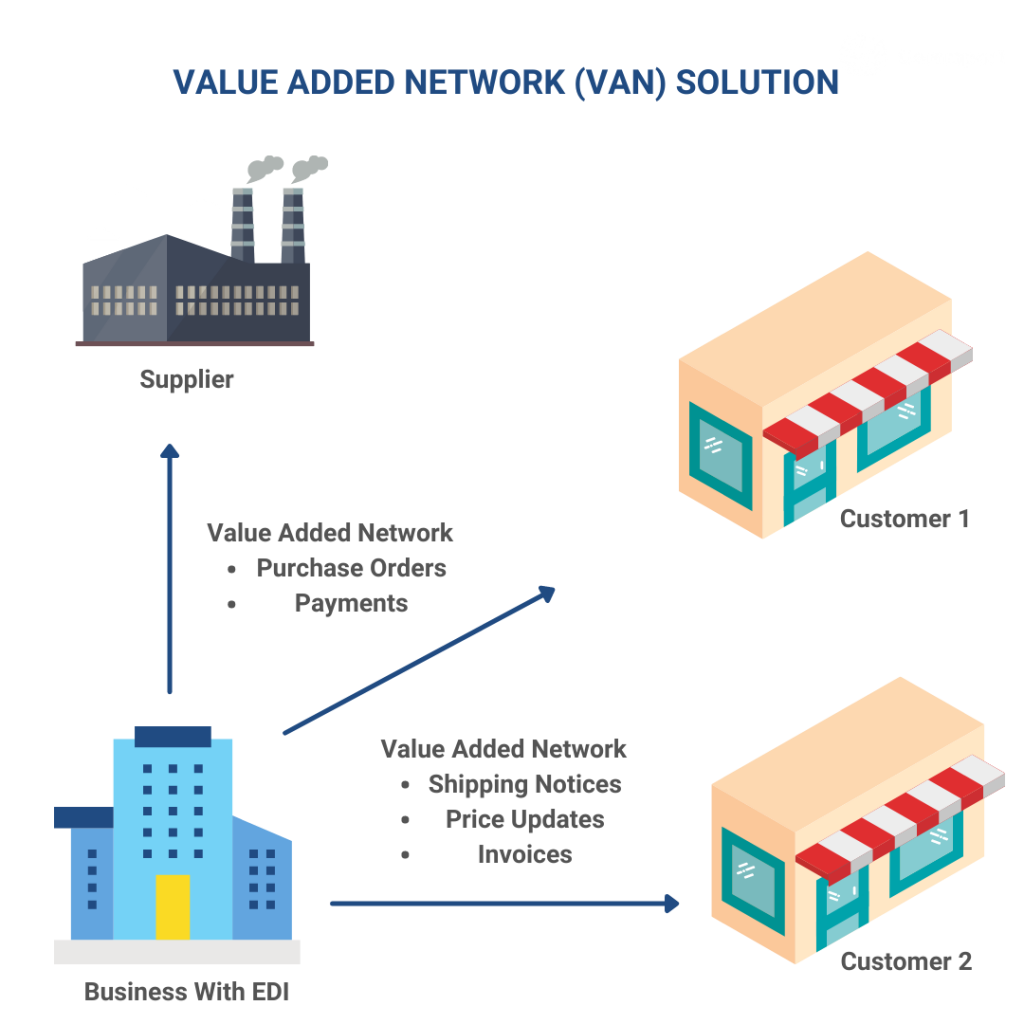
The majority of EDI exchanged today occurs through EDI Value-Added Network (VAN). As long as two organizations are using the same VAN, communication is possible regardless of which EDI protocol is used to transfer information. Unlike Direct EDI this means organizations can manage one connection with the EDI VAN instead of separate lines of communication with each potential partner. Many businesses prefer this model to save them from the ongoing complexities of supporting the varying communication protocols required by different business partners.
How it Works
An organization will be provided with a virtual mailbox by the EDI VAN provider. From there documents are sent and received. A trading partner retrieves messages by connecting to the VAN, which validates the message and verifies the recipient’s identity. It then provides a full audit trail, and all messages are tracked and accurately recorded.
Benefits of Value Added Network (VAN)
- 1. Error correction
- 2. Improved exchange
- 3. Secure
- 4. Standardized
6. Cloud EDI
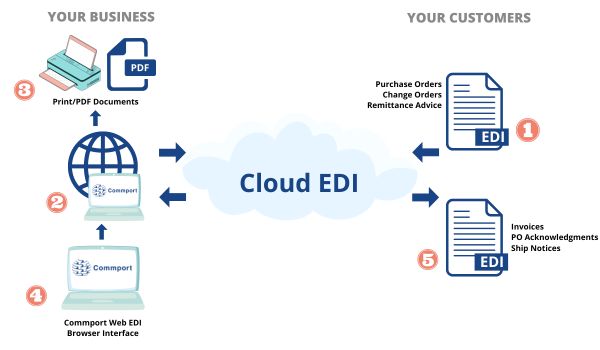
Cloud EDI is simply conducting EDI through an Internet browser. It replicates paper-based documents in a web form.
Cloud EDI enables small – and medium-sized businesses to create, receive, turn around, and manage electronic documents using an internet browser. The Cloud EDI interface is meant to be user-friendly and does not require a lot of experience with EDI systems. It is popular with small to medium businesses as setup is quick, and easy and business partners anywhere in the world can connect without dedicating IT resources to their EDI implementation.
Benefits of Cloud EDI
- Management capabilities for hundreds of trading partners
- MH10 shipping labels
- Proactive notification email alerts
- Business rule validations
- Duplicate checking
- Reports for all inbound transactions
- Retrievable archive
- Document import and export to enable partial integration
7. EDI Outsourcing
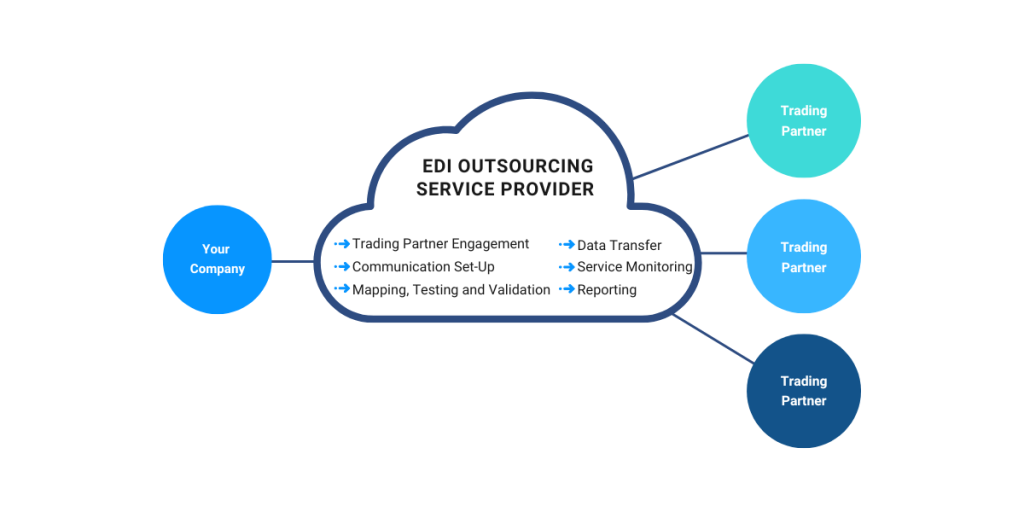
EDI Outsourcing also referred to as B2B Managed Services is an option that enables companies to use external specialist resources to manage their EDI environment on a day-to-day basis. This includes software and or hardware, infrastructure, and ongoing updates or changes to EDI specs or maps.
There are many benefits to outsourcing your EDI:
- Small set-up fees and a lower total cost of ownership
- Pay-per-use model
- Human errors are eliminated
- Access to EDI experts
- Managed connectivity, testing and setup, updates, and support are covered
If you have implemented a fully integrated EDI-compliant system but still have partners who want to send you faxes a managed EDI Service can be your clearinghouse for fax automation.
8. Integrated EDI Solution
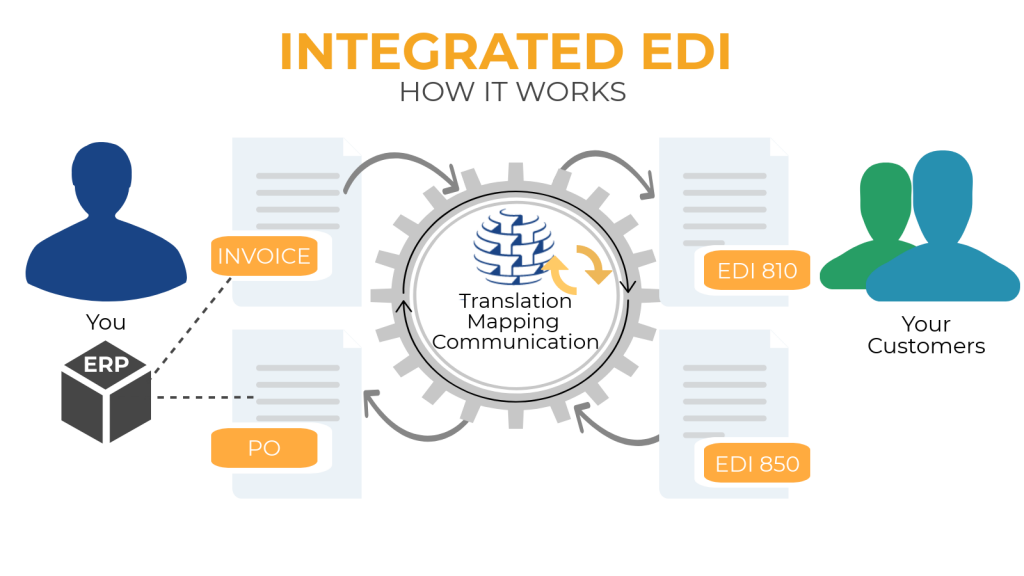
An Integrated EDI solution translates your inbound documents, like purchase orders, from your trading partners’ EDI files into a format that can be imported directly into your ERP, accounting or other business system.
When you’re ready to send out invoices, PO acknowledgments, or other outbound documents, it takes the format exported from your system and translates it into the EDI formats required by your trading partners.
Translation is fast and reliable – so you can focus on your business.
The solution grows easily as your business grows and adding new customers is easy.
Conclusion
Understanding the various types of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is essential for businesses seeking efficient and standardized electronic communication. Whether it’s through traditional EDI, cloud-based EDI, AS2, or other protocols, choosing the right type of EDI depends on specific business requirements and the nature of transactions with trading partners. Exploring the options available ensures that businesses can leverage EDI effectively to streamline processes and enhance collaboration with trading partners.
Download: EDI Buyers Guide
Unlock the full potential of your supply chain with our comprehensive EDI Buyer's Guide — your first step towards seamless, efficient, and error-free transactions
Frequently Asked Questions
There are various types of EDI, including traditional EDI, cloud-based EDI, AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), and more. They differ in the methods and protocols used for electronic data exchange, catering to different business needs and preferences.
Traditional EDI involves the exchange of EDI documents through a direct point-to-point connection, often using Value-Added Networks (VANs). Web-based EDI, on the other hand, utilizes web-based platforms, making it accessible through standard web browsers without the need for specialized software.
AS2, or Applicability Statement 2, is a widely used protocol for secure and reliable EDI communication over the internet. It ensures data integrity and privacy through encryption and digital signatures, making it a preferred choice for many businesses engaged in electronic data exchange.
Yes, there are industry-specific EDI standards such as EDIFACT, X12, and others. These standards define the structure and format of EDI documents within specific industries, ensuring consistency and interoperability among trading partners in a given sector.
Yes, businesses can use a combination of different EDI types based on their requirements. For example, a company might use traditional EDI for some trading partners and web-based EDI for others, allowing flexibility and customization to meet diverse business needs.